Abstract
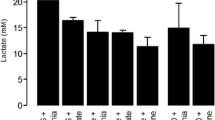
Construction of an end-to-side portocaval anastomosis in the rat resulted, 4 weeks later, in sustained hyperammonemia and two- to threefold increases in brain ammonia. Measurement of cerebral amino acids using a sensitive double-isotope dansyl microtechnique revealed substantial increases in the glutamine content of cerebral cortex and brain stem. Glutamate levels were found to be concomitantly reduced in both brain regions compared to those of sham-operated controls. The γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) content of cerebral cortex and brain stem was unaffected by portocaval shunting, as were activities of the GABA nerveterminal marker enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). These findings suggest that impaired GABA function may not play a major role in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy associated with portocaval shunts. Preliminary evidence suggests that decreased cerebral glutamate may reflect its loss from the releasable (neurotransmitter) pool.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaubernard, C., Salomon, F., Grange, D., Thangapregassam, M. J., and Bismuth, J. (1977). Experimental hepatic encephalopathy. Changes of the level of wakefulness in the rat with portocaval shunt.Biomedicine 27: 169–171.
Butterworth, R. F. (1985). Double-isotope dansyl microassay for cerebral amino acids. In Boulton, A. A., Baker, G. B., and Wood, J. D. (eds.),Neuromethods, Humana Press, Clifton, N.J., pp. 81–95.
Butterworth, R. F., and Giguère, J. F. (1984). Region-selective glutamine changes in the CNS in relation to function in experimental subacute hepatic encephalopathy, In Kleinberger, G., Ferenci, P., Riederer, P., and Thaler, H. (eds.),Advances in Hepatic Encephalopathy and Urea Cycle Diseases, Karger, Basel, pp. 394–401.
Butterworth, R. F., Merkel, A. D., and Landreville, F. (1982). Regional amino acid distribution in relation to function in insulin hypoglycaemia.J. Neurochem. 38: 1483–1489.
Butterworth, R. F., Giguère, J. F., Samii, A., and Bergeron, M. (1986a). Regional glutamate changes in experimental hepatic encephalopathy.Trans. Am. Soc. Neurochem. 17: 242.
Butterworth, R. F., Giguère, J. F., Lavoie, J., Pomier-Layrargues, G., and Michaud, J. (1986b). Ammonia: Key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy.Neurochem. Pathol. (in press).
Cooper, A. J. L., Ehrlich, M. E., and Plum, F. (1984). Hepatic encephalopathy: GABA or ammonia?Lancet 1: 158–159.
Cremer, J. E., Heath, D. F., Teal, H. M., Woods, M. S., and Cavanagh, J. B. (1975). Some dynamic aspects of brain metabolism in rats given a portocaval anastomosis.Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 3: 293–311.
Fonnum, F. (1985). Determination of transmitter amino acid turnover. In Boulton, A. A., Baker, G. B., and Wood, J. D. (eds.)Neuromethods, Vol. 3, Humana Press, Clifton, N. J., pp. 201–237.
Giguère, J. F., and Butterworth, R. F. (1982). Glutamic acid abnormalities in the central nervous system in hepatic encephalopathy.Clin. Biochem. 15: 95–96.
Giguère, J. F., and Butterworth, R. F. (1984). Amino acid changes in regions of the CNS in relation to function in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy.Neurochem. Res. 9: 1309–1321.
Glowinski, J., and Iversen, L. L. (1966). Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of3H-norepinephrine,3H-dopamine and3H-dopa in various regions of the brain.J. Neurochem. 13: 655–669.
Hamberger, A., Hedquist, B., and Nystrom, B. (1979). Ammonium ion inhibition of evoked release of endogenous glutamate from hippocampal slices.J. Neurochem. 33: 1295–1302.
Hindfelt, B., Plum, F., and Duffy, T. E. (1977). Effect of acute ammonia intoxication on cerebral metabolism in rats with portacaval shunts.J. Clin. Invest. 59: 386–396.
Holmin, T., and Siesjo, B. K. (1974). The effect of porta-caval anastomosis upon the energy state and acid-base parameters of the rat brain.J. Neurochem. 22: 403–412.
Kun, E., and Kearney, E. B. (1974). Ammonia. In Berkmeyer, H. V. (ed.),Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, Academic Press, New York, pp. 1802–1806.
Kvamme, E., and Lenda, K. (1982). Regulation of glutaminase by exogenous glutamate, ammonia and 2-oxoglutarate in synaptosomal enriched preparation from rat brain.Neurochem. Res. 7: 667–677.
Lee, S. H., and Fisher, B. (1961). Portocaval shunt in the rat.Surgery 50: 668–672.
Mans, A. M., Biebuyck, J. F., Davis, D. W., and Hawkins, R. A. (1984). Portacaval Anastomosis: Brain and plasma metabolite abnormalities and the effect of nutritional therapy.J. Neurochem. 43: 697–705.
Norenberg, M. D. (1977). A light and electron microscopic study of experimental portal-systemic (ammonia) encephalopathy.Lab. Invest. 36: 618–627.
Plum, F., and Hindfelt, B. (1976). The neurological complications of liver disease. In Vinken, P. J., and Bruyn, G. W. (eds.),Metabolic and Deficiency Diseases of the Nervous System, Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol. 27, American Elsevier, New York, pp. 349–377.
Raabe, W. A. (1982). Hepatic encephalopathy.Lancet 1: 1020–1021.
Schafer, D. F., and Jones, E. A. (1982). Hepatic encephalopathy and the γ-aminobutyric acid neurotransmitter system.Lancet 1: 18–20.
Schenker, S., and Hoyumpa, A. M., Jr. (1984). Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy.Hosp. Pract. 99–121.
Theoret, Y., Davies, M. F., Esplin, B., and Capek, R. (1985). Effects of ammonium chloride on synaptic transmission in the rat hippocampal slice.Neuroscience 14: 798–806.
Trebecis, A. K. (1973). Transmitters and reticulospinal neurons.Exp. Neurol. 40: 297–308.
van Gelder, N. M. (1974). Glutamate dehydrogenase, glutamic acid decarboxylase and GABA aminotransferase in epileptic mouse cortex.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 52: 952–959.
Warbritton, J. D., Geyer, M. A., Jeppsson, B. W., and Fisher, J. E. (1979). Behavioural model of early hepatic encephalopathy in ratsSurg. Forum 30: 394–396.
Watanabe, A., Takei, N., Higashi, T., Nakatsukasa, H., Fujiwara, M., Sakata, T., and Nagashima, H. (1984). Glutamic acid and glutamine levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid in hepatic encephalopathy.Biochem. Med. 32: 225–231.
Zanchin, G., Maggioni, F., Salassa, D., and Vassanelli, P. (1984). GABA and dopamine receptors after chronic porta-caval shunt in the rat, In Kleinberger, G., Ferenci, P., Riederer, P., and Thaler, H. (eds.),Advances in Hepatic Encephalopathy and Urea Cycle Diseases, Karger, Basel, pp. 360–367.
Zieve, L. (1982). Hepatic encephalopathy. In Schiff, L., and Schiff, E. R. (eds.),Diseases of the Liver, Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp. 433–4159.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butterworth, R.F., Giguère, JF. Cerebral aminoacids in portal-systemic encephalopathy: Lack of evidence for altered γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) function. Metab Brain Dis 1, 221–228 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01001783
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01001783