Abstract
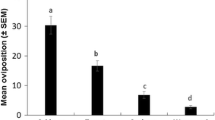
The role of plant allelochemicals on the oviposition behavior ofHeliothis virescens (F.),H. subflexa (Guenee), andH. zea (Boddie) was investigated in the laboratory using a “choice” bioassay system. Fresh young leaves of tobacco,Desmodium tortuosum (Swartz) de Candolle, groundcherry (Physalis angulata L.), and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) squares (flower buds) were washed in methylene chloride or methanol, concentrated to 1 g equivalent of washed material, and applied to a cloth oviposition substrate. Each of the extracts—including groundcherry, a nonhost—stimulated oviposition byH. virescens. H. subflexa were stimulated to oviposit by groundcherry extract, its normal host, and extract from cotton squares, a nonhost. None of the extracts stimulated oviposition byH. zea, although all except groundcherry were from reported hosts. The sensitivity of the bioassay was confirmed by givingH. virescens andH. subflexa an opportunity to choose between extracts that showed stimulant qualities when tested independently versus only solvent-treated controls. In these tests, tobacco showed the highest level of stimulant activity forH. virescens; groundcherry exhibited the highest level of stimulation forH. subflexa.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Alborn, H. 1988. Plant allelochemicals as insect oviposition regulators. PhD thesis. Department of Chemical Ecology, University of Goteborg, Karragatan 6, S-431 33 Molndal, Sweden.
Brazzel, J.R., Newsome, L.D., Rousel, T.S., Lincoln, C., Williams, F.J., andBarnes, G. 1953. Bollworm and tobacco budworm as cotton pests in Louisiana and Arkansas.La. Agric. Exp. Stn. Bull. 482:47.
Duncan, D.B. 1955. Multiple range and multiple F tests.Biometrics 11:1–42.
Guy, R.H., Leppla, N.C., Rye, J.R., Green, C.W., Barrette, S.L., andHollien.K.A. 1985.Trichoplusia ni, pp. 487–494,in Pritam Singh and R.F. Moore, (eds.). Handbook of Insect Rearing, Vol. 2. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam.
Jackson, D.M., andMitchell, E.R. 1984. Growth and survival of tobacco budworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae fed Florida beggarweed (Fabaceae) and tobacco (Solanaceae).J. Econ. Entomol. 77:960–965.
Jackson, D.M., Cheatham, J.S., Pitts, J.M., andBaumhover, A.H. 1983. Ovipositional response of tobacco budworm moths (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to tobacco Introduction 1112 and NC 2326 in cage tests.J. Econ. Entomol. 76:1303–1308.
Jackson, D.M., Severson, R.F., Johnson, A.W., Chaplin, J.F., andStephenson, M.G. 1984a. Ovipositional response of tobacco budworm moths (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to cuticular chemical isolates from green tobacco leaves.Environ. Entomol. 13:1023–1030.
Jackson, D.M., Tingle, P.C., andMitchell, E.R. 1984b. Survey ofHeliothis spp. larvae found on Florida beggarweed and postharvest tobacco in Florida.Fla. Entomol. 67:130–141.
Jackson, D.M., Severson, R.F., Johnson, A.W., andHerzog, G.A. 1986. Effects of cuticular duvane diterpenes from green tobacco leaves on tobacco budworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) oviposition.J. Chem. Ecol. 12:1349–1359.
Johnson, M.W., Stinner, R.E., andRabb, R.L. 1975. Ovipositional response ofHeliothis zea (Boddie) to its major hosts in North Carolina.Environ. Entomol. 4:291–297.
King, E.G., andMoore, R.F. 1985.Heliothis virescens, pp. 323–328,in Pritam Singh and R.F. Moore (eds.). Handbook of Insect Rearing, Vol. 2. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam.
Laster, M.L., Pair, S.D., andMartin, D.F. 1982. Acceptance and development ofHeliothis subflexa andH. virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), and their hybrid and backcross progeny on several plant species.Environ. Entomol. 11:979–980.
Mitchell, E.R., andHeath, R.R. 1985. Influence ofAmaranthus hybridus L. allelochemics on oviposition behavior ofSpodoptera exigua andS. eridania (Lepidoptera Noctuidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 11:609–618.
Mitchell, E.R., andHeath, R.R. 1987.Heliothis subflexa (GN.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Demonstration of oviposition stimulant from groundcherry using novel bioassay.J. Chem. Ecol. 13:1849–1858.
Mitchell, E.R., Hines, R.W., andCopeland, W.W. 1988.Heliothis subflexa (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Establishment and maintenance of a laboratory colony.Fla. Entomol. 71:21–214.
Rembold, H., andTober, H. 1985. Kairomones as pigeonpea resistance factors againstHeliothis armigera.Insect Sci. Applic.6:249–252.
Roome, R.E. 1975. Activity of adultHeliothis armigera (Hb.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) with reference to the flowering of sorghum and maize in Botswana.Bull. Entomol. Res. 65:523–530.
Saray, M.C., andLoya-Ramirez, J. 1978. El cultivo del tomate cascara en el estado de Morelos.El Campo (Mexico) 54:30–38.
Steel, R.G.D., andTorrie, J.H. 1960. Principles and Procedures of Statistics. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Tingle, F.C., andMitchell, E.R. 1984. Aqueous extracts from indigenous plants as oviposition deterrents forHeliothis virescens (F.).J. Chem. Ecol. 10:101–113.
Tingle, F.C., andMitchell, E.R. 1986. Behavior ofHeliothis virescens (F.) in presence of oviposition deterrents from elderberry.J. Chem. Ecol. 12:1523–1531.
Tingle, F.C., Heath, R.R., andMitchell, E.R. 1989. Flight response ofHeliothis subflexa (GN.) females to an attractant from groundcherry,Physalis angulata L.J. Chem. Ecol. 15:221–231.
Wiseman, B.R., Gross, H.R., Widstrom, N.M., Waiss, A.C., andJones, R.L. 1988. Resistance of corn toHeliothis zea.South. Coop. Ser. Bull. 337:21–30.
Williams, A.L., Mitchell, E.R., Heath, R.R., andBarfield, C.S. 1986. Oviposition deterrents for fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from larval frass, corn leaves, and artificial diet.Environ. Entomol. 15:327–330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article reports the results of research only. Mention of a proprietary product does not constitute an endorsement or the recommendation of its use by USDA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell, E.R., Tingle, P.C. & Heath, R.R. Ovipositional response of threeHeliothis species (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to allelochemicals from cultivated and wild host plants. J Chem Ecol 16, 1817–1827 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01020496
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01020496