Abstract
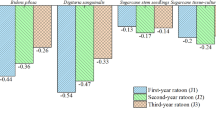
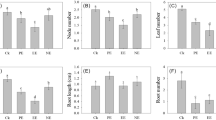
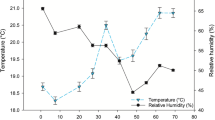
We previously reported thatPolygonum aviculare has a strong allelopathic action againstCynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. and other test species. Moreover, we found that several phenolic compounds appeared to be important allelochemics in this activity. We have now isolated other potential inhibitors fromP. aviculare residues and soil underPolygonum stands, and none of these occurred in soil underC. dactylon stands. GC-MS analysis revealed that these additional inhibitors are long-chain fatty acids with 14–22 carbons. Nine were identified inP. aviculare residues and seven in soil underP. aviculare. Sodium salts of all the identified fatty acids inhibited seedling growth ofC. dactylon and at least some test strains of the nitrogen-fixing bacteria,Azotobacter andRhizobium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsaadawi, I.S., andRice, E.L. 1982a. Allelopathic effects ofPolygonum aviculare L. I. Vegetational patterning.J. Chem. Ecol. 8:993–1009.
Alsaadawi, I.S., andRice, E.L. 1982b. Allelopathic effects ofPolygonum aviculare L. II. Isolation, characterization, and biological activities of phytotoxins.J. Chem. Ecol. 8:1011–1023.
Cathey, H.M., Steffens, G.L., Stuart, N.W., andZimmerman, R.H. 1966. Chemical pruning of plants.Science 153:1382–1383.
Chou, C.H., andPatrick, Z.A. 1976. Identification and phytotoxic activity of compounds produced during decomposition of corn and rye residues in soil.J. Chem. Ecol. 2:369–387.
McCracken, M.D., Middaugh, R.E., andMiddaugh, R.S. 1980. A chemical characterization of an algal inhibitor obtained fromChlamydomonas.Hydrobiologia 70:271–276.
Patrick, Z.A. 1971. Phytotoxic substances associated with the decomposition in soil of plant residues.Soil Sci. 111:13–18.
Proctor, V.W. 1957. Studies of algal antibiosis usingHaematococcus andChlamydomonas.Limnol. Oceanogr. 2:125–139.
Society of American Bacteriologists. 1957. Manual of Microbiological Methods. McGraw Hill, New York.
Spoehr, H.A., Smith, J.H.C., Strain, H.H., Milner, H.W., andHardin, G.J. 1949. Fatty Acid Antibacterials From Plants. Pub. 586. Carnegie Institution of Washington, Washington, D.C.
Tang, C.S., andWaiss, A.C., Jr. 1978. Short-chain fatty acids as growth inhibitors in decomposing wheat straw.J. Chem. Ecol. 4:225–232.
Tso, T.C. 1964. Plant-growth inhibition by some fatty acids and their analogues.Nature 202:511–512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alsaadawi, I.S., Rice, E.L. & Karns, T.K.B. Allelopathic effects ofPolygonum aviculare L.. J Chem Ecol 9, 761–774 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988781
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988781