Synopsis
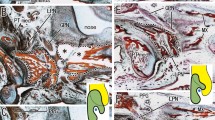
The palatal shelf epithelium of normal and irradiated mice was examined morphologically and histochemically, utilizing the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) technique for the demonstration of the basement membrane and the Nitro BT method for succinate dehydrogenase activity in order to demonstrate the metabolic competence of its cells. The ‘programmed cell death theory’ was not supported by the present investigation, since the cells of the medial ridge epithelium retained their structural and metabolic integrity even subsequent to the formation of cell nests. Additionally, the medial ridge epithelium of mice with radiation-induced cleft palates demonstrated normal structural and metabolic integrity long past the prospective time of fusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelici, D. &Pourtois, M. (1968). The role of acid phosphatase in the fusion of the secondary palate.J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 20, 15–23.
Barry, A. (1961). Development of the branchial region of human embryos with special reference to the fate of epithelia. In:Congenital anomalies of the face and associated structures (ed. S. Pruzansky), pp. 46–62. Springfield: Charles C. Thomas.
Callas, G. &Walker, B. (1963). Palate morphogenesis in mouse embryos after X-irradiation.Anat. Rec. 145, 61–71.
Deangelis, V. &Nalbandian, J. (1968). Ultrastructure of mouse and rat palatal processes prior to and during secondary palate formation.Arch. oral Biol. 13, 601–8.
Farbman, A. I. (1968). Electron microscope study of palate fusion in mouse embryos.Dev. Biol. 18, 93–116.
Farbman, A. I. (1969). The epithelium-connective tissue interface during closure of the secondary palate in rodent embryos.J. Dent. Res. 48, 617–24.
Gartner, L. P., Hiatt, J. L. & Provenza, D. V. (1978). Succinic dehydrogenase activity during palate formation in the Mongolian gerbil.J. Anat (in press).
Creene, R. &Pratt, R. (1976). Developmental aspects of secondary palate formation.J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 36, 225–45.
Hassell, J. R. (1975). The development of rat palatal shelvesin vitro. An ultrastructural analysis of the inhibition of epithelial cell death and palate fusion by the epidermal growth factor.Dev. Biol. 45, 90–102.
Hayward, A. F. (1969). Ultrastructural changes in the epithelium during fusion of the palatal processes in rats.Arch oral Biol. 14, 661–78.
Hinrichsen, C. F. L. &Stevens, G. S. (1974). Epithelial morphology during closure of the secondary palate in the rat.Arch. oral Biol. 19, 969–80.
Holmstedt, J. O. V. & Han, S. S. (1973). Monograph on histogenesis of secondary palate in mice. Parts I–IV. CBL Monograph Number 1. Laboratory of Cell Biology, School of Dentistry and Department of Anatomy, Medical School, The University of Michigan.
Hughes, L. V., Furstman, L. L. &Bernick, S. (1967). Prenatal development of the rat palate.J. dent. Res. 46, 373–80.
Idoyaga-Vargas, V., Nasjleti, C. E. &Azcurra, J. M. (1972). Cytodifferentiation of the mouse secondary palatein vitro: morphological, biochemical and histochemical aspects.J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 27, 413–30.
Konegin, J. S., Chan, B. C., Moriarty, T. M., Weinstein, S. &Gibson, R. D. (1965). A comparison of standard organ culture and standard transplant techniques in the fusion of the palatal processes of rat embryos.Cleft Palate J. 3, 219–28.
Koziol, C. A. &Steffek, A. J. (1969). Acid phosphatase activity in palates of developing normal and chlorcyclizine treated rodents.Arch. oral Biol. 14, 317–21.
Mato, M., Akawa, E. &Katahira, M. (1966). Appearance of various types of lysosomes in the epithelium covering lateral palatine shelves during the secondary palate formation.Gunma J. Med. Sci. 15, 46–56.
Mato, M., Akawa, E. &Katahira, M. (1967). Alteration of fine structure of the epithelium on the lateral palatine shelf during the secondary palate formation.Gunma J. Med Sci. 16, 79–99.
Mato, M., Smiley, G. R. &Dixon, A. D. (1972). Epithelial changes in the presumptive regions of fusion during secondary palate formation.J. dent. Res. 51, 1451–6.
Matthiessen, M. &Andersen, H. (1972). Disintegration of the junctional epithelium of human fetal hard palate.Z. Anat. Entwicklungs. Gesch. 137, 153–69.
Morgan, P. R. (1976). The fate of the expected fusion zone in rat fetuses with experimentally-induced cleft palate. An ultrastructural study.Develop. Biol. 51, 225–40.
Nachlas, M. M., Tsou, K. C., De Souza, E., Chang, C. S. &Seligman, A. M. (1957). Cytochemical demonstration of succinic dehydrogenase by the use of a newp-nitrophenyl substituted ditetrazole.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 5, 420–36.
Pourtois, M. (1966). Onset of the acquired potentiality for fusion in the palatal shelves of rats.J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 16, 171–82.
Pourtois, M. (1968). La fusion des cretes palatines et son alternative par quelques agents teratogenes.Arch. Biol. 79, 1–74.
Pourtois, M. (1970). The fate of rat palatal shelves cultivatedin vitro in the presence of periodic acid.Arch. oral Biol. 16, 503–8.
Pratt, R. &Martin, G. (1975). Epithelial cell death and cyclic AMP increase during palatal development.Proc. Natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 874–7.
Shah, R. M. &Chaudry, A. P. (1974a). Ultrastructural observation on closure of the soft palate in hamsters.Teratology 10, 17–29.
Shah, R. M. &Chaudry, P. (1974b). Light microscopic and histochemical observations on the development of the palate in the golden Syrian hamster.J. Anat. 117, 1–15.
Shapiro, B. L. (1968). Cell death and developing oral structures.J. dent. Res. 47, 934.
Shapiro, B. L. &Sweeney, L. R. (1969). Electron microscopic and histochemical examination of oral epithelial-mesenchymal interaction (Programmed cell death).J. dent. Res. 48, 652–60.
Shapiro, B. L., Feigal, R. J. &Sweeney, L. R. (1969). Krebs cycle enzymes in embryonic oral ectoderm.J. dent. Res. 48, 165.
Smiley, G. R. (1970). Fine structure of mouse embryonic palatal epithelium prior to and after midline fusions.Arch. oral Biol. 15, 287–96.
Smiley, G. R. &Koch, W. E. (1971). Fine structure of mouse secondary palate developmentin vitro.J. dent. Res. 50, 1671–7.
Smiley, G. R. &Koch, W. E. (1972). Anin vitro andin vivo study of single palatal processes.Anat. Rec. 173, 405–16.
Smiley, G. R. &Koch, W. E. (1975). A comparison of secondary palate development with differentin vitro techniques.Anat. Rec. 181, 711–24.
Sweeney, L. R. &Shapiro, B. L. (1970). Histogenesis of Swiss white mouse secondary palate from nine and one half days to fifteen and one half daysin utero. I. Epithelial-mesenchymal relationships-light and electron microscopy.J. Morph. 130, 435–50.
Tsai, H. M. &Verrusio, A. C. (1973). Epithelial breakdown in single palatal shelves.Teratology 7, A29 (Abstract).
Tsai, H. M. &Verrusio, A. C. (1977). Epithelial breakdown in the palatal processes of mouse fetuses with spontaneous cleft lip and palate.Teratology 15, 121–6.
Tyler, M. S. &Koch, W. E. (1975).In vitro development of palatal tissues from embryonic mice. I. Differentiation of the secondary palate from 12-day mouse embryos.Anat. Rec. 182, 297–304.
Vargas, V. I. (1967). Palatal fusion in vitro in the mouse.Arch. oral Biol. 12, 1283–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gartner, L.P., Hiatt, J.L. & Provenza, D.V. Palatal shelf epithelium: A morphologic and histochemical study in X-irradiated and normal mice. Histochem J 10, 45–52 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01003413
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01003413