Abstract
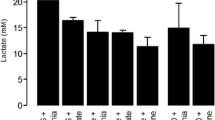
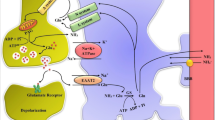
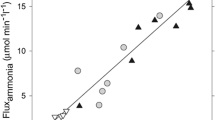
The pathogenesis of brain edema in fulminant hepatic failure is incompletely understood. Our previous studies in models of this disease suggest the presence of a cytotoxic mechanism; as cortical astrocytes appeared predominantly swollen, we hypothesized that ammonia, metabolized to glutamine solely within this cell, could play a role in brain water accumulation. We determined ammonia levels in different brain regions of rats after hepatic devascularization, a model previously shown to exhibit brain edema. Concentrations of 2.5 mM were observed in the edematous cerebral cortex. We then added several concentrations of ammonium chloride to the first cortical brain slice, a preparation used to study cytotoxic brain edema. At a final bath concentration of ammonia of 5 and 10 mM, swelling could be detected; a decrease in the space of distribution of inulin was seen at the 10 mM concentration, suggesting intracellular water accumulation. Neuropathologically, astrocytes appeared involved even at subswelling doses of ammonia. Octanoic acid, at a 10 mM concentration, also resulted in demonstrable swelling. Ammonia, at concentrations in the incubation bath that approach the levels seen in anin vivo model of brain edema, results in water accumulation of cortical brain slices. Toxins implicated in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy, such as ammonia and octanoic acid, may, result in brain water accumulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamin, A. M., Okamoto, K., and Quastel, J. H. (1978). Effects of ammonia ions on spontaneous action potentials and on contents of sodium, potassium, ammonium and chloride ions in brains in vitro.J. Neurochem. 30: 131–143.
Brunner, G., Windus, G., and Schmidt, F. W. (1984). Intracranial pressure and brain edema in experimental hyperammonemia. InAdvances in Hepatic Encephalopathy and Urea Cycle Diseases, Klinberger, G. (ed.), Karger, Basel, pp. 325–330.
Chan, P. H., and Fishman, R. A. (1978). Brain edema: Induction in cortical slices by polyunsaturated fatty acids.Science 201: 358–360.
Chan, P. C., Fishman, R. A., Lee, J. L., and Quan, S. C. (1980). Arachidonic acid-induced swelling in incubated rat brain cortical slices. Effect of bovine serum albumin.Neurochem. Res. 5: 629–640.
Cohen, S. R. (1969). A rapid, sensitive, semimicro gel filtration procedure for detecting and removing low molecular weight fragments from3H or14C-labeled inulin.Anal. Biochem. 31: 539–544.
Cooper, A. J. L., Mora, S. N., Cruz, N. F., and Gelbard, A. S. (1985). Cerebral ammonia metabolism in hyperammonemic rats.J. Neurochem. 44: 1716–1723.
Dahl, D. R. (1968). Short chain fatty acid inhibition of rat brain Na-K adenosine triphosphatase.J. Neurochem. 15: 815–820.
Dunnett, C. W. (1955). A multiple comparison procedure for comparing several treatments with a control.J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 50: 1096–1121.
Ede, R., Gove, C. D., Hughes, R. D., Marshall, W. and Williams, R. (1987). Reduced brain Na+, K+-ATPase activity in rats with galactosamine-induced hepatic failure: relationship to encephalopathy and cerebral oedema.Clin. Sci. 72: 365–371.
Giguere, J. F., and Butterworth, R. F. (1981). Amino acid changes in regions of the CNS in relation to function in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy.Neurochem. Res. 9: 1309–1311.
Gregorios, J. B., Mozes, L. W., Norenberg, L.-O. B., and Norenberg, M. D. (1985a). Morphologic effects of ammonia on primary astrocyte cultures. I. Light microscopic studies.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 44: 397–403.
Gregorios, J. B., Mozes, L. W., and Norenberg, M. D. (1985b). Morphologic effects of ammonia on primary astrocyte cultures. II. Electron microscopic studies.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 44: 404–414.
Harvey, A., and McIlwain, H. (1969). Electrical phenomena and isolated tissues from the brain. In Lajtha, A. (ed.),Handbook of Neurochemistry, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 115–121.
Holmin, T., and Siesjö, B. K. (1974). The effect of portacaval anastomosis upon the energy state and upon acid-base parameters of the rat brain.J. Neurochem. 22: 403–412.
Horowitz, M. E., Schafer, D. F., Molnar, P., Jones, E. A., Blasberg, L. E., Patlak, C. S., Waggoner, J., and Fernstermacher, J. D. (1983). Increased blood-brain transfer in a rabbit model of acute liver failure.Gastroenterology 84: 1003–1011.
Jones, E. A., and Schafer, D. F. (1981) Fulminant hepatic failure. In Zakim, D., and Boyer, T. A., (eds.),Hepatology, W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp. 415–445.
Kempski, O., Chaussy, L., Gross, U., Zimmer, M., and Baethmann, A. (1983). Volume regulation and metabolism of suspended C6 glioma cells: An in vitro model to study cytotoxic brain edema.Brain Res. 279: 217–228.
Kindt, G. W., Brock, M., Altenau, L. L., and Poll, W. (1977). Blood/brain barrier and brain oedema in ammonia intoxication.Lancet 1: 201.
Klatzo, I. (1967). Neuropathological aspects of brain edema.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 26: 1–14.
Kun, E., and Kearney, E. B. (1974). Ammonia. InMethods of Enzymatic Analysis, Berkmeyer, H. V. (ed.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 1802–1806.
Kvamme, E., and Lenda, K. (1982). Regulation of glutaminase by exogenous glutamate, ammonia and 2-oxoglutarate in synaptosomal enriched preparation from rat brain.Neurochem. Res. 7: 667–678.
Lo, W. D., Ennis, S. R., Goldstein, G. W., McNeely, D. L., and Betz, A. L. (1987). The effects of galactosamine-induced hepatic failure upon blood-brain barrier permeability.Hepatology 7: 452–456.
Mans, A. M., Saunders, S. J., Kirsch, R. E., and Biebuyck, J. F. (1979). Correlation of plasma and brain aminoacid and putative neurotransmitter alterations during acute hepatic coma in the rat.J. Neurochem. 32: 285–292.
Moller, M., Hertz, L., Molgaard, K., and Lund-Andersen, H. (1974). Concordance between morphological and biochemical estimates of fluid spaces in rat brain cortex.Exp. Brain Res. 22: 299–314.
Norenberg, M. D. (1981). The astroeyte in liver disease.Adv. Cell Neurobiol. 2: 303–352.
O'Grady, J. G., Gimson, A. E. S., O'Brien, C. J., Pucknell, A., Hughes, R. D., and Williams, R. (1988). Controlled trials of charcoal hemoperfusion and prognostic factors in fulminant hepatic failure.Gastroenterology 94: 1186–1191.
Record, C. O., Buxton, B., Chase, R. A., Curzon, G., Murray-Lyon, I. M., and Williams, R. (1976). Plasma and brain aminoacids in fulminant hepatic failure and their relationship to hepatic encephalopathy.Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 6: 387–394.
Seda, H. W. M., Hughes, R. D., Grove, C. D., and Williams, R. (1984). Inhibition of rat brain Na+-K+ ATPase activity by serum from patients with fulminant hepatic failure.Hepatology 4: 74–79.
Traber, P. G., Ganger, D. R., and Blei, A. T. (1986). Brain edema in rabbits with galactosamine-induced fulminant hepatitis: regional differences and effects on intracranial pressure.Gastroenterology 91: 1347–56.
Traber, P. G., DalCanto, M., Ganger, D. R., and Blei, A. T. (1987). Electron microscopic evaluation of brain edema in rabbits with galactosamine-induced fulminant hepatic failure: Ultrastructure and integrity of the blood-brain barrier.Hepatology 7: 1272–1277.
Traber, P. G., DalCanto, M., Ganger, D. R., and Blei, A. T. (1989). Effect of temperature on brain edema and encephalopathy in the rat after hepatic devascularization.Gastroenterology 96: 885–891.
Trauner, D. A., and Adams, H. (1981). Intracranial pressure elevations during octanoate infusions in rabbits: An experimental model of Reye's syndrome.Pediat. Res. 15: 1097–1099.
VanGelden, N. M. (1983). Metabolic interactions between neurons and astroglia: Glutamine synthetase, carbonic anhydrase and water balance. In Ward, A. (ed.),Basic Mechanisms of Neuronal Hyperexcitability, A. L. Liss, New York, pp. 5–29.
Walz, W. (1988). Analysis of ion fluxes and fluid compartmentation in brain slices. In Boulton, A. B., Baker, G. B., and Walz, W. (eds.),Neuronal Microenvironment, Humana, Clifton, N. J., pp. 421–440.
Zieve, F. L., Zieve, L., Doizaki, W. M., and Gilsdorf, R. B. (1974). Synergism between ammonia and fatty acids in the production of coma: Implications for hepatic coma.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 191: 10–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganz, R., Swain, M., Traber, P. et al. Ammonia-induced swelling of rat cerebral cortical slices: Implications for the pathogenesis of brain edema in acute hepatic failure. Metab Brain Dis 4, 213–223 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000297
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000297