Abstract
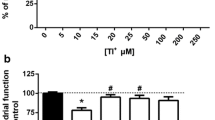
The effects of Cu2+ on glycolysis and several glycolytic enzymes were studied in rat brain extracts in vitro. At concentrations reportedly found in Wilson's disease, Cu2+ significantly inhibited lactate production from glucose or glucose-6-phosphate in rat brain postnuclear supernatant with an IC50 of about 3 μM. Cu2+ also inhibited several glycolytic enzymes. Amongst the latter, Cu2+ was most effective in inhibiting hexokinase (IC50 for Cu2+=7 μM), moderately effective in inhibiting pyruvate kinase (IC50 for Cu2+=56 μM), but least effective in inhibiting lactate dehydrogenase (IC50 for Cu2+=300 μM). These results suggest that inhibition of brain glycolysis may have pathophysiological importance in copper poisoning and in Wilson's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Underwood, E. J. 1977. Copper. Pages 56–108.in Trace elements in human and animal nutrition, 4th edition, Academic Press, New. York.
Chuttani, H. K., Grupta, P. S., Gulati, S., andGupta, D. N. 1965. Acute copper sulfate poisoning. Am. J. Med. 38:849–854.
Wilson, A. K. 1912. Progressive lenticular degeneration: a familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis of the liver. Brain 32:295–509.
Scheinberg, I. H., andSternlieb, I. 1965. Wilson's disease. Ann. Rev. Med. 16:119–134.
Sherlock, S. 1975. Hepatolenticular degeneration. Pages 477–489.In Desease of the liver and the biliary system, 5th edition, Blackwell, Oxford.
Cumings, J. N. 1959. Pages 3–71,in Heavy metals and the brain, Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, Ill.
Curzon, G. 1975. Metals and melanins in the extrapyramidal centers. Pharmacol. Ther. B. 1:673–684.
Shulman, S. 1968. Wilson's disease. Pages 1139–1152,in Minckler, J. (ed.), Pathology of the nervous sytem, Vol. 1, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Scheinberg, I. H., Sternlieb, I. 1969. The liver in Wilson's disease. Gastroenterol. 37:550–564.
Goldfischer, S., andSternlieb, I. 1968. Changes in the distribution of hepatic copper in relation to the progress of Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration). Am. J. Pathol. 53:883–901.
Peters, R., andWalshe, J. M. 1966. Studies on the toxicity of copper. I. The toxic action of copper in vivo and in vitro. Proc. Roy. Soc. B. 166:273–284.
Epstein, P. S., anMcIlwain, H. 1966. Actions of cupric salts on isolated cerebral tissues. Proc. Roy. Soc. B. 166:295–302.
Peters, R., Shorthouse, M., andWalshe, J. M. 1966. Studies on the toxicity of copper. II. The behavior of microsomal membrane ATPase of the pigeon's brain tissue to copper and some other metallic substances. Proc. Roy. Soc. B. 166:285–294.
Donaldson, J., St.-Pierre, T., Minnich, J., andBarbeau, A. 1971. Seizures in rats associated with divalent cation inhibition of Na+−K+-ATP'ase. Can. J. Biochem. 49:1217–1224.
Ting-Beall, H. P., Clark, D. A., Suelter, C. H., andWells, W. W. 1973, Studies on the interaction of chick brain microsomal (Na++K+)-ATPase with copper. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 291:229–236.
Prakash, N. J., Fontana, J., andHenkin, R. I. 1973. Effect of transitional metal ions on (Na++K+)ATPase activity and the uptake of norepinephrine and choline by brain synaptosomes. Life Sci. 12:249–259.
Hexam, T. D. 1974. Studies on the reaction catalyzed by transport (Na+, K+) adenosine triphosphatase: I—Effects of divalent metals. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23:3441–3447.
Lai, J. C. K., andBlass, J. P. 1983. Aluminum selectively inhibits brain hexokinase. Trans. Am. Soc. Neurochem. 14:122.
Lai, J. C. K., andBlass, J. P. 1984. Inhibition of brain glycolysis by aluminum. J. Neurochem. 42:438–446.
Lai, J. C. K., Baker, A., Blass, J. P. 1983. Differential inhibitory effects of metal ions on brain hexokinase. Fed. Proc. 42:627.
Lai, J. C. K., andClark, J. B. 1979. Preparation of synaptic and non-synaptic mitochondria from mammalian brain. Methods Enzymol. 55, Part F: 51–60.
Glowinski, J., andIversen, L. L. 1966. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]-norepinephrine, [3H]-dopamine and [3H]-dopa in various regions of the brain. J. Neurochem. 13:655–669.
Lai, J. C. K., Walsh, J. M., Dennis, S. C., andClark, J. B. 1977. Synaptic and non-synaptic mitochondria from rat brain: isolation and characterization. J. Neurochem. 28:625–631.
Lowry, O. H., andPassonneau, J. V. 1972. A collection of metabolite assays. Pages 194–200, in a Flexible system of enzymatic analysis, Academic Press, New York.
Lai, J. C. K., Leung, T. K. C., Marr, W., andLim, L. 1980. The activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in liver and hypothalamus of the female rat: effects of administration of ethinyl oestradiol and the progestogens norethisterone acetate and dnorgestrel. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 8:64.
Leong, S. F., Lai, J. C. K., Lim, L., andClark, J. B. 1981. Energy-metabolizing enzymes in brain regions of adult and aging rats. J. Neurochem. 37:1548–1556.
Clark, J. B., andNicklas, W. J. 1970. The metabolism of rat brain mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 245:4724–4731.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., andRandall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurements with Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Lai, J. C. K., Chan, A. W. K., Minski, M. J., Leung, T. K. C., Lim, L., andDavison, A. N. 1984. Instrumental neutron activation analysis of metals in the nervous sytem. In press inGabay, S., Harris, J., andHo, B. T. (eds.), Metal ions in neurology and psychiatry, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Blass, J. P. 1980. Aging of the brain and dementia. Pages 261–270,in Amaducci, L., Davison, A. N., andAntuono, P. (eds.), Aging, Vol. 13, Raven Press, New York.
Blass, J. P., andGibson, G. E. 1979. Carbohydrates and acetylcholine synthesis: implications for cognitive disorders. Pages 215–236,in Davis, K. L., andBerger, P. A. (eds.), Brain acetylcholine and neuropsychiatric disease, Plenum Press, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, J.C.K., Blass, J.P. Neurotoxic effects of copper: Inhibition of glycolysis and glycolytic enzymes. Neurochem Res 9, 1699–1710 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00968080
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00968080