Abstract
The effect of hypoglycemia on the uptake of [1-14C]arachidonate and [1-14C]oleate into a synaptosomal and microsomal glycerophospholipids was investigated. In the presence of ATP, Mg2+ and CoA, rat brain synaptosomes and micorsomes catalyze the transfer of arachidonate and oleatc into glycerophospholipids. Arachidonate was mainly incorporated into phosphatidylinositol (PI) and phosphatidylcholine (PC), whereas oleate was incorporated into phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE).
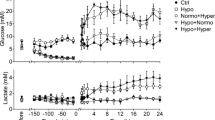
Hypoglycemia was produced by intraperitoneal injection of 10 or 100 units of crystalline insulin per kg body weight. Two hours after injection the blood glucose level decreased to 10–20 mg%. The content of brain phospholipids was slightly decreased but the change was not statistically significant. The level of free fatty acids (FFA) was increased. More pronounced and reproducible changes were found when hypoglycemia was produced by injection of 100 units of insulin per/kg body weight. Changes in brain cortex were similar to those observed in microsomes and synaptosomes. Hypoglycemia affected the incorporation of arachidonic acid into glycerophospholipids of brain membranes. Uptake of [1-14C]arachidonate was decreased selectively by 50% (into phosphatidic acid /PA/) when hypogiycemia was produced by injection of 10 units of insulin per kg body weight. The Higher dose of insulin 100 units per kg body weight produced a 20% inhibition of arachidonate incorporation into synaptosomal PI and a 13% decrease of incorporation into microsomal phosphatidylcholine. Incorporation of [1-14C]oleate into membrane phospholipids was not changed by hypoglycemic insult. It is proposed that the disturbances in fatty acid level, particularly arachidonate, and decreased uptake of arachidonic acid by synaptosomal glycerophospholipids may be responsible for alteration of membrane function and changes of synaptic processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, G. Y., andSun, A. Y. 1972. Phospholipids and acyl groups of synaptosomal and myelin membranes isolated from the cerebral cortex of squirrel monkey. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 280:306–315.
Corbin, D. R., andSun, G. Y. 1978. Characterization of the enzymic transfer of arachidonoyl groups to 1-acyl phosphoglycerides in mouse synaptosomes fraction. J. Neurochem. 30:77–82.
Wojtczak, L. 1976. Effect of long-chain fatty acids and acyl-CoA on mitochondrial permeability transport and energy coupling processes. J. Bioenerget. Biomembr. 8:293–311.
Farias, R. N., Bloj, B., Morero, R. D., Sineriz, F., andTrucco, R. E. 1975. Regulation of allosteric membrane-bound enzymes through changes in membrane lipid composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 415:231–251.
Kimelberg, H. K., andPapahadjopoulos, D. 1972. Phospholipid requirements for Na+ +K+-ATPase activity: head-group specificity and fatty acid fluidity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 228:277–292.
Bazan, N. G. 1970. Effect of ischemia and electroconvulsive shock on free fatty acid pool in the brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 218:1–10.
Bazan, N. G., Bazan, H. E. P., Kennedy, W. G., andJoel, C. D. 1971. Regional distribution and rate of production of free fatty acids in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 18:1387–1393.
Strosznajder, J., Gromek, A., andLazarewicz, J. W. 1972. Effect of ischemia on the free fatty acids level in guinea pig brain. (in Polish). Neuropat. Pol. 10:447–455.
Galli, C., andSpagnuolo, C. 1976. The release of brain fatty acids during ischemia in essential fatty acid deficient rats. J. Neurochem. 26:401–404.
Marion, J., andWolfe, L. S. 1978. Increase in vivo of unesterified fatty acids prostaglandin F2 but not tromboxane B2 in rat brain during drug induced convulsions. Prostaglandins 16:99–110.
Strosznajder, J. 1980. Incorporation of linoleic acid into membrane glycerophospholipids from rat brain submitted to ischemia and hypoxia. Neurochem. Res. 12:1265–1277.
Strosznajder, J., andSun, G. Y. 1981. Effects of acute hypoxia on incorporation of [1-14C] arachidonic acid into glycerophospholipids of rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 6:767–774.
Agardh, C. D., Westerberg, E., andSiesjo, B. K. 1980. Severe hypoglycemia leads to accumulation of arachidonic acid in brain tissue. Acta Physiol. Scand. 109:115–116.
Agardh, C. D., Chapman, A. G., Nilsson, B., andSiesjo, B. K. 1981. Endogenous substrates utilized by rat brain in severe insulin induced hypoglycemia. J. Neurochem. 36:490–500.
Strosznajder, J. 1982. Metabolism of fatty acids by brain membranes after isolation from rats subjected to hypoglycemia. Basic and Clinical Aspects of Molecular Neurobiology. Proceedings of the fourth Meeting of the European Society for Neurochemistry, eds.A. M. Giuffrida Stalla, G. Gombos, G. Benzi, H. S. Bachelard, p. 317.
Knauff, H. G., Mark, D., andMayer, G. 1961. Das Verhalten der Proteine und der serin- und colaminhaltigen Phosphatide des Zentralnervensystems während der Insulinhypoglykämie. Hoppe-Seylers Z Physiol. Chemie 326:227–234.
Knauff, H. G., andBöck, F. 1961. Über die freien Gehirnaminosäuren und das Athanolamine der normalen Ratte sowie über der Verhalten dieser Stoffe nach experimentaller Insulin-Hypoglykämie. J. Neurochem. 6:171–182.
Pappenheimer, J. R., andSetchell, B. P. 1973. Cerebral glucose transport and oxygen consumption in sheep and rabbits. J. Physiol. (London) 233:529–551.
Hinzen, D. H., Becker, P., andMüller, U. 1970. Wirkung von Insulin auf den regionalen Phospholipidstoffwechsel des Kaninchengehirns in vivo Pflügers Arch. 321:1–14.
Twes, J. K., Carter, S. H., andStone, W. E. 1965. Chemical changes in the brain during insulin hypoglycaemia and recovery. J. Neurochem. 12:679–693.
Ansell, G. B., andSpanner, S. 1959. The effect of insulin on the formation of phosphorylcholine and phosphorylethanolamine in the brain. J. Neurochem. 4:325–331.
De Ropp, R. S., andSnedeker, E. H. 1961. Effect of drugs on amino acid levels in rat brain: hypoglycemic agents. J. Neurochem. 7:128–134.
Schmidt, F. H. 1961. Die enzymatische Bestimmung von Glucose and Fructose nebeneinander. Klin. Wschr. 39:1244–1247.
Booth, R. F., andClark, J. B. 1978. A rapid method for the preparation of relatively pure metabolically competent synaptosomes from rat brain. Biochem. J. 176:365–370.
Rafalowska, U., Erecinska, M., andWilson, D. F. 1980. Energy metabolism in rat brain synaptosomes from nembutal anesthetize and nonanesthetized animals. J. Neurochem. 34:1380–1386.
Strosznajder, J., andDabrowiecki, Z. 1977. Enzymic synthesis of ethanolamine plasmalogens in the microsomal fraction of rat brain under oxygen deficiency. Bull. Acad. Polon. Sci. Ser. Biol 25:133–139.
Folch, J., Lees, M., andSloane-Stanley, G. H. 1957. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226:497–509.
Bartlett, G. R. 1959. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 234:466–468.
Horrocks, L. A., andSun, G. Y. 1972. Ethanolamine plasmalogens. Pages 223–231,in Rodnight, R., andMarks, N. (eds.). Research Methods in Neurochemistry, Plenum Press, New York.
Dole, V. P., andMeinertz, H. 1960. Micro-determination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 235:2595–2599.
Itaya, K., andUi, H. 1965. Colorimetric determination of free fatty acid in biological fluids. J. Lipid Res. 6:16–21.
Bazan, N. G., andRakowski, H. 1970. Increased levels of brain free fatty acids after electroconvulsive shock. Life Sci. 9:501–507.
Bazan, N. G. 1976. 1976. Free arachidonic acid and other lipids in the nervous system during early ischemia and after electroshock. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 72:317–335.
Rodriguez De Turco, E. B., Cascone, G. D., Pediconi, M. F., andBazan, N. G. 1977. Phosphatidate, phosphatidylinositol, diacylglycerol and free fatty acids in the brain following electroschock, anoxia and ischemia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 83:389–396.
Strosznajder, J., Foudin, L., Tang, W., andSun, G. Y. 1983. Serum albumin washing specifically enhances arachidonate incorporation into synaptosomal phosphatidylinositols. J. Neurochem. 40:84–90.
Irvine, R. F. 1982. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells. Biochem. J. 204:3–16.
Yamashita, S., Nakaya, N., Miki, Y., andNume, S. 1975. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72:600–603.
Lands, W. E. M., andSamuelsson, B. 1968. Phospholipid precursors of prostaglandins. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 164:426–429.
Vonkeman, H., andVan Dorp, D. A. 1968. The action of prostaglandin synthetase on 2-arachidonyl-lecithin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 164:430–432.
Van Den Bosch. 1980. Intracellular phospholipase A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 604:191–246.
Edgar, A. D., Stroszanjder, J., andHorrocks, L. A. 1982. Activation of ethanolamine phospholipase A2 in brain during ischemia. J. Neurochem. 39:1111–1116.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strosznajder, J. Effect of hypoglycemia on the brain free fatty acid level and the uptake of fatty acids by phospholipids. Neurochem Res 9, 465–476 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964373
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964373