Abstract
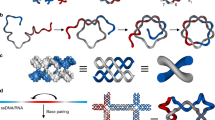
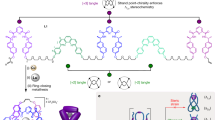
A general strategy is described for the synthesis of single-stranded nucleic acid knots. Control of nucleic acid sequence is used to direct the formation of secondary structures that produce the target topology. The key feature of the strategy is the equation of a half-turn of double helical DNA or RNA with a node in a knot. By forming nodes from complementary DNA sequences, it appears possible to direct the assembly of any simple knot. Stabilization of individual nodes may be achieved by constructing them from long regions containing both B-DNA and Z-DNA. Control over the braiding of DNA that acts as a link between node-forming domains can be realized by condensing the nodes into well-defined DNA structures, such as extended domains of linear duplex, branched junctions, antijunctions or mesojunctions. Further topological control may be derived from the pairing of linker regions to complementary single-stranded molecules, thereby preventing them from braiding in an undesirable fashion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. L. Frisch and E. Wasserman,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 83, 3789 (1961).
H. K. Moffat,Nature 347, 367 (1990).
D. M. Walba,Tetrahedron 41, 3161 (1985).
J.-P. Sauvage,Accts. of Chem. Res. 23, 319 (1990).
C. O. Dietrich-Buchecker, J. Guilham, C. Pascard, and J.-P. Sauvage,Ang. Chem., Int. Ed. 29, 556 (1990).
K. Mizuuchi, L. M. Fisher, M. H. O'Dea, and M. Gellert,Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (U.S.A.)77, 1847 (1980).
S. A. Wasserman and N. R. Cozzarelli,Science 232, 951 (1986).
J. D. Griffith and H. A. Nash,Nat. Acad. Sci. (U.S.A.)82, 3124 (1985).
L. F. Liu, C. C. Liu, and B. M. Alberts,Cell 19, 697 (1980).
L. F. Liu, R. E. Depew, and J. C. Wang,J. Mol. Biol. 106, 439 (1976).
J. C. Wang,Sci. Am. 247, 94 (1982).
N. C. Seeman,J. Biomol. Str. & Dyns. 5, 997 (1988).
J. E. Mueller, S. M. Du, and N. C. Seeman,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113, 6306 (1991).
S. M. Du and N. C. Seeman,J. Am. Chem. Soc., in press.
V. F. R. Jones,Bull. Am. Mat. Soc. 12, 103 (1985).
J. H. van de Sande, N. B. Ramsing, M. W. Germann, W. Elhorst, B. W. Kalisch, E. von Kitzing, R. T. Pon, R. C. Clegg, and T. M. Jovin,Science 241, 551 (1988).
N. C. Seeman,J. Biomol. Str. & Dyns. 8, 573 (1990).
J. Chen and N. C. Seeman,Nature 350, 361 (1991).
G. W. Ashley and D. M. Kushlan,Biochemistry 30, 2927 (1991).
A. Rich, A. Nordheim, and A. H.-J. Wang,Ann. Rev. Biochem. 53, 791 (1984).
T. M. Jovin, L. P. McIntosh, D. J. Arndt-Jovin, D. A. Zarling, M. Robert-Nicoud, J. H. van de Sande, K. F. Jorgenson and F. Eckstein,J. Biomol. Str. & Dyns. 1, 21 (1983).
M. Behe and G. Felsenfeld,Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (U.S.A.)78, 1619 (1981).
K. B. Hall, P. Cruz, I. Tinoco, T. M. Jovin, and J. H. van de Sande,Nature 311, 584 (1984).
S. A. Winkle and R. D. Sheardy,Biochemistry 29, 6514 (1990).
N. C. Seeman,J. Theor. Biol. 99, 237 (1982).
S. M. Du, S. Zhang, and N. C. Seeman,Bikochemistry, is press.
P. J. Hagerman,Ann. Rev. Biophys. & Biophys. Chem. 17, 265 (1988).
R. Holliday,Genet. Res. 5, 282 (1964).
Y. Wang, J. E. Mueller, B. Kemper, and N. C. Seeman,Biochemistry 30, 5667 (1991).
N. C. Seeman and N. R. Kallenbach, in J. J. Stezowski, J.-L. Huang, and M.-C. Shao (eds.),Molecular Structure, Chemical Reactivity and Biological Activity. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p. 189 (1988).
N. B. Leontis, W. Kwok, and J. S. Newman,Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 759 (1991).
R.-I. Ma, N. R. Kallenbach, R. D. Sheardy, M. L. Petrillo, and N. C. Seeman,Nucl. Acids Res. 14, 9745 (1986).
M. L. Petrillo, C. J. Newton, R. P. Cunningham, R.-I. Ma, N. R. Kallenbach, and N. C. Seeman,Biopolymers 27, 1337 (1988).
J. H. White, K. C. Millett, and N. R. Cozzarelli,J. Mol. Biol. 197, 585 (1987).
R. Jin, K. J. Breslauer, R. A. Jones, and B. L. Gaffney,Science 250, 543 (1990).
G. Felsenfeld, D. R. Davies, and A. Rich,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79, 2023 (1957).
N. C. Seeman,DNA & Cell Biol. 10, 475 (1991).
E. Jablonski, E. W. Mooman, R. H. Tullis, and J. L. Ruth,Nucl. Acids Res. 14, 6115 (1986).
M. Wolters and B. Wittig,Nucleic Acids Res. 13, 5163 (1989).
J. Jenkins, Master's Thesis, University of California (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seeman, N.C. The design of single-stranded nucleic acid knots. Mol Eng 2, 297–307 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999532
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999532