Abstract
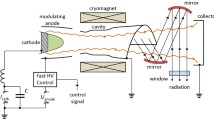
In the course of developing a low-power, tuneable millimeter-wave source, two gyrotrons have been constructed. Gyrotron I was a fixed-frequency device operating at 120 GHz while Gyrotron II produced more than 20 lines in the frequency range 130 to 260 GHz. The design of tuneable gyrotrons is discussed with reference to the Gyrotron II results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Hirshfield, “Infrared and Millimeter Waves”, Vol. 1, p. 1, Ed., K.J. Button (Academic Press, New York, 1979).
H.R. Jory et al., Seventh Symposium on Engineering Problems of Fusion Research, Knoxville, Tennessee (Oct. 25–28, 1977).
A.V. Gapanov et al., Soviet Radiophys.18, 204 (1975). The shape parameter 734-1 on page 206 should be 734-2.
S.N. Vlasov et al., Radiophysics and Quantum Electronics121, 972 (1969) describes the method for calculating the diffraction Q.
G.F. Brand, Amer. J. Phys.,50, 254 (1982).
K.E. Kreischer and R.J. Temkin, Int. J. Infrared and Millimeter Waves1, 195 (1980).
K.E. Kreischer and R.J. Temkin, Int. J. Infrared and Millimeter Waves2, 175 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brand, G.F., Douglas, N.G., Gross, M. et al. Tuneable millimeter-wave gyrotrons. Int J Infrared Milli Waves 3, 725–734 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01009730
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01009730