Abstract
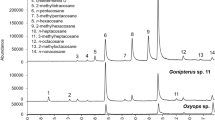
The degree of similarity among cuticular hydrocarbon profiles of four populations ofCoptotermes formosanus Shiraki in the United States is reported. Sixteen individual or isomeric mixtures of hydrocarbons were identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Hydrocarbon components consist ofn-alkanes, 2-methylalkanes, 3-methylalkanes, internally branched monomethylalkanes on carbons 9–15, and dimethylalkanes. The predominant hydrocarbons have 27 carbons in the parent chain. Methyl-branched hydrocarbons are more abundant thann-alkanes. No qualitative differences were apparent in the hydrocarbon components of workers or soldiers from any of the four populations. Quantitative differences in the hydrocarbon components separate castes and populations into different concentration profiles. Stepwise discriminant analysis and canonical discriminant analysis were used to choose and display seven hydrocarbon components for workers and three for soldiers that best reveal the differences among populations. Within-population variation is low compared to the differences among populations. These results suggest thatC. formosanus from Hallandale, Florida; New Orleans, Louisiana; and Lake Charles, Louisiana, are not related to those from Honolulu, Hawaii, and probably originated from other geographical locations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beal, R.H. 1987. Introductions ofCoptotermes formosanus Shiraki to the continental United States, pp. 48–53,in M. Tamashiro and N.-Y. Su (eds.). Biology and Control of the Formosan Subterranean Termite. Research Extension Series 083, University of Hawaii, Honolulu.
Blomquist, G.J., Nelson, D.R., andde Renobales, M. 1987. Chemistry, biochemistry, and physiology of insect cuticular lipids.Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 6:227–265.
Carlson, D.A., andBolten, A.B. 1984. Identification of Africanized and European honey bees, using extracted hydrocarbons.Bull. Entomol. Soc. Am. 30:32–35.
Carlson, D.A., andBrenner, R.J. 1988. Hydrocarbon-based discrimination of three North AmericanBlattella cockroach species (Orthoptera: Blattellidae) using gas chromatography.Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 81:711–723.
Carlson, D.A., andService, M.W. 1980. Identification of mosquitoes ofAnopheles gambiae species complexes A and B by analysis of cuticular components.Science 207:1089–1091.
Chambers, D.M., Zungoli, P.A., andHill, H.S., Jr. 1988. Distribution and habitats of the Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in South Carolina.J. Econ. Entomol. 81:1611–1619.
Gastner, J.L., andNation, J.L. 1986. Cuticular lipids for species recognition of mole crickets (Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae): II.Scapteriscus abbreviatus, S. acletus, S. vicinus, S. sp. andNeocurtilla hexadactyla.Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 3:126–134.
Haverty, M.I., andThorne, B.L. 1989. Agonistic behavior correlated with hydrocarbon phenotypes in dampwood termites,Zootermopsis (Isoptera: Termopsidae).J. Insect Behav. 2:523–543.
Haverty, M.I., Page, M., Nelson, L.J., andBlomquist, G.J. 1988. Cuticular hydrocarbons of dampwood termites,Zootermopsis: Intra- and intercolony variation and potential as taxonomic characters.J. Chem. Ecol. 14:1035–1058.
Howard, R.W., McDaniel, C.A., Nelson, D.R., Blomquist, G.J., Gelbaum, L.T., andSalkow, L.H. 1982. Cuticular hydroccarbonsas possible species and caste-recognition cues inReticulitermes sp.J. Chem. Ecol 8:1227–1239.
Howard, R.W., Thorne, B.L., Levings, S.C., andMcDaniel, C.A. 1988. Cuticular hydrocarbons as chemotaxonomic characters forNasutitermes corniger (Motschulsky) andN. ephratae (Holmgren) (Isoptera: Termitidae).Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 81:395–399.
Kistner, D.H. 1985. A new genus and species of termitophilous Aleaocharinae from mainland China associated withCoptotermes formosanus and its zoogeographical significance (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae).Sociobiology 10:93–104.
La Fage, J.P. 1987. Practical considerations of the Formosan subterranean termite in Louisiana: A 30-year-old problem, pp. 37–42,in M. Tamashiro and N.-Y. Su (eds.). Biology and Control of the Formosan Subterranean Termite. Research Extension Series 083, University of Hawaii, Honolulu.
Lockey, K.H. 1982. Hydrocarbons of adultOnymacris plana (Peringuey) andOnymacris rugatipennis (Haag) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae).Insect Biochem. 12:69–81.
Nelson, D.R., Fatland, C.L., Howard, R.W., McDaniel, C.A., andBlomquist, G.J. 1980. Re-analysis of the cuticular methylalkanes ofSolenopsis invicta andS. richteri.Insect Biochem. 10:409–418.
Page, M., Nelson, L.J., Haverty, M.I., andBlomquist, G.J. 1990. Cuticular hydrocarbons of eight species of North American cone beetles,Conophthorus Hopkins.J. Chem. Ecol. 16:1173–1198.
Pomonis, J.G., Nelson, D.R., andFatland, C.L. 1980. Insect hydrocarbons. 2. Mass spectra of dimethylalkanes and the effect of the number of methylene units between methyl groups on fragmentation.J. Chem. Ecol. 6:965–972.
Prestwich, G.D. 1983. Chemical systematics of termite exocrine secretions.Annu. Rev. Entomol. 14:287–311.
Sas. 1985. SAS User's Guide: Statistics, Version 5 Edition. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina. 956 pp.
Sponsler, R.C., Jordan, K.S., andAppel, A.G. 1988. New distribution record of the Formosan subterranean termite,Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae), in Auburn, Alabama.Entomol. News 99:87–89.
Su, N.-Y., andScheffrahn, R.H. 1986. A method to access, trap, and monitor field populations of the Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in the urban environment.Sociobiology 12:299–304.
Su, N.-Y., andTamashiro, M. 1987. An overview of the Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in the world, pp. 3–15,in M. Tamashiro and N.-Y. Su (eds.). Biology and Control of the Formosan Subterranean Termite. Research Extension Series 083, University of Hawaii, Honolulu.
Swezey, O.H. 1914. Notes and exhibitions.Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 3:27.
Tamashiro, M., Fujii, J.K., andLai, P.-Y. 1973. A simple method to observe, trap and prepare large numbers of subterranean termites for laboratory and field experiments.Environ. Entomol. 2:721–722.
Tamashiro, M., Yates, J.R., andEbesu, R.H. 1987. The Formosan subterranean termite in Hawaii: Problems and control, pp. 15–22,in M. Tamashiro and N.-Y. Su (eds.). Biology and Control of the Formosan Subterranean Termite. Research Extension Series 083, University of Hawaii. Honolulu.
Thorne, B.L., andHaverty, M.I. 1989. Accurate identification ofZootermposis species (Isoptera: Termopsidae) based on a mandibular character of nonsoldier castes.Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 82:262–266.
Vander Meer, R.K. 1986. Chemical taxonomy as a tool for separatingSolenopsis sp., pp. 316–326,in C.S. Lofgren and R.K. Vander Meer (eds.). Fire Ants and Leaf Cutting Ants: Biology and Management. Westview Press, Boulder, Colorado.
Waller, D.A., andLa Fage, J.P. 1987. Food quality and foraging response by the subterranean termite,Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae).Bull. Entomol. Res. 77:417–424.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haverty, M.I., Nelson, L.J. & Page, M. Cuticular hydrocarbons of four populations ofCoptotermes formosanus Shiraki in the united states. J Chem Ecol 16, 1635–1647 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01014096
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01014096