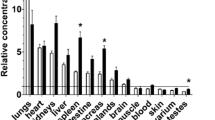
Abstract
Using an indwelling cisterna magna catheter technique, serial CSF samples were analyzed for amino acid content in rats at various stages of portal-systemic encephalopathy resulting from ammonium acetate administration following portacaval anastomosis. Anastomosis alone resulted in increased CSF concentrations of glutamine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, glutamate and alanine. GABA levels, on the other hand were not significantly changed. Onset of severe neurological symptoms following ammonium acetate administration resulted in selectively increased CSF alanine. Other amino acids were not further increased at severe stages of encephalopathy. Increased CSF alanine probably results from increased glutamine transamination in the brains of portacaval shunted rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergeron, M., Pomier Layrargues, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (1989). Aromatic and branched-chain amino acids in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy.Metab Brain Dis 4: 169–176.
Bergeron, M., Swain M.S., Reader, T.A., and Butterworth, R.F. (1991). Increased mesocortical dopaminergic function following portacaval anastomosis in the rat. Abstract, IBRO meeting, Montréal, August 1991.
Bergeron, M., Swain, M.S., Reader, T.A., Grondin, L., and Butterworth, R.F. (1990). Effect of ammonia on brain serotonin metabolism in relation to function in the portacaval shunted rat.J. Neurochem. 55, 222–229.
Bouman, H.J., and Greidanus, T.B. van W. (1979). A rapid and simple cannulation technique for repeated sampling of cerebrospinal fluid in freely moving rats.Brain Res Bull 4: 575–577.
Butterworth, R.F. and Giguère, J.F. (1986). Cerebral aminoacids in portal-systemic encephalopathy: Lack of evidence for altered g-aminobutyric acid (GABA) function.Metab. Brain Dis. 1: 221–228.
Butterworth, R.F., Girard, G., and Giguère, J.F. (1988a). Regional differences in the capacity for ammonia removal by brain following portocaval anastomosis.J Neurochem. 51: 486–490.
Butterworth, R.F., Lavoie, J., Giguère, J.F., Pomier Layrargues, G. (1988b). Affinities and densities of high-affinity [3H] muscimol (GABA-A) binding sites and of central benzodiazepine receptors are unchanged in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy.Hepalology 8: 1084–1088.
Butterworth, R.F., Le, O., Lavoie, J. and Szerb, J.C. (1991). Effect of portacaval anastomosis ion electrically-stimulated release of glutamate from rat hippocampal slices.J. Neurochem. 56, 1481–1484.
Cremer, J.E., Heath, D.F., Teal, H.M., Woods, M.S., and Cavanagh, J.B. (1975). Some dynamic aspects of brain metabolism in rats given a portocaval anastomosis.Neuropathol. Appl, Neurobiol. 3: 293–311.
Ferenci, P., Schafer, D.F., Schafer, G. J. and Hodgson, P.E. (1983). g-aminobutyric acid plasma levels and brain binding in Eck fistula dogs.J. Surg. Res. 38, 143–148.
Giguère, J.F. and Butterworth, R.F. (1984). Amino acid changes in regions of the CNS in relation to function in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy.Neurochem. Res. 9, 1309–1319.
Lavoie, J., Giguère, J.F., Layrargues, G.P., and Butterworth, R.F. (1987). Amino acid changes in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy.J. Neurochem. 49: 692–697.
Lavoie, J., Pomier Layrargues, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (1990). Increased densities of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in brain autopsy samples from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy.Hepatology 11: 874–878.
Lee, S.H., and Fisher, B. (1961). Portocaval shunt in the rat.Surgery 50: 668–672.
Maddison, J.E., Dodd, P.R., Morrison, M., Farrell, G.C. and Johnston, G.A.R. (1987). Plasma GABA concentrations and cerebrocortical GABA receptor binding and function in dogs with congenital portal-systemic encephalopathy. In “Advances in Ammonia Metabolism and Hepatic Encephalopathy” (P.B. Soeters, J.H.P. Wilson, A.J. Meijer and E. Holm, eds), Excepta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 265–274.
Mans, A.M., Biebuyck, J.F., Davis, D.W., and Hawkins, R.A. (1984). Portacaval Anastomosis: Brain and plasma metabolite abnormalities and the effect of nutritional therapy.J. Neurochem. 43: 697–705.
Moroni, F., Lombardi, G., Moneti, G., and Cortesini, C. (1983). The release and neosynthesis of glutamic acid are increased in experimental models of hepatic encephalopathy.J Neurochem. 40: 850–854.
Moroni, F., Riggio, O., Carla, V., Festuccia, V., Ghinelli, F., Marino, I.R., Merli, M., Natali, L., Pedretti, G., Fiaccadori, F. and Capocaccia, L. (1987). Hepatic Encephalopathy: lack of changes of g-aminobutyric acid content in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid.Hepatology 7, 817–820.
Norenberg, M.D. (1989). The use of cultured astrocytes in the study of hepatic encephalopathy. In“Hepatic Encephalopathy: pathophysiology and treatment” (R.F. Butterworth and G. Pomier Layrargues, eds), Humana Press, Clifton, New Jersey, pp 215–229.
Plum, F., and Hindfelt, B. (1976). The neurological complications of liver disease. In Vinken, P.J., and Bruyn, G.W. (eds.),Metabolic and Deficiency Diseases of the Nervous System, Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol. 27, American Elsevier, New York, pp. 349–377.
Roy, S., Pomier-Layrargues, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (1988). Hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic and portacaval shunted dogs: lack of changes in brain GABA uptake, brain GABA levels, brain glutamic acid decarboxylase activity and brain postsynaptic GABA receptors.Hepatology 8: 845–849.
Swain, M., Butterworth, R.F. and Blei, A.T. (1991). Ammonia-related amino acids in the pathogenesis of brain edema in acute liver failure in rats.Hepatology (in press)
Tossman, U., Delin, A., Eriksson, L.S., and Ungerstedt, U.(1987). Brain cortical amino acids measured by inracerebral dialysis in portacaval shunted rats.Neurochem Res. 12: 265–269.
Yudkoff, M., Nissim, I. and Pleasure, D. (1988). Astrocyte metabolism of [15N] glutamine: implications for the glutamine-glutamate cycle.J. Neurochem. 51, 843–850.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Therrien, G., Butterworth, R.F. Cerebrospinal fluid amino acids in relation to neurological status in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy. Metabolic Brain Disease 6, 65–74 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999904
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999904