Summary
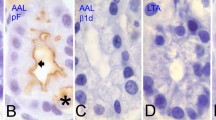
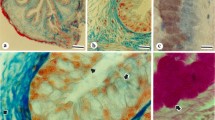
Various fixation and staining procedures have been examined in order to obtain optimal numbers and acceptable morphology of the mucosal mast cells and granular intraepithelial cells in the rat jejunum. For subsequent staining with Alcian Blue, the best fixation of the jejunum was obtained with a methanol-formaldehyde-acetic acid mixture. Specific staining of the granules of these cells has been obtained using Alcian Blue at pH 5.8, at which hydrogen ion concentration more cells stain than in the usual very acid conditions. Specificity is achieved by the use of magnesium chloride concentrations above the critical electrolyte concentrations for staining of protein and nucleic acid by Alcian Blue, and by the use of Safranin O as a competitive counterstain.
The critical electrolyte concentration technique has also been applied to a comparative study of the glycosaminoglycan in the two cell types. Evidence is presented that the glycosaminoglycan in the granular intraepithelial cell has either a lower degree of sulphation or a lower molecular weight or both than the material in mucosal mast cells. This finding may support the possibility that the granular intraepithelial lymphocyte is a precursor of the mucosal mast cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloom, G. &Kelly, J. W. (1960) The copper phthalacyanin dye ‘Astrablau’ and its staining properties, especially the staining of mast cells.Histochemie 2, 48–57.
Collan, Y. (1972) Characteristics of nonepithelial cells in the epithelium of normal rat ileum. A light and electron microscope study.Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 7, Suppl. 18, 1–66.
Combs, J. W., Lagunoff, D. &Benditt, E. P. (1965) Differentiation and proliferation of embryonic mast cells of the rat.J. Cell Biol. 25, 577–92.
Enerbäck, L. (1966a) Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 1. Effects of fixation.Acta path. microbiol. scand. 66, 289–302.
Enerbäck, L. (1966b) Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 2. Dye-binding and metachromatic properties.Acta pathol. microbiol. scand. 66, 303–12.
Guy-Grand, D., Griscelli, C. &Vassalli, P. (1978) The mouse gut T lymphocyte, a novel type of T cell. Nature, origin, and traffic in mice in normal and graft-versus-host conditions.J. expl med. 148, 1661–7.
Michels, N. A. (1938) The mast cells.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 103, 491.
Miller, H. R. P. &Jarrett, W. F. H. (1971) Immune reactions in mucous membranes. 1. Intestinal mast cell response during helminth expulsion in the rat.Immunology 20, 277–88.
Miller, H. R. P. &Walshaw, R. (1972) Immune reactions in mucous membrases. IV. Histochemistry of intestinal mast cells during helminth expulsion in the rat.Am. J. Pathol. 69, 195–206.
Newcomer, E. H. (1953) A new cytological and histochemical fixing fluid.Science, N.Y. 118, 161.
Quintarelli, G., Scott, J. E. &Dellovo, M. C. (1964) The chemical and histochemical properties of Alcian Blue. II. Dye binding of tissue polyanions.Histochemie 4, 86–98.
Romeis, B. (1948)Mikroskopische Technik. R. Oldenburg, München.
Scott, J. E., Quintarelli, G. &Dellovo, M. C. (1964) The chemical and histochemical properties of Alcian Blue. I. The mechanisms of Alcian Blue staining.Histochemie 4, 73–85.
Scott, J. E. &Dorling, J. (1965) Differential staining of glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) by Alcian Blue in salt solutions.Histochemie 5, 221–33.
Scott, J. E. &Stockwell, R. A. (1967) On the use and abuse of the critical electrolyte concentration approach to the localization of tissue polyanions.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 111–3.
Scott, J. e., Dorling, J. &Stockwell, R. A. (1968) Reversal of protein blocking of basophilia in salt solutions: implications in the localization of polyanions using Alcian Blue.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 16, 383–6.
Spicer, S. S. (1963) Histochemical properties of mucopolysaccharide and basic protein in mast cells.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 103, 322–32.
Tas, J. (1977) The Alcian Blue and combined Alcian Blue-Safranin O staining of glycosaminoglycans studied in a model system and in mast cells.Histochem. J. 9, 205–30.
Tas, J. &Geenen, L. H. M. (1975) Microspectrophotometric detection of heparin in mast cells and basophilic granulocytes stained metachromatically with Toluidine blue O.Histochem. J. 7, 231–48.
Tas, J. &Berndsen, R. G. (1977) Does heparin occur in mucosal mast cells of the rat small intestine?J. Histochem. Cytochem. 25, 1058–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayrhofer, G. Fixation and staining of granules in mucosal mast cells and intraepithelial lymphocytes in the rat jejunum, with special reference to the relationship between the acid glycosaminoglycans in the two cell types. Histochem J 12, 513–526 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01011925
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01011925