Abstract
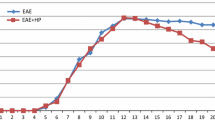
Intraperitoneal administration of pepstatin (2 mg/day for 5 weeks) to Lewis rats subjected to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) (induced by guinea pig spinal cord and pertussis vaccine) suppressed the appearance of clinical signs of disease, and reduced the severity and incidence of CNS lesions normally associated with this disease. Administration of pepstatin for shorter periods to Lewis rats, or BSVS mice, or guinea pigs challenged with myelin basic protein delayed, but did not prevent clinical signs of EAE, but was accompanied in all cases by a less severe histopathology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvord, E. C., Shaw, C. M., Hruby, S., andKies, M. W. 1965. Encephalitogen-induced inhibition of EAE: Prevention, suppression and therapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 122:333–345.
Driscoll, B. F., Kies, M. W., andAlvord, E. C. Jr. 1974. Successful treatment of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in guinea pigs with homologous myelin basic protein. J. Immunol. 112:392–397.
Levine, S., Sowinski, R., andKies, M. W. 1972. Treatment of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with encephalitogenic basic proteins (36174). Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 139:506–510.
Hashim, G. A., andSchilling, F. J. 1973. Prevention of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by nonencephalitogenic basic peptides. Arch. Biochem. 156:287–297.
Paterson, P. Y., andHanson, M. A. 1969. Studies of cyclophosphamide suppression of EAE in Wistar rats. J. Immunol. 103:795–803.
Boehme, D. H., Fordice, M. W., andMarks, N. 1974. Proteolytic activity in brain and spinal cord in sensitive and resistant strains of rat and mouse subjected to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 75:153–162.
Marks, N., Grynbaum, A., andLevine, S. 1977. Proteolytic enzymes in ordinary, hyperacute, monocytic and passive transfer forms of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 123:147–157.
Smith, M. 1977. The role of proteolytic enzymes in demyelination in EAE. Neurochem. Res. 2:233–246.
Umezawa, H., andAoyagi, T. 1977. Activities of proteinase inhibitors of microbial origin. Res. Monographs in Cell and Tissue Physiology 2:637–662. elsevier, North-Holland, Amsterdam.
Marks, N., Grynbaum, A., andLajtha, A. 1973. Pentapeptide (pepstatin) inhibition of brain acid proteinase. Science 181:949–951.
Marks, N., Grynabaum, A., andLajtha, A. 1976. The breakdown of myelin-bound proteins by intra- and extracellular proteases. Neurochem. Res. 1:93–111.
Marks, N., D'Monte, B., andLajtha, A. 1973. Inhibition of cerebral proteolytic enzymes. Texas Reports Biol. Med. 31:345–365.
Benuck, M., Marks, N., andHashim, G. 1975. Metabolic instability of myelin proteins: Breakdown of basic protein induced by brain cathepsin D. Eur. J. Biochem. 52:615–621.
Dean, R. T. 1975. Direct evidence of importance of lysosomes in degradation of intracellular proteins. Nature 257:414–416.
Miyamoto, M., Terayama, H., andOhnishi, T. 1973. Effects of protease inhibitors on liver regeneration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 55:84–90.
Bazin, S., Mady, L. L., andDelaney, A. 1975. Cathepsin D and catabolism of proteoglycans in granulation tissue. C.R. Hebd. Seances. Acad. Sci. Ser D., 280:1927–1929.
Dingle, J. T., Barrett, A. J., andPoole, A. R. 1972. Inhibition by pepstatin of human cartilage degradation. Biochem. J. 127:443–447.
Arnason, B. G. W. 1972. Immunosuppression in experimental demyelinating diseases. Pages 487–509,In Wolfgram, R., Ellison, G. W., Stevens, V. G., and Andrews, J. M. (eds.) Multiple Sclerosis—Immunology Virology and Ultrastructure. Academic Press, New York.
Hashim, G., Shapre, R., Carvalho, E., andStevens, L. E. 1976. Suppression and reversal of EAE in guinea pigs with a nonencephalitogenic analog of the Trp region of the myelin basic protein. J. Immunol. 116:126–130.
Hashim, G. Myelin basic protein: Structure, function, and antigenic determinants. Immunol. Rev. 39 (in press).
Swanborg, R. H. 1975. Antigen-induced inhibition of EAE. J. Immunol. 114:191–194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boehme, D.H., Umezawa, H., Hashim, G. et al. Treatment of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with an inhibitor of cathepsin D (pepstatin). Neurochem Res 3, 185–194 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964059
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964059