Abstract
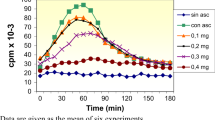
In this study, we describe the lipoperoxidative effect of quinolinic acid (QUIN) in vitro. The formation of thiobarbituric acid reactive products (TBA-RP), an index of lipid peroxidation, was measured in rat brain homogenates after incubation at 37°C for 30 min in the presence of QUIN and some structurally and metabolically related compounds such as Kynurenine, Kynurenic acid, Glutamate, Aspartate and Kainate. Concentrations of QUIN in the range of 20 to 80 μM increased lipid peroxidation in a concentration-dependent manner from about 15% to about 50%. Kynurenic acid, a compound metabollically related to QUIN that can block its neurotoxic actions in vivo, also inhibited completely the QUIN-induced TBA-RP formation in our system. Lipid fluorescent material, another index of lipid peroxidation was also found increased by 49% after incubation with 40 μM QUIN. It is concluded that lipid peroxidation may be a damaging process involved in the neurotoxicity of QUIN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruyn, R. P. M., and Stoof, J. C. 1990. The quinolinic acid hypothesis in Huntington's chorea. J. Neurol. Sci. 95:29–38.
Heyes, M. P., Wyler, A. R., Devinsky, O., Yergey, J. A., Markey, S. P., and Nadi, S. 1990. Quinolinic acid concentrations in brain and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with intractable complex partial seizures. Epilepsia. 31:172–177.
Feldblum, S., Rougier, A., Loiseau, H., Loiseau, P., Cohadon, F., Morselli, P. L., and Lloyd, K. G. 1988. Quinolinic-phosphoribosyl transferase activity is decreased in epileptic human brain tissue. Epilepsia. 29:523–529.
Beal, M. F., Kowall, N. W., Ellison, D. W., Mazurek, M. F., Swartz, K. J., and Martin, J. B. 1986. Replication of the neurochemical characteristics of Huntington's disease by quinolinic acid. Nature 321:168–171.
Lapin, I. P. 1981. Kynurenines and seizures. Epilepsia 22:257–265.
Perkins, M. N., and Stone, T. W. 1983. Pharmacology and regional variations of quinolinic acid-evoked excitations in the rat central nervous system. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 226:551–557.
Moroni, F., Lombardi, G., Carla, V., Pellegrini, D., Corassale, G., and Cortessini, C. 1986. Content of quinolinic acid and of other triptophan metabolites increases in brain regions of rats used as experimentals models of hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurochem. 46:869–874.
Schwarcz, R., Foster, A. C., French, E. D., Whetsell, Jr., N. O., and Kohler, C. 1984. Excitotoxic models for neurodegenerative disorders. Life Sciences 35:19–32.
Choi, D. W. 1988. Calcium-mediated neurotoxicity: relationship to specific channel types and role in ischemic damage. Trends Neurosci. 11:465–469.
Foster, A. C., Collins, J. F., and Schwarcz, R. 1983. On the excitotoxic properties of quinolinic acid, 2,3-piperidine dicarboxylic acid and structurally related compounds. Neuropharmacol. 22:1331–1342.
Halliwell, B., and Gutteridge, M. C. 1984. Oxygen toxicity oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. Biochem. J. 219:1–14.
Zaleska, M. A., and Floyd, R. A. 1985. Regional lipid peroxidation in rat brain in vitro: possible role of endogenous iron. Neurochem. Res. 10:397–410.
Kogure, K. B. D., Watson, B., Busto, R., and Abe, K. 1982. Potentiation of lipid peroxides by ischemia in rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 7:437–454.
Calabrese, V., and Fariello, R. G. 1988. Regional distribution of malondialdehyde in mouse brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 37:2287–2288.
Willmore, L. J., and Rubin, J. J. 1981. Antiperoxidant pretreatment and iron-induced epileptiform discharges in the rat: EEG and histopathologic studies. Neurology 31:63–69.
Fong, T. M., and McNamme, G. M. 1986. Correlation between acetylcholine receptor function and structural properties of membranes. Biochemistry. 25:830–840.
Braughler, J. M. 1985. Lipid peroxidation-induced inhibition of gamma-aminobutiric acid uptake in rat brain synaptosomes: protection by gluco-corticoids. J. Neurochem. 44:1282–1288.
Singh, R., and Pathak, D. N. 1990. Lipid peroxidation and glutathione reductase, superoxide dismutase, catalase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activities in FeCl3-induced epileptogenic foci in the rat brain. Epilepsia 31:15–26.
Wilbur, K. M., Bernheim, F., and Shapiro, O. W. 1949. The thiobarbituric acid reagent as a test for the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids by various agents. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 24:305–313.
Waravdekar, V. S., and Saslaw, L. D. 1959. A sensitive colorimetric method for the estimation of 2-deoxy-sugars with the use of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 234:1945–1950.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Triggs, W. J., and Willmore, L. J. 1984. In vivo lipid peroxidation in rat brain following intracortical Fe++ injection. J. Neurochem. 42:976–979.
Calza, L., Giardino, L., Velardo, A., Battistini, N., and Marrama, P. 1990. Iron-dependent peroxidation of rat brain: a regional study. J. Neurosci. Res. 26:224–232.
Steel, R. G. D., and Torrie, J. H. 1980. Principles and procedures of statistics. 2nd edition. McGraw-Hill.
Rehncrona, S., Smith, D. S., Akeson, B., Westergerd, E., and Siesjo, B. K. 1980. Peroxidative changes in brain cortical fatty acids and phospholipids as characterized during Fe++ and ascorbic acid stimulated lipid peroxidation in vitro. J. Neurochem. 34:1630–1638.
Chan, P. H., Yurko, M., and Fishman, R. A. 1982. Phospholipid degradation and cellular edema induced by free radicals in brain cortical slices. J. Neurochem. 38:525–531.
Garthwaite, G., and Garthwaite, J. 1987. Quinolinate mimics neurotoxic actions of the N-methyl-d-aspartate in rat cerebellar slices. Neurosci. Lett. 79:35–39.
Whetsell, W. O. 1984. The use of organotypic tissue culture for the study of aminoacid neurotoxicity and its antagonism in the mammalian CNS. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 7:238–250.
Sztriha, L. 1986. Increased lipid peroxide formation in the rat forebrain during kainic acid seizures. Biomed. Biochem. Acta. 45:491–494.
Foster, A. C., Vezzani, A., French, E. D., and Schwarcz, R. 1984. Kynutrenic acid blocks neurotoxicity and seizures induced in rats by the related brain metabolite quinolinic acid. Neurosci. Lett. 48:273–278.
Crawford, M., Roberts, P. J. 1989. 1-hydroxy-3-aminopyrrolid-2-one (HA 966) and kynureninate antagonize N-methyl-D-aspartate induced enchancement of 3H-dopamine release from rat striatal slices. Biochem. Pharmacol. 38:4165–4168.
Pullan, L. M., and Cler, J. A. 1989. Schild plot analysis of glycine and kynurenic acid at the N-methyl-D-aspartate excitatory amino acid receptor. Brain Res. 497:59–63.
Bors, W., Buettner, G. R., Michel, C., and Saran, M. 1990. Calcium in lipid peroxidation: Does calcium interact with superoxide? Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 278:269–272.
Tsuzuki, K., Iino, M., Ozawa, S. 1989. Change in calcium permeability caused by quinolinic acid in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 105:269–274.
Halliwell, B., and Gutteridge, M. C. 1985. Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford-Claredon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rios, C., Santamaria, A. Quinolinic acid is a potent lipid peroxidant in rat brain homogenates. Neurochem Res 16, 1139–1143 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00966592
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00966592