Abstract
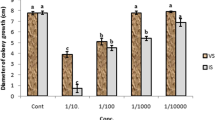
Experiments were conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of some weed extracts against field dodderCuscuta campestris Yunck. on alfalfa (Medicago stiva L.) and to identify and quantify the phytotoxic agents of these extracts. All concentrations of aqueous extract of every weed showed significant effectiveness on dodder when compared to the untreated plant under lath house and field conditions. Control percentages of the (0.5 g) of Bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) and wall goosefoot (Chenopodium murale) ranged between 83 and 96, and the same concentration caused injury to alfalfa foliage up to 43% when applied in the field. Phytotoxic agents were identified as phenolic compounds such as chlorogenic, isochlorogenic,p-coumaric acids, and scopoletin. Their quantities varied with species; Bermuda grass had the highest content (32.2 μg/g dry weight) followed by Johnson grass (Sorghum halepense), well goosefoot, and tumble pigweed (Amaranthus albus). These results might aid in screening for effective alternate approaches for controlling dodder on alfalfa planted for seeds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Rhaman, A.A.S. 1983. Allelopathic Potential ofCynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. onGossypium hirsutum L. MSc thesis, University of Baghdad, College of Science.
Al-Algawi, A.K.S. 1980. Ecological studies of the weeds of barley, clover, cotton, and sorghum in El. Nai farm. MSc thesis. University Baghdad, College of Science.
Al-Saadawi, I.S., Arif, M.B., andAlrubeaa, A.H. 1985. Allelopathic effects ofCitrus aurantium L. II. Isolation, characterization, and biological activities of phytotoxins.J. Chem. Ecol. 11:1527–1534.
Ashton, F.M., 1976.Cuscuta spp. (doddler): A literature review of its biology and control. Department Botany. USDA Bulletin No. 1880. Division of Agricultural Science, University of California, Davis. 22 pp.
Bray, H.G., Thorp, W.V., andWhite, K. 1950. The fate of certain organic acids and amids in the rabbit. 10. The application of paper chromatography to metabolic studies of hydroxybenzoic acid amides.Biochem. J. 46:271–275.
Chou, C.H., andYoung, C.C. 1975. Phytotoxic substances in twelve subtropical grasses.J. Chem. Ecol. 1:183–193.
Dawson, J.H. 1970. Control of dodder in alfalfa with dichlorobenil.Weed Sci. 18:225–230.
Dawson, J.H. 1978. Control of dodderCuscute spp. in alfalfa with pronamide.Weed Sci. 26:660–664.
Fay, P.K., andDuke, W.B. 1977. An assessment of allelopathic potential inAvena germplasm.Weed Sci. 25:224–228.
Langdale, G.W., andCiddens, J.E. 1967. Phytotoxic phenolic compounds insericea lespedeza residues,Agron. J. 59:581–584.
Leather, G.R. 1983 Sunflowers (Helianthus annuus) are allelopathic to weeds.Weed Sci. 31:37–42.
Lee, W.O., andTimmons, F.L. 1956. Evaluation of preemergence and stubble treatment for control of fodder in alfalfa seed crop.Agronomy 48:6–10.
Lodhi, M.A.K. 1975. Allelopathic effects of hackberry in a bottom land forest community.J. Chem. Ecol. 1:171–182.
Massantini, F.,Caporali, F., andZellini. 1977. Evidence for allelopathic control of weeds in lines of soybeans, p. 23–28,in Proceedings European Weed Research Society (EWRS) Symposium, Vol. 1.
Owens, L.D. 1973. Herbicidal potential of Rhizobitoxine.Weed Sci. 21:63–66.
Pearson, D. 1970. The Chemical Analysis of Foods, 6th ed. Journal & Achrollill, London, p. 142.
Putnam, A.R., andDuke, W.B. 1974. Biological suppression of weeds: Evidence for allelopathy in accessions of cucumbers.Science 185:370–372.
Rasmussen, J.A., andRice E.L. 1971. Allelopathic effects ofSporobolus pyramidatus on vegetational patterning.Am. Midl. Nat. 86:309–236.
Shettel, N.A., andBalke, N.E. 1983. Plant growth response to several allelopathic chemicals.Weed Sci. 31:293–298.
Smith, I. (ed.). 1960. Chromatographic and Electrophoretic Techniques, Vol. 1, Chromatography. Interscience Publishers, New York.
Sondheimer, E. 1964. Chlorogenic acid and related depsides.Bot. Rev. 30:667–712.
Steel, R.G., andTorrie, J.H. 1980. Principles and Procedures of Statistics. McGraw-Hill, New York. p. 481.
Wang, P.L., Du, C.T., andFrancis, F.J. 1978. Isolation and characterization of polyphenolic compounds in cranberries.J. Food Sci. 43:1402–1404.
Zenk, M.H., andMuller, G. 1963. In Vivo destruction of exogenously applied indoly-3-acetic acid as influenced by naturally occurring phenolic acids.Nature 200:761–763.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habib, S.A., Rahman, A.A.A. Evaluation of some weed extracts against field dodder on alfalfa (Medicago sativa). J Chem Ecol 14, 443–452 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01013896
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01013896