Abstract
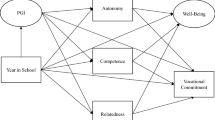
The purpose of this paper was to develop and test a model of college gains using Pace's conceptual theory of student responsibility and perceived college environment as a guide. An analysis of student responses at 11 selected institutions was accomplished using EQS, a covariance structure modeling technique. Findings suggest that the principal determinant of student gains is the effort that students put into their academic and social experiences. This finding held for gains in general education, personal growth, and vocational preparedness. Results suggest that what students do while at college is more important in defining what is accomplished than their backgrounds. Student involvement is enhanced by the perception that the college provides a generally supportive and facilitative environment. Observed effects of major and gender are complex and suggest the importance of the microenvironment in college outcomes research. While these variables are important in understanding the process by which gains are made, they are unimportant in accounting for gains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astin, A. (1985).Achieving Educational Excellence: A Critical Assessment of Priorities and Practices in Higher Education. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Bean, J. (1982). Student attrition, intentions, and confidence: Interaction effects in a path model.Research in Higher Education 17(4): 291–320.
Belenky, M., Clinchy, B., Goldberger, N., and Tarule, J. (1986).Women's Ways of Knowing: The Development of Self, Voice and Mind. New York: Basic Books.
Bentler, P. (1989).EQS Structural Equations Program Manual. Los Angeles: BMDP Statistical Software.
Dubin, R. (1969).Theory Building. New York: Macmillan.
Glymour, C., Scheines, R., Spirtes, P., and Kelly, K. (1987).Discovering Causal Structure. Orlando, FL: Academic Press.
Hanneman, R. (1988).Computer Assisted Theory Building. Newbury Park, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc.
Kolb, D. (1984).Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Kuh, G., Schuh, J., Whitt, E., and Associates (1991).Involving Colleges. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Pace, R. (1979a).College Student Experiences, Los Angeles: UCLA Laboratory for Research on Higher Education.
Pace, R. (1979b).Measuring Outcomes of College. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Pace, R. (1984).Measuring the Quality of College Student Experiences. Los Angeles: UCLA Center for the Study of Evaluation.
Pace, R. (1987).CSEQ: Test Manual & Norms. Los Angeles. UCLA Center for the Study of Evaluation.
Pace, R. (1992).College Student Experiences Questionnaire: Norms for the Third Edition, 1990. Los Angeles: UCLA Center for the Study of Evaluation.
Pascarella, E. (1991). The impact of college on students: The nature of the evidence.Review of Higher Education 14(4): 453–466.
Pascarella, E., and Terenzini, P. (1983). Predicting voluntary freshman year persistence/withdrawal behavior in a residential university: A path analytic validation of Tinto's model.Journal of Educational Psychology 75: 215–226.
Pascarella, E., and Terenzini, P. (1991).How College Affects Students. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Popper, K. (1961).The Logic of Scientific Discovery. New York: Science Editions.
Terenzini, P., and Wright, T. (1987). Influences on students' academic growth during four years of college.Research in Higher Education 26(2): 161–179.
Tinto, V. (1975). Dropout from higher education: A theoretical synthesis of recent research.Review of Educational Research 45: 89–125.
Van Dalen, D. (1966).Understanding Educational Research. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, T.M., Murrell, P.H. A structural model of perceived academic, personal, and vocational gains related to college student responsibility. Res High Educ 34, 267–289 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00991846
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00991846