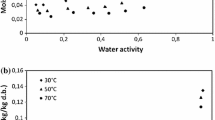
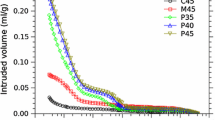
Abstract
The pore size distribution of cement mortar is studied in relation to water sorption experiments with the help of mercury intrusion and nitrogen sorption. The importance of adsorbed water is pointed out. Isothermal imbibition experiments at four temperatures are presented. The temperature-dependence of the mass transfer coefficients is compared to the one predicted by the classical model. Significant discrepancies are noticed.
On the basis of the knowledge of the pore structure, a modelisation of the transfer process at moderate water content is proposed. It particularly takes into account Knudsen's vapor diffusion and effects of the presence of a discontinuous capillary phase interacting with vapor diffusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D o :
-
coefficient of free diffusion of the water vapor in air
- D r :
-
coefficient of diffusion of vapor in the presence of a solid matrix (see eq. 16)
- D h v:
-
coefficient of pure vapor diffusion of the medium
- D′ h v:
-
coefficient of vapor diffusion of the medium in the presence of a dis continuous capillary phase
- D θ :
-
(with subscript L or V, or not) coefficient of mass transfer (see eq. 14)
- e a :
-
thickness of the adsorbed layer
- h :
-
relative humidity of the gaseous phase (h =pv/pvs =ϱv/ϱvs)
- J :
-
(with subscript L or V, or not) mass flux
- K L :
-
permeability (see Equation 11)
- l m :
-
mean free path of water molecules in air
- ln:
-
natural logarithm
- log:
-
logarithm to the base ten
- M :
-
molecular weight of water
- p c :
-
capillary pressure
- p v :
-
partial pressure of water vapor
- pvs:
-
pressure of saturated water vapor
- r :
-
radius of a cylindrical pore
- R :
-
gas constant
- ℛ:
-
radius of curvature of a capillary interface
- S 0 :
-
total area of pores per unit volume
- S(r) :
-
area of pores of radius larger thanr per unit volume
- T :
-
temperature
- t :
-
time
- x :
-
distance from origin
- γ, γ r :
-
shape factor of the capillary phase (of a class of pores)
- δ r :
-
equivalent coefficient of diffusion of pores filled with capillary water (see eq. 18 and 19)
- Δη r :
-
volumic fraction of a class of pores
- η 0 :
-
total porosity
- η(r) :
-
volume of pores of radius less thanr per unit volume
- θ :
-
volumetric water content
- μ :
-
dynamic viscosity of liquid water
- v :
-
kinematic viscosity of water
- ϱ V :
-
mass density of vapor
- ϱ VS :
-
mass density of saturated water vapor
- ϱ l :
-
mass density of liquid water
- σ :
-
surface tension coefficient
- τ :
-
tortuosity factor
- Φ:
-
matric potential
- L:
-
liquid
- V:
-
vapor
References
Barrett, E. P., Joyner, L. G., and Halenda, P. H., 1951,J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 73, 373.
Bhatnagar, P. L., Gross, E. P., and Krook, M., 1954, A model for collision processes in gases.Phys. Rev. 94, 511–525.
Bonnetain, L. and Ginoux, J. L., 1982, Influence de la surface externe aux pores sur la détermination du spectre de meso-adsorption à partir des isothermes d'adsorption, in J. Rouquerol and K. S. W. Sing (eds.),Adsorption at the Gas-Solid and Liquid-Solid Interface, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Bradley, R. S., 1936, Polymolecular adsorbed films,J. Chem. Soc. PartI, p. 1467, PartII, p. 1799.
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., and Teller, E., 1938, Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers,J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 60, 309.
Chapman, S. and Cowling, T. G., 1970,The Mathematical Theory of Non-Uniform Gases, Cambridge University Press, London.
Constantz, J., 1982, Temperature dependence of unsaturated hydraulic conductivity of two soils,Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 46, 466–470.
Crausse, P., Bacon, G., and Bories, S., 1981, Etude fondamentale des transferts couplés chaleurmasse en milieu poreux.Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 24, 991–1004.
Daian, J. F., 1986, Processus de condensation et de transfert d'eau dans un matériau méso et macroporeux. Etude expérimentale du mortier de ciment. Thèse de Doctorat, Université Scientifique, Technique et Médicale de Grenoble.
De Vries, D. A., 1952, The thermal conductivity of granular materials, Annex 1952, 1.Bull. Inst. Intern. du Froid, 115–131.
De Vries, D. A., 1958, Simultaneous transfert of heat and moisture in porous media.Trans. Am. Geo. Union 39, 909–916.
De Vries, D. A., 1962, Thermal properties of soils, in W. R. Van Wijk (ed.),Physics of Plant Environment, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 2nd edn., pp. 210–235.
De Vries, D. A., 1972, Heat Transfert in soil, inHeat and Mass Transfer in the Biosphere. John Wiley, New York.
De Vries, D. A. and Kruger, A. J., 1966, On the value of the diffusion coefficient of water vapour in air,Colloques Intern, du CNRS n∘ 160: Phénomènes de transport avec changement de phase dans les milieux poreus ou colloïdaux. Paris 18–20 avril 1966, Editions du CNRS, pp. 61–72.
Dullien, F. A. L., 1979,Porous Media: Fluid Transport and Pore Structure, Academic Press, New York.
Fagerlund, G., 1973, Determination of the specific surface by the BET method,Materials and Structures 6, 33, 239–245.
Gertis, K. and Wolfseher, U., 1976, Isothermer Gastransport in porosen Stoffen aus Gas kinetischer Sicht,Deutscher Ausschuss für Stahlbeton, 258, 36–62.
Gertis, K. and Kiessl, K., 1976, Isothermer Feuchte transport in porosen Baustoffen,Deutscher Ausschuss für Stahlbeton, 258, 85–110.
Grad, H., 1952, The profile of a steady plane shock wave,Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 5, 257–300.
Gregg, S. J. and Sing, K. S. W., 1982,Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York.
Grismer, M. E., McWhorther, D. B., and Klute, A., 1986, Monitoring water and salt movement in soils at low solution contents.Soil Sci. 141, 163.
Halsey, G., 1948, Physical adsorption on non-uniform surfaces.J. Chem. Phys. 16, 10, 931–937.
Haridasan, M. and Jensen, R. D., 1972, Effect of temperature on pressure heat-water content relationship and conductivity of two soils,Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 36, 703–708.
Hillel, D., 1980,Applications of Soil Physics, Academic Press, New York.
Hopmans, J. W. and Dane, J. H., 1986, Temperature dependence of soil hydraulic properties,Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 4–9.
Jackson, R. D., 1964–65, Water vapor diffusion in relatively dry soils (I to IV),Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 28, 172, 464, 466,29, 144.
Mason, E. A., Malinauskas, A. P., Evans III, R. B., 1967, Flow and diffusion of gases in porous media,J. Chem. Phys. 46, 3199–3216.
Perrin, B., Foures, J. C., and Javelas, R., 1983, Détermination du coefficient de diffusion isotherme de l'humidité dans des matériaux de construction,Materials and Structure,16, 91, 27–33.
Philip, J. R. and De Vries, D. A., 1957, Moisture movement in porous materials under temperature gradients,Trans. Am. Geoph. Union 38, 222–232.
Powers, T. C., 1962, inProc. 4th Int. Symposium on the Chemistry of Cement, Natl. Bureau Stds, Washington,2, 577.
Present, R. D., 1958,Kinetic Theory of Gases, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Rahi, G. S. and Jensen, R. D., 1975, Effect of temperature on soil water diffusivity,Geoderma 14, 115–124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daian, JF. Condensation and isothermal water transfer in cement mortar Part I — Pore size distribution, equilibrium water condensation and imbibition. Transp Porous Med 3, 563–589 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00959103
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00959103