Summary
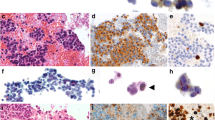
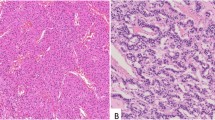
Endocrine cells of human small intestinal mucosa, small intestinal carcinoids and carcinoid liver metastases were stained with an immunocytochemical technique using an antiserum against neuron-specific enolase (NSE), with the argyrophil technique of Grimelius and with the argentaffin technique of Masson. In the normal mucosa, scattered NSE-immunoreactive cells were seen mainly in the deeper parts of the crypts. These cells, as shown in the same sections, corresponded to the argentaffin and/or argyrophil cells indicating that they were of endocrine type.
All intestinal carcinoids (16 cases) displayed NSE immunoreactivity. However, this reaction did not correlate on the cellular level with the silver techniques employed. Thus, many tumour cells were NSE immunoreactive but lacked an argentaffin or argyrophil reaction and vice versa. On the light microscopical level the silver techniques reveal the presence of neurohormonal granules in the tumour cells, while the NSE immunoreactivity appears to disclose neuroendocrine differentiation of the tumour cells irrespective of their hormone and granular content.
Out of 13 carcinoid liver metastases, eight displayed strong NSE immunoreactivity, three were weakly stained and two were unreactive. Consecutive or the same tumour sections showed an argentaffin and argyrophil reaction in all carcinoid metastases. Since silver staining provides one type of information and NSE immunocytochemistry another, they provide in combination a good discriminator for neuroendocrine tumours.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bock, E. (1975) Demonstration of enolase activity connected to the brain-specific protein 14-3-2.Scand. J. Immun. 4, Suppl. 2, 31–6.
Capella, C., Colcia, E., Frigerio, B. &Buffa, R. (1976) Endocrine cells of the human intestine. An ultrastructural study. InEndocrine Gut and Pancreas (edited byFujita, T.), pp. 43–49. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Facer, P., Polak, J. M., Marangos, P. J. &Pearse, A. G. E. (1980) Immunohistochemical localization of neuron specific enolase (NSE) in the gastro-intestinal tract.Proc. microsc. Soc. 15, 113–4.
Fletcher, L., Rider, C. C. &Taylor, C. B. (1976) Enolase isoenzymes chromatographic and immunological characteristics of rat brain enolase.Biochim. biophys. Acta 452, 245–52.
Grimelius, L. (1968) A silver nitrate stain for α2 cells of human pancreatic islets.Acta. Soc. Med. upsal. 73, 243–70.
Grimelius, L. &Wilander, E. (1980) Silver stains in the study of endocrine cells of the gut and pancreas.Invest. Cell. Path. 1013, 3–12.
Lundqvist, M. &Wilander, E. (1983) A simple procedure for immunocytochemical and silver staining of endocrine cells in the same section.Acta path. scand. microbiol., Ser. A 91, 493–4.
Marangos, P. J., Polak, J. M. &Pearse, A. G. E. (1982) Neuron specific enolase. A probe for neurons and neuroendocrine cells.TINS 5, 193–6.
Moore, B. W. &McGregor, D. (1965) Chromatographic and electrophoretic fractionation of soluble proteins of brain and liver.J. biol. Chem. 240, 1647–53.
Påhlman, S., Esscher, T., Bergh, J., Steinholtz, L., Nöu, E. &Nilsson, K. (1984) Neuron-specific enolase as a marker for neuroblastoma and small-cell carcinoma of the lung.Tumour Biol. 5, 119–26.
Pickel, V. M., Reis, D. J., Marangos, P. J. &Zomzely-Neurath, C. (1976) Immunocytochemical localization of nervous system specific protein (NSP-R) in rat brain.Brain Res. 105, 184–7.
Polak, J. M., Sullivan, S. N., Bloom, S. R., Bachan, A. M. J., Farer, P., Brown, M. R. &Pearse, A. G. E. (1977) Specific localization of neurotensin to the N-cell in human intestine by radioimmunoassay and immunocytochemistry.Nature, Lond. 270, 183–4.
Portela-Gomes, G. M. (1982)Enterochromaffin cells. A qualitative and quantitative study. Doctoral thesis, University of Uppsala.
Printz, R. A., Bermes, E. W., Kinnal, J. R. &Marangos, P. J. (1983) Serum markers for pancreatic islet cell and intestinal carcinoid tumors: A comparison of neuron-specific enolase β-human chorionic gonadotropin and pancreatic polypeptide.Surgery 94, 101–23.
Printz, R. A. &Marangos, P. J. (1983) Serum neuron-specific enolase: A serum marker for nonfunctioning pancreatic islet cell carcinoma.Am. J. Surg. 145, 77–81.
Rider, C. C. &Taylor, C. B. (1974) Enolase isoenzymes in rat tissues. Electrophoretic, chromatographic, immunological and kinetic properties.Biochim. biophys. Acta 365, 285–300.
Schmechel, D., Marangos, P. J. &Brightman, M. (1978a) Neuron-specific enolase is a molecular marker for peripheral and central neuroendocrine cells.Nature, Lond. 276, 834–6.
Schmechel, D. E., Marangos, P. J., Zis, A. P., Brightman, M. W. &Goodwin, F. K. (1978b) Brain enolase as a specific marker of neuronal and glial cells.Science 199, 313–5.
Tapia, F. J., Polak, J. M., Barbosa, A. J. A., Bloom, S. R., Marangos, P. J., Dermody, C. &Pearse, A. G. E. (1981) Neuron-specific enolase is produced by neuroendocrine tumours.Lancet i, 808–11.
Vassalo, G., Capella, C. &Solcia, E. (1971) Endocrine cells of the human gastric mucosa.Z. Zellforsch. 118, 49–67.
Wilander, E., Portela-Gomes, G. M., Grimelius, L. &Westermark, P. (1977) Argentaffin and argyrophil reactions of human gastrointestinal carcinoids.Gastroenterology 73, 733–6.
Williams, E. D. &Sandler, M. (1963) The classification of carcinoid tumours.Lancet i, 238–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lundqvist, M., Wilander, E., Esscher, T. et al. Neuron-specific enolase in mucosal endocrine cells and carcinoid tumours of the small intestine: A comparative study with neuron-specific enolase immunocytochemistry and silver stains. Histochem J 17, 323–331 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01004594
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01004594