Abstract
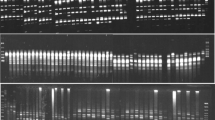
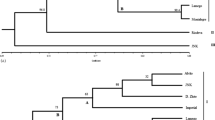
Twenty-six accessions of wildArachis species and domesticated peanuts,A. hypogaea, introduced from South America were analyzed for random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). The objective of the study was to investigate inter- and intraspecific variation and affinities among species of sect.Arachis which have been proposed as possible progenitors for the domesticated peanut. Ten primers resolved 132 DNA bands which were useful for separating species and accessions. The most variation was observed among accessions ofA. cardenasii andA. glandulifera whereas the least amount of variation was observed inA. hypogaea andA. monticola. The two tetraploid species could not be separated by using RAPDs.Arachis duranensis was most closely related to the domesticated peanut and is believed to be the donor of the A genome. The data indicated thatA. batizocoi, a species previously hypothesized to contribute the B genome toA. hypogaea, was not involved in its evolution. The investigation showed that RAPDs can be used to analyze both inter- and intraspecific variation in peanut species. Southern hybridization of RAPD probes to blots containing RAPD of theArachis species provided information on genomic relationships and revealed the repetitive nature of the amplified DNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianchi-Hall, C., Keys, R. D., Stalker, H. T., Murphy, J. P., 1993: Diversity of seed storage proteins in wild peanut (Arachis species). — Pl. Syst. Evol.186: 1–15.
Demeke, T., Adams, R. P., Chibbar, R., 1992: Potential taxonomic use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD): a case study inBrassica. — Theor. Appl. Genet.84: 990–994.
Devos, K. M., Gale, M. D., 1992: The use of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers in wheat. — Theor. Appl. Genet.84: 567–572.
Dice, L. R., 1945: Measures of the amount of ecological association between species. — Ecology26: 295–302.
Gregory, M. P., Gregory, W. C., 1979: Exotic germplasm ofArachis L. interspecific hybrids. — J. Heredity70: 185–193.
Gregory, W. C., Gregory, M. P., 1976: Groundnut.Arachis hypogaea (Leguminosae, Papilionatae). — InSimmonds, N. W., (Ed.): Evolution of crop plants, pp. 151–154. — London: Longman.
—, 1973: Structure and genetic resources of peanut. — In Peanut's: culture and uses. — Stillwater, Oklahoma: American Peanut Research and Education.
Grieshammer, U., Wynne, J. C., 1990: Isozyme variability in mature seeds of U.S. peanut cultivars and collections. — Peanut Sci.18: 72–75.
Halward, T., Stalker, T., La Rue, E., Kochert, G., 1992: Use of single- primer DNA amplifications in genetic studies of peanut (Arachis hypogeae L.) — Pl. Molec. Biol.18: 315–325.
Harlan, J. R., De Wet, J. M. J., 1971: Toward a rational classification of cultivated plants. — Taxon3: 509–517.
He, S., Ohm, H., Machenzie, S., 1992: Detection of DNA polymorphisms among wheat varieties. — Theor. Appl. Genet.84: 573–581.
Hilu, K. W., 1994a: Evidence from RAPD markers in the evolution ofEchinochloa millets (Poaceae). — Pl. Syst. Evol.189: 247–257.
—, 1994b: Evolution of domesticated plants. — InArntzen, C. J., (Ed.): Encyclopedia of agricultural science,2, pp. 117–127. — London: Academic Press.
Kochert, G., Halward, T., Branch, W. D., Simpson, C. E., 1991: RFLP variability in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars and wild species. — Theor. Appl. Genet.81: 565–570.
- -Stalker, H. T., 1996: Genetic variation in peanut and its implications in plant breeding. — InPickersgill, B., (Ed.): Advances in legume science3. Proc. Kew Conference. — London (in press).
Krapovickas, A., Gregory, W. C., 1994: Taxonomy of the genusArachis (Leguminosae). — Bonplandia8: 1–186.
Lanham, P. G., Fennel, S., Moss, J. P., Powell, W., 1992: Detection of polymorphic loci inArachis germplasm using random amplified polymorphic DNAs. — Genome35: 885–889.
M'Ribu, H. K., Hilu, K. W., 1994: Detection of interspecific and intraspecific variation inPanicum millets through random amplified polymorphic DNA. — Theor. Appl. Genet.88: 412–416.
Nei, M., Li, W. H., 1979: Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restrictions endonucleases. — Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA76: 5269–5273.
Paik-Ro, O. G., Smith, R. L., Knauft, D. A., 1992: Restriction fragment length polymorphism evaluation of six peanut species within theArachis section. — Theor. Appl. Genet.84: 201–208.
Quiros, C. F., Ceada, A., Georgescu, A., Hu, J., 1993: Use of RAPD markers in potato genetics: segregations in diploid and tetraploid families. — Amer. Potato J.70: 35–42.
Raman, V. S., 1958: Studies in the genusArachis. IV. Hybrid betweenA. hypogaea andA. monticola. — Indian Oilseeds J.2: 20–23.
Reed, K. C., Mann, D. A., 1985: Rapid alkaline transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. — Nucl. Acid Res.13: 7207–7221.
Rohlf, F. J., 1993: NTSYS-PC numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, ver. 1.80. — Setauket, New York: Exeter
Saghai-Maroof, M. A., Soliman, K. M., Jorgensen, R. A., Allard, R. W., 1984: Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. — Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA81: 8014–8018.
Seetharam, A., Nayar, K. M. D., Sreekantaradhya, R., Achar, D. K. T., 1973: Cytological studies on the interspecific hybrid ofArachis hypogaea ×Arachis duranensis. — Cytologia38: 277–280.
Singh, A. K., 1988: Putative genome donors ofArachis hypogaea (Fabaceae), evidence from crosses with synthetic amphiploids. — Pl. Syst. Evol.160: 143–151.
Singsit, C., Ozias-Akins, P., 1993: Genetic variation in monoploids of diploid potatoes and detection of clone-specific random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. — Pl. Cell. Rep.12: 144–148.
Smartt, J., Gregory, W. C., Gregory, M. P., 1978a: The genomes ofArachis hypogaea. 1. Cytogenetic studies of putative genome donors. — Euphytica27: 665–675.
—, 1987b: The genomes ofArachis hypogaea. 2. Implications in interspecific breeding. — Euphytica27: 677–680.
Sneath, P. H. A., Sokal, R. R., 1973: Numerical taxonomy. — San Francisco: Freeman.
Stalker, H. T., 1985: Cytotaxonomy ofArachis. — InMoss, J. P., (Ed.): Proceedings of the international workshop on cytogenetics ofArachis, Hyderabad, India, 31 Oct. — 2 Nov. 1983, pp. 65–79. — Patancheru, India: Icrisat.
—, 1990: A morphological appraisal of wild species in sectionArachis of peanuts. — Peanut Sci.17: 117–122.
—, 1991: A new species in sectionArachis of peanuts with a D genome. — Amer. J. Bot.78: 630–637.
—, 1986: Karyotype analysis and relationships among varieties ofArachis hypogaea. — Caryologia51: 617–629.
—, 1987: Speciation, cytogenetics and utilization ofArachis species. — Adv. Agron.41: 1–40.
—, 1995: Germplasm resources inArachis. — InPattee, H. E., Stalker, H. T., (Eds): Advances in peanut science. — Research Education Society. North Carolina, USA: American Peanut (in press).
—, 1994: Diversity of isozyme patterns inArachis species. — Theor. Appl. Genet.87: 746–755.
Varisai Muhammad, S., 1973: Cytological investigations in the genusArachis L. II. Triploid hybrids and their derivatives. — Madras Agric. J.60: 1414–1427.
Vierling, R. A., Nguyen, H. T., 1992: Use of RAPD markers to determine the genetic diversity of diploid wheat genotypes. — Theor. Appl. Genet.84: 835–838.
Welsh, J., McClelland, M., 1990: Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. — Nucl. Acids Res.18: 7213–7218.
Williams, J. G. K., Kubelik, A. R., Livak, K. J., Rafalski, J. A., Tingey, S. V., 1990: DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. — Nucl. Acids Res.18: 6531–6535.
Xu, Y., Clark, M. S., Pehu, E., 1993: Use of RAPD markers to screen somatic hybrids betweenSolanum tuberosum andS. brevidens. — Pl. Cell Rep.12: 107–109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hilu, K.W., Stalker, H.T. Genetic relationships between peanut and wild species ofArachis sect.Arachis (Fabaceae): Evidence from RAPDs. Pl Syst Evol 198, 167–178 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984735
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984735