Abstract
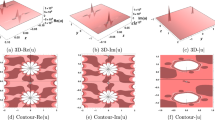
The time-dependent generalized Ginzburg-Landau equation is an equation that is related to many physical systems. Solutions of this equation in the presence of low-level external noise are studied. Numerical solutions of this equation in thestationary frame of reference and with anonzero group velocity that is greater than a critical velocity exhibit a selective spatial amplification of noise resulting in spatially growing waves. These waves in turn result in the formation of a dynamic structure. It is found that themicroscopic noise plays an important role in themacroscopic dynamics of the system. For certain parameter values the system exhibits intermittent turbulent behavior in which the random nature of the external noise plays a crucial role. A mechanism which may be responsible for the intermittent turbulence occurring in some fluid systems is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Shaw,Z. Naturforsch. 36a:80 (1981).
E. Ott,Rev. Mod. Phys. 53(4) Part 1:655 (1981).
Y. Kuramoto,Prog. Theor. Phys. 56:679 (1976);Suppl. Prog. Theor. Phys. 64:346 (1978).
R. G. Deissler,Rev. of Mod. Phys. 56(2) Part 1:223 (1984).
A. Brandstater, J. Swift, H. L. Swinney, A. Wolf, J. D. Farmer, E. Jen, and J. P. Crutchfield,Phys. Rev. Letters 51(16):935 (1983).
F. H. Busse, inChaos and Order in Nature, H. Haken, ed. (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1981).
J. D. Farmer, Sensitive dependence to noise without sensitive dependence to initial conditions (1982), Los Alamos Preprint LA-UR-83-1450; and Deterministic noise amplifiers (1984), Los Alamos Preprint, submitted toJ. Stat. Phys.
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshitz,Fluid Mechanics (Pergamon Press, London, 1959).
J. Watson,J. Fluid Mech. 14:211 (1962).
P. A. Sturrock,Phys. Rev. 112:1488 (1958).
R. J. Deissler,Phys. Lett. 100A:451 (1984).
A. C. Newell and J. A. Whitehead,J. Fluid Mech. 38:279 (1969).
S. Kogelman and R. C. Di Prima,Phys. Fluids 13:1 (1970).
K. Stewartson and J. T. Stuart,J. Fluid Mech. 48:529 (1971).
P. J. Blennerhassett,Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London 298A:43 (1980).
T. Watanabe,J. Phys. Soc. Japan 27:1341 (1969).
H. T. Moon, P. Huerre, and L. G. Redekopp,Phys. Rev. Lett. 49:458 (1982);Physica 7D:135 (1983).
K. Nozaki and N. Bekki,Phy. Rev. Lett. 51:2171 (1983).
L. R. Keefe, Dynamics of perturbed wavetrain solutions to the Ginzburg-Landau equation, Ph. D. thesis (1984).
Y. Kuramoto and S. Koga,Phys. Lett. 92A:1 (1982).
R. J. Briggs,Electron-Stream Interaction with Plasmas (M. I. T. Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1964).
A. Bers, inPlasma Physics, C. DeWitt and J. Peyraud, ed. (Gordon and Breach, New York, 1975).
P. Huerre and P. A. Monkewitz, Absolute and convective instabilities in free shear layers (1984) (submitted toJ. Fluid Mech.)
G. Dee and J. S. Langer,Phys. Rev. Lett. 50:383 (1983).
C. M. Bender and S. A. Orszag,Advanced Mathematical Methods for Scientists and Engineers (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1978).
L. Lapidus and G. F. Pinder,Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations in Science and Engineering (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1982).
G. D. Smith,Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations: Finite Difference Methods (Claredon Press, Oxford, 1978).
H. F. Hameka,Quantum Theory of The Chemical Bond (Hafner Press, New York, 1975).
H. Schlichting,Boundary-Layer Theory (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1968).
F. M. White,Viscous Fluid Flow (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1974).
T. B. Benjamin and J. E. Feir,J. Fluid Mech. 27:417 (1983).
W. Eckhaus,Studies in Nonlinear Stability Theory (Springer, Berlin, 1965).
J. T. Stuart and R. C. DiPrima,Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 362:27 (1978).
H. L. Dryden, inTurbulent Flows and Heat Transfer, C. C. Lin, ed. (Princeton University Press, Princeton New Jersey, 1959).
J. Matthews and R. L. Walker,Mathematical Methods of Physics (W. A. Benjamin, Menlo Park, California, 1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deissler, R.J. Noise-sustained structure, intermittency, and the Ginzburg-Landau equation. J Stat Phys 40, 371–395 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01017180
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01017180
Key words
- Dynamical systems
- nonlinear dynamics
- chaos
- turbulence
- intermittent turbulence
- intermittency
- noise
- external noise
- fluctuations
- external fluctuations
- Ginzburg-Landau equation
- amplitude equation
- spatially growing waves
- convective instability
- spatial instability
- secondary instability
- noise-sustained structure
- noise amplification
- spatial noise amplification
- pattern formation