Abstract
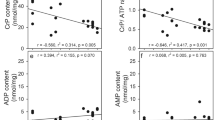
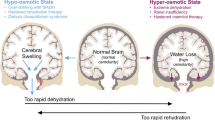
Cellular volume regulation following swelling in hypo-osmotic phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and ATP and phosphocreatine concentrations of cells incubated in iso-osmotic or hypo-osmotic PBS were measured in primary cultured rat cerebral astrocytes exposed for 30 min to NH4Cl, salicylate, hexanoate, octanoate, and/or dodecanoate. These compounds have been implicated in the pathogenesis of cerebral edema in Reye's Syndrome. NH4Cl (0.10–10 raM) had no effect on astrocyte volume regulation or ATP concentration. Salicylate significantly reduced ATP concentrations at 3.0 mM and 10 mM but had no effect on volume regulation. Hexanoate (10 mM and 30 mM) decreased astrocyte ATP content by over 80% while octanoate (10 mM) reduced ATP content by more than 50%. Concentrations of these fatty acids at or below 3.0 mM had no effect on ATP content. Volume regulation was inhibited by 3.0 mM hexanoate and 3.0 mM octanoate but not lower concentrations. Dodecanoate (0.1–3.0 mM) decreased cellular ATP content by 33–51% in iso-osmotic PBS solutions. Phosphocreatine content was reduced by exposure to salicylate or octanoate at concentrations which had no effect on ATP content. These results indicate that astrocyte energy metabolism and volume regulation may be compromised by agents associated with cerebral edema in Reye's Syndrome. Analysis of the dose-dependence of these effects suggests that inhibition of astrocyte energy metabolism is not sufficient to affect volume regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansevin, C.F. (1980) Reye Syndrome: Serum-induced alterations in brain mitochondrial function are blocked by fatty-acid-free albumin.Neurol. 30: 160–166.
Aprille, J.R., Austin, J., Costello, C.E., and Royal, N. (1980) Identification of the Reye's syndrome “serum factor”.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 94: 381–389.
Asimakis, G.K., and Aprille, J.R. (1977) Reye's Syndrome: The effect of patient serum on mitochondrial respirationin vitro.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 79: 1122–1129.
Bender, A.S., Neary, J.T., Blicharska, J., Norenberg, L.B., and Norenberg, M.D. (1992) Role of calmodulin and protein kinase C in astrocytic cell volume regulation.J. Neurochem. 58: 1874–1882.
Brody, T.M. (1956) Action of sodium salicy late and related compounds on tissue metabolismin vitro.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 117: 39–51.
Burgin, H., and Schatzmann, H.J. (1978) The relation between net calcium, alkali cation and chloride movements in red cells exposed to salicylate.J. Physiol. 287: 15–32.
Chamberlin, M.E., and Strange, K. (1989) Anisosmotic cell volume regulation: A comparative view.Am. J. Physiol. 257: C159-C173.
DeLong, G.R., and Glick, T.H. (1982) Encephalopathy of Reye's Syndrome: Areview of pathogenic hypotheses.Pediatr. 69: 53–63.
Derr, R.F., and Zieve, L. (1976) Effect of fatty acids on the disposition of ammonia.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 197: 675–680.
Dezateux, C.A., Dinwiddie, R., Helms, P., and Matthew, D.J. (1986) Recognition and early management of Reye's syndrome.Arch. Dis. Child. 61: 647–651.
Drewes, L.R., and Leino, R.L. (1985) Neuron-specific mitochondrial degradation induced by hyperammonemia and octanoic acidemia.Brain Res. 340: 211–218.
Eveloff, J.L., and Warnock, D.G. (1987) Activation of ion transport systems during cell volume regulation.Am. J. Physiol. 252: F1-F10.
Fitzpatrick, S.M., Cooper, A.J.L., and Hertz, L. (1988) Effects of ammonia and ±-methylene-d1-aspartate on the oxidation of glucose and pyruvate by neurons and astrocytes in primary culture.J. Neurochem. 51: 1197–1203.
Fromm, D. (1976) Ion selective effects of salicylate on antral mucosa.Gastroent. 71: 743–749.
Glasgow, A.M., and Chase, P. (1975) Production of the features of Reye's Syndrome in rats with 4-pentenoic acid.Pediatr. Res. 9: 133–138.
Gregorios, J.B., Mozes, L.W., Norenberg, L.B., and Norenberg, M. (1985) Morphologic effects of ammonia on primary astrocyte cultures. I. Light microscope studies.J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol. 44: 397–403.
Haas, R., Parker, W.D., Stumpf, D., and Eguren, L.A. (1985) Salicylate-induced loose coupling: protonmotive force measurements.Biochem. Pharmacol. 34: 900–902.
Hawkins, R.A., and Jessy, J. (1991) Hyperammonaemia does not impair brain function in the absence of net glutamine synthesis.Biochem. J. 277: 697–703.
Heubi, J.E., Partin, J.C., Partin, J.S., and Schubert, W.K. (1987) Reye's Syndrome: Current concepts.Hepatol. 7: 155–164.
Jeffery, S.W., and Smith, M.J.H. (1959) Some effects of salicylate on mitochondria from rat liver.Biochem. 72: 462–465.
Kang, E.S., Olson, G., Jabbour, J.T., Solomon, S.S., Heimberg, M., Sabesin, S., and Griffith, J.F. (1984) Development of encephalopathic features similar to Reye's Syndrome in rabbits.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 81: 6169–6173.
Kimelberg, H.K., and Frangakis, M.V. (1985) Furosemide and bumetanide sensitive ion transport and volume control in primary astrocyte cultures from rat brain.Brain Res. 361: 125–134.
Lai, J.C.K., and Cooper, A.J.L., (1991) Neurotoxicity of ammonia and fatty acids: Differential inhibition of mitochondrial dehydrogenases by ammonia and fatty acyl coenzyme A derivatives.Neurochem. Res. 16: 795–803.
Levitan, H., and Barker, J.L. (1972) Membrane permeability: cation selectivity reversibly altered by salicylate.Science 178: 63–64.
Lovejoy, F.H., Smith, A.L., Bresnan, M.J., Ward, J.N., Victor, D.I., and Adams, P.L. (1974) Clinical staging in Reye's syndrome.Am. J. Dis. Child. 128: 36–41.
Lowry, O., and Passoneau, J. (1972)A Flexible System of Enzymatic Analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp. 151–156.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265–275.
Macknight, A.D.C. (1987) Volume maintenance in isosmotic conditions. In Gilles, R., Kleinzeller, A., and Bolis, L. (eds.),Current Topics in Membranes and Transport, Vol. 30. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 343.
Macknight, A.D.C., and Leaf, A. (1985) Cellular Responses to extracellular osmolality. In Seldin, D.W., and Giebisch, G. (eds.),The Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Raven Press, New York, pp. 117–132.
Mamunes, P., DeVries, G.H., Miller, C.D., and David, R.B. (1975) Fatty acid quantitation in Reye's Syndrome, In Pollack, J.D. (ed.),Reye s Syndrome, Grune and Stratton, New York, pp. 245–254.
Norenberg, M.D., Baker, L., Norenberg, L.O.B., Blicharska, J., Bruce-Gregorios, J.H., and Neary, J.T. (1991) Ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling in primary culture.Neurochem. Res. 16: 833–836.
Ogburn, P.L., Sharp, H., Lloyd-Still, J.D., Johnson, S.B., and Holman, R.T. (1982) Abnormal polyunsaturated fatty acid patterns of serum lipids in Reye's syndrome.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 79: 908–911.
Olson, J.E. (1990) Pulse-capture circuit for microcomputer data acquisition.Med. Biol. Engin. Comput. 28: 91–95.
Olson, J.E., and Evers, J. A. (in press) Correlations between energy metabolism, ion transport, and water content in astrocytes.Can. J. Pharmacol. Physiol.
Olson, J.E., and Goldfinger, M.D. (1990) Amino acid content of rat cerebral astrocytes adapted to hyperosmotic mediumin vitro.J. Neurosci. Res. 27: 241–246.
Olson, J.E., and Holtzman, D. (1980) Respiration in rat cerebral astrocytes from primary culture.J. Neurosci. Res. 5: 497–506.
Olson, J.E., and Holtzman, D. (1981) Factors influencing the growth and respiration of rat cerebral astrocytes in primary culture.Neurochem. Res. 6: 1337–1343.
Olson, J.E., Sankar, R., Holtzman, D., James, A., and Fleischhacker, D. (1986) Energy dependent volume regulation in primary cultured cerebral astrocytes.J. Cell. Physiol. 128: 209–215.
Olson, J.E., Holtzman, D., Sankar, R., Lawson, C., and Rosenberg, R. (1989) Octanoic acid inhibits astrocyte volume control: Implications for cerebral edema in Reye's Syndrome.J. Neurochem. 52: 1197–1202.
Olson, J.E., Murray, W.B., Fleischhaker, D., and Holtzman, D. (1990) Control of astrocyte volume by intracellular and extracellular Ca++.Glia. 3: 405–412.
Parker, W.D., Haas, R., Stumpf, D.A., and Eguren, L.A. (1983) Effects of octanoate on rat brain and liver mitochondria.Neurol. 33: 1374–1377.
Partin, J.S., McAdams, A.J., Partin, J.C., Schubert, W.K., and McLaurin, R.L. (1978) Brain ultrastructure in Reye's Disease. II. Acute injury and recovery processes in three children.Neuropath. Exp. Neurol. 37: 796–819.
Pasantes-Morales, H., and Schousboe, A. (1988) Volume regulation in astrocytes: A role for taurine as an osmoeffector.J. Neurosci. Res. 20: 505–509.
Pressman, B.C., and Lardy, H.A. (1956) Effect of surface active agents on the latent ATPase of mitochondria.Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 21: 458–466.
Roos, A., and Boron, W.F. (1981) Intracellular pH.Physiol. Rev. 61: 296–34.
Sinniah, D., Schwartz, P.H., Mitchell, R.A., and Arcinue, E.L. (1985) Investigation of an animal model of a Reye-like syndrome caused by margosa oil.Pediatr. Res. 19: 1346–1355.
Starko, K.M., Ray, C.G., Dominguez, L.B., Stromberg, W.L., and Woodall, D.F. (1980) Reye's Syndrome and salicylate use.Pediatr. 66: 859–864.
Tonsgard, J.H. (1985) Urinary dicarboxcylic acids in Reye Syndrome.J. Pediatr. 107: 79–84.
Tonsgard, J.H., and Getz, G.S. (1985) Effect of Reye's Syndrome serum on isolated chinchilla liver mitochondria.J. Clin. Invest. 76: 816–825.
Trauner, D.A. (1982) Pathologic changes in a rabbit model of Reye's Syndrome.Pediatr. Res. 16: 950–953.
Trauner, D.A. (1982) Reye's syndrome.Trends. Neurosci. 5: 131–133.
Trauner, D.A., and Adams, H. (1982) Effect of chain length of short-chain fatty acids on their effect on intracranial pressure in rabbits.J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 45: 428–430.
Waldman, R.J., Hall, W.N., McGee, H., and Van Amburg, G. (1982) Aspirin as a risk factor in Reye's Syndrome.JAMA 247: 3089–3094.
Walker, C.O., and Schenker, S. (1970) Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy with special reference to the role of ammonia.Amer. J. Clin. Nutr. 23: 619–632.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olson, J.E., Evers, J.A. & Holtzman, D. Astrocyte volume regulation and ATP and phosphocreatine concentrations after exposure to salicylate, ammonium, and fatty acids. Metabolic Brain Disease 7, 183–196 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000245
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000245