Abstract
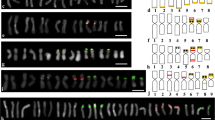
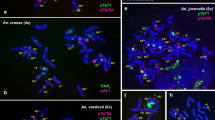
C-banding patterns and polymorphisms were analyzed in several accessions of the diploidAegilops speciesAe. uniaristata, Ae. mutica, andAe. comosa subsp.comosa and subsp.heldreichii, and standard karyotypes of these species were established. Variation in C-band size and location was observed between different accessions, but did not prevent chromosome identification. One accession ofAe. uniaristata was homozygous for whole-arm translocations involving chromosomes 1N and 5N. The homoeologous relationships of these chromosomes were established by comparison of chromosome morphologies and C-banding patterns to other diploidAegilops species with known chromosome homoeology. In addition, in situ hybridization analysis with a 5S rDNA probe was used to identify homoeologous groups 1 and 5 chromosomes. The present analysis permitted the assignment of allAe. mutica, comosa subsp.comosa, andAe. comosa subsp.heldreichii chromosomes, and three of the sevenAe. uniaristata chromosomes according to their homoeologous groups. The data presented will be useful analyzing genome differentiation in polyploidAegilops species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chennaveeraiah, M. S., 1960: Karyomorphologic and cytotaxonomic studies inAegilops. — Acta Horti Gothob.23: 85–178.
Dvorak, J., Zhang, H.-B., Kota, R. S., 1989: Organization and evolution of the 5S rRNA gene family in wheat and related species. — Genome32: 1003–1016.
Feldman, M., Strauss, I., Vardi, A., 1979: Chromosome pairing and fertility of F1 hybrids ofAegilops longissima andAe. searsii. — Canad. J. Genet. Cytol.21: 261–272.
Friebe, B., Gill, B. S., 1996: Chromosome banding and genome analysis in diploid and cultivated polyploid wheats. — InJauhar, P. P., (Ed.): Methods of genome analysis in plants, pp. 39–60. — Boca Raton: CRC Press.
—, 1992a: C-banding polymorphisms in several accessions ofTriticum tauschii (Aegilops squarrosa). — Genome35: 192–199.
—, 1992b: C-banding pattern and polymorphism ofAegilops caudata and chromosomal constitutions of the amphiploidT. aestivum-Ae. caudata and six derived chromosome addition lines. — Theor. Appl. Genet.83: 589–596.
—, 1993: Standard karyotype ofTriticum longissimum and its cytogenetic relationship withT. aestivum. — Genome36: 731–742.
—, 1995a: Standard karyotype ofTriticum umbellulatum and the characterization of derived chromosome addition and translocation lines in common wheat. — Theor. Appl. Genet.90: 150–156.
Friebe, B., Jiang, J., Tulleen, N., 1995b: Standard karyotype ofTriticum searsii and its relationship with other S-genome species and common wheat. — Theor. Appl. Genet.91: 248–255.
—, 1995c: Detection of 5S rDNA and other repeated DNA on supernumerary B chromosomes ofAegilops species (Poaceae). — Pl. Syst. Evol.196: 131–139.
Gerlach, W. L., Dyer, T. A., 1980: Sequence organization of the repeated units in the nucleus of wheat which contains 5S-rRNA genes. — Nucleic Acids Res.8: 4851–4865.
Gill, B. S., 1981: Evolutionary relationships based on heterochromatin bands in six species of theTriticinae. — J. Heredity72: 391–394.
—, 1974: Giemsa C-banding and the evolution of wheat. — Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71: 4086–4090.
—, 1991: Standard karyotype and nomenclature system for description of chromosome bands and structural aberrations in wheat (Triticum aestivum). — Genome24: 830–839.
Hammer, K., 1980: Vorarbeiten zur monographischen Darstellung von Wildpflanzensortimenten:Aegilops L. — Kulturpflanze28: 33–180.
—, 1987: Resistenzmerkmale und Reproduktionssystem als Indikatoren für evolutionäre Tendenzen in der GattungAegilops L. — Biol. Zentralbl.106: 273–282.
—, 1993: Variation in breeding systems in theTriticinae. — InDamania, A. B., (Ed.): Biodiversity and wheat improvement, pp. 51–58. — Chichester, NY: Wiley.
Jiang, J., Gill, B. S., 1994: Different species-specific chromosome translocations inTriticum timopheevii andT. turgidum support the diphyletic origin of polyploid wheats. — Chromosome Res.2: 59–64.
Kihara, H., 1937: Genomanalyse beiTriticum undAegilops. VII. Kurze Übersicht über die Ergebnisse der Jahre 1934–36. — Mem. Coll. Agr. Kyoto Imp. Univ. No.42 (Genet. Ser. No. 7), 1–61.
Mochizuki, A., 1957: B chromosomes inAegilops mutica Boiss. — Wheat Inform. Serv.5: 9–11.
—, 1960: A note on the B chromosomes in natural population ofAegilops mutica Boiss. in central Turkey. — Wheat Inform. Serv.11: 31.
Mukai, Y., Endo, T. R., Gill, B. S., 1990: Physical mapping of the 5S rRNA multigene family in common wheat. — J. Heredity81: 290–295.
Ohta, S., 1991: Phylogenetic relationship ofAegilops mutica Boiss. with the diploid species of congenericAegilops-Triticum complex, based on the new method of genome analysis using its B-chromosomes. — Mem. Coll. Agric., Kyoto Univ. No.137: 1–116.
Riley, R., Chapman, V., Johnson, R., 1968a: The incorporation of alien disease resistance in wheat by genetic interference with the regulation of meiotic chromosome synapsis. — Genet. Res.12: 198–219.
Riley, R., Chapman, V., Johnson, R., 1968b: Introduction of yellow rust resistance ofAegilops comosa into wheat by genetically induced homoeologous recombination. — Nature217: 383–384.
Simchen, G., Zarchi, Y., Hillel, J., 1971: Supernumerary chromosomes in the second outbreeding species of the wheat group. — Chromosoma33: 63–69.
Teo, S. B., Hutchinson, J., 1983: Interspecific variation in C-banded chromosomes of diploidAegilops species. — Theor. Appl. Genet.65: 31–40.
—, 1983: Intraspecific variation in C-banded chromosomes ofAegilops comosa andAe speltoides. — Theor. Appl. Genet.65: 343–348.
Van Slageren, M. W., 1994: Wild wheats: a monograph ofAegilops L. andAmblyopyrum (Jaub. & Spach)Eig (Poaceae). — Wageningen Agricultural University Papers94-7: 512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friebe, B., Badaeva, E.D., Kammer, K. et al. Standard karyotypes ofAegilops uniaristata, Ae. mutica, Ae. comosa subspeciescomosa andheldreichii (Poaceae). Pl Syst Evol 202, 199–210 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00983382
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00983382