Abstract
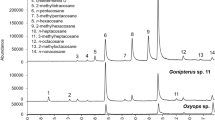
The alkanes (methylalkanes) were analyzed from both sexes of four members of thepalpalis group of tsetse flies,Glossina fuscipes fuscipes, G. palpalis gambiensis, G. palpalis palpalis, G. tachinoides plus onefusca group member, G. brevipalpis, to determine structures, abundances, and the presence of unique or specific methylalkanes. These insects are unique in that trimethylalkanes were major components except in femaleG. tachinoides and both sexes ofG. brevipalpis where 2-methylalkanes were the major components. The identification of novel long-chain tetramethylalkanes, including 11,15,19,23-tetramethylpentatriacontane, a minor component of femaleG. f. fuscipes, G. p. gambiensis, andG. p. palpalis, is reported here. Tetramethylalkanes were significant components of both sexes ofG. brevipalpis. The major tetramethylalkane in G.brevipalpis is 3,7,11,15-tetramethylhen-triacontane. The use of the methylalkanes as taxonomic indicators in tsetse is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, J.E., Sukkestad, D.R., Nelson, D.R., andFatland, C.L. 1979. Cuticular lipids of larvae and adults of the cigarette beetle,Lasioderma serricorne.Insect Biochem. 9:603–611.
Baker, J.E., Woo, S.M., Nelson, D.R., andFatland, C.L. 1984. Olefins as major components of epicuticular lipids of threeSitophilus weevils.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 77B:877–884.
Blomquist, G.J., Howard, R.W., andMcdaniel, C.A. 1979. Structures of the cuticular hydrocarbons of the termiteZootermopsis angusticollis (Hagen).Insect Biochem. 9:365–370.
Brophy, J.J., Cavill, G.W.K., Davies, N.W., Gilbert, T.D., Philp, R.P., andPlant, W.D. 1983. Hydrocarbon constituents of three species of dolichoderine ants.Insect Biochem. 13:381–389.
Carlson, D.A. 1982. Chemical taxonomy: Analysis of cuticular hydrocarbons for identification ofSimulium, Anopheles, andGlossina species, pp. 131–154,in B.N. Newton and F. Michal (eds.). New Approaches to the Identification of Parasites and Their Vectors. Schwabe, Basel.
Carlson, D.A. 1983. Chemical taxonomy in tsetse flies (Glossina species) by analysis of cuticular components. Proc. 17th Biannual OAU/STRC Mtg., ISCTRC, Arusha, Tanzania, No. 110, 1981. pp. 422–430.
Carlson, D.A., andLangley, P.A. 1986. Tsetse alkenes: Appearance of novel sex-specific compounds as an affect of mating.J. Insect Physiol. 32:781–790.
Carlson, D.A., Langley, P.A. andHuyton, P.M. 1978. Sex pheromone of the tsetse fly: Isolation, identification and synthesis of contact aphrodisiacs.Science 201:750–753.
Carlson, D.A., Langley, P.A. andCoates, T.W. 1983. Sex pheromone ofGlossina pallidipes. Proc. 17th Biannual OAU/STRC Mtg., ISCTRC, Arusha, Tanzania, 1981. pp. 431–440.
Carlson, D.A., Nelson, D.R., Langley, P.A., Coates, T.W., Davis, T.L., andLeegwater-Vander Linden, M. 1984. Contact sex pheromone in the tsetse flyGlossina pallidipes(Austen): Identification and synthesis.J. Chem. Ecol. 10:429–450.
Dame, A.A. 1978.In Surveillance and Collection of Arthropods of Veterinary Importance. USDA Agricultural Handbook No. 518, U.S. Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
Howard, R.W., Mcdaniel, C.A. andBlomquist, G.J. 1980. Chemical minicry as an integrating mechanism: Cuticular hydrocarbons of a termitophile and its host.Science 210:431–433.
Huyton, P.M., Langley, P.A., Carlson, D.A., andSchwarz, M. 1980. Specificity of contact sex pheromones in tsetse flies,Glossina spp.Physiol. Entomol. 5:253–264.
Jackson, L.L. 1983. Cuticular hydrocarbons of the milkweed bug,Oncopeltus fasciatus by age and sex.Insect Biochem. 13:19–25.
Langley, P.A., andCarlson, D.A. 1983. Biosynthesis of contact sex pheromone in the female tsetse fly,Glossina morsitans morsitans Westwood.Insect Biochem. 11:825–831.
Langley, P.A., Coates, T.W., andCarlson, D.A. 1982. A sex recognition pheromone in the tsetse fly,Glossina pallidipes Austen.Experientia 38:473–475.
Lockey, K.H. 1982. Cuticular hydrocarbons of adultOnymacris marginipennis (Breme) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae).Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 73B:275–282.
Lockey, K.H. 1984. Hydrocarbons ofMetriopus depressus (Haag) andRenatiella scrobipennis (Haag) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae).Insect Biochem. 14:65–75.
Lockey, K.H., andDularay, B. 1986. Cuticular methylalkanes of adult cockroaches,Blatta orientalis andPeriplaneta americana, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 85B:567–572.
McDowell, P.G., Whitehead, D.L., andChaudhury, F.B. 1981. The isolation and identification of the cuticular sex-stimulant pheromone of the tsetseGlossina pallidipes Austen (Diptera: Glossinidae).Insect Sci. Appl. 2:181–187.
Mold, J.D., Means, R.E., Stevens, R.K. andRuth, J.M. 1966. The paraffin hydrocarbons of wool wax. Homologous series of methyl alkanes.Biochemistry 5:455–461.
Nelson, D.R., andCarlson, D. A. 1986. Cuticular hydrocarbons of the tsetse fliesGlossina morsitans morsitans, G. austeni andG. pallidipes.Insect Biochem. 16:403–416.
Nelson, D.R., andSukkestad, D.R. 1970. Normal and branched aliphatic hydrocarbons from eggs of the tobacco homworm.Biochemistry 9:4601–4611.
Nelson, D.R., Fatland, C.L., andCardwell, D.L. 1977. Long-chain methylalkanes from haemolymph of larvae of Japanese beetles,Popillia japonica.Insect Biochem. 7:439–446.
Nelson, D.R., Fatland, C.L., Howard, R.W., Mcdaniel, C.A., andBlomquist, G.J. 1980. Re-analysis of the cuticular methylalkanes ofSolenopsis invicta andS. richteri.Insect Biochem. 10:163–168.
Nelson, D.R., Dillwith, J.W., andBlomquist, G.J. 1981. Cuticular hydrocarbons of the housefly,Musca domestica.Insect Biochem. 11:187–197.
Nelson, D.R., Nunn, N.J., andJackson, L. 1984. Re-analysis of the methylalkanes of the grasshoppers,Melanoplus differentialis, M. packardi andM. sanguinipes.Insect Biochem. 14:677–683.
Offor, I.I., Carlson, D.A., Gadzama, N.N., andBozimo, H.T. 1981. Sex recognition pheromone in the West African tsetse fly,Glossina palpalis palpalis (Robineau-Desvoidy).Insect Sci. Appl. 1:417–420.
Pomonis, J.G., andHakk, H. 1984. Alkanes from surface lipids of sunflower stem weevil,Cylindrocopturus adspersus (LeConte).J. Chem. Ecol. 10:1335–1347.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelson, D.R., Carlson, D.A. & Fatland, C.L. Cuticular hydrocarbons of tsetse flies II:Glossina fuscipes fuscipes, G. palpalis palpalis, G. p. gambiensis, G. tachinoides, andG. brevipalpis . J Chem Ecol 14, 963–987 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01018787
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01018787