Summary
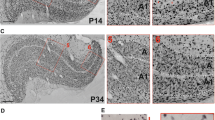
The time course of the morphological differentiation of non-pyramidal neurons in the rat hippocampus shows an area specificity. Thus, non-pyramidal neurons in CA3 appear more mature than in CA1 at early postnatal stages. Physiological data provide evidence for an earlier maturation of GABA-mediated inhibition in CA3 in comparison to CA1. As the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin (PARV) is thought to be a marker for highly active inhibitory neurons, we analyzed the area-specific appearance of PARV in GABAergic neurons during development. Employing combined light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry, we revealed an area specificity in the time course of the neurochemical and morphological maturation of this functionally important subpopulation of non-pyramidal cells. The first appearance of PARV-immunoreactivity was observed at P7 and was exclusively located in cell bodies in CA3. At P8, neurons in CA3 exhibited PARV-immunoreactivity in cell bodies and dendrites, but very rarely in axon terminals. These neurons displayed the typical light and electron microscopic characteristics of GABAergic non-pyramidal cells. At P10, axon terminals formed typical baskets surrounding the pyramidal cells. The appearance of PARV-immunoreactivity in cell bodies, dendrites and axon terminals in CAq was noticed about 1 to 2 days later. In the fascia dentata, non-granule cells displayed immunoreactivity not before P10. These data indicate a sequential neurochemical and morphological maturation of non-pyramidal neurons that may be related to differences in the maturation of inhibition during hippocampal development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral DG, Kurz J (1985) The time of origin of cells demonstrating glutamic acid decarboxylase-like immunoreactivity in the hippocampal formation of the rat. Neurosci Lett 599:33–39
Bayer SA (1980) Development of the hippocampal region in the rat. I. Neurogenesis examined with [3H]-thymidine autoradiography. J Comp Neurol 190:87–114
Braun K, Scheich H, Schachner M, Heizmann CW (1985) Distribution of parvalbumin, cytochrome oxidase activity and14C-2-deoxyglucose uptake in the brain of the zebra finch. I. Auditory and vocal motor systems. Cell Tissue Res 240:101–115
Celio MR, Baier W, Schärer PA, DeViragh PA, Gerday C (1988) Monoclonal antibodies directed against the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin. Cell Calcium 9:81–86
Deller T, Leranth C (1990) Synaptic connections of neuropeptide Y (NPY) immunoreactive neurons in the hilar area of the rat hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 300:433–447
Heizmann CW (1984) Parvalbumin, an intracellular calcium-binding protein; distribution, properties and possible roles in mammalian cells. Experientia 40:910–921
Kawaguchi Y, Katsumaru H, Kosaka T, Heizmann CW, Hama K (1987) Fast spiking cells in rat hippocampus (CA1 region) contain the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin. Brain Res 416:369–374
Kosaka T, Katsumaru H, Hama K, Wu JY, Heizmann CW (1987) GABAergic neurons containing the Ca2+-binding protein parvalbumin in the rat hippocampus and dentate gyrus. Brain Res 419:119–130
Lang U, Frotscher M (1990) Postnatal development of non-pyramidal neurons in the rat hippocampus (areas CA1 and CA3): a combined Golgi-electron microscope study. Anat Embryol 181:533–545
Leranth C, Frotscher M (1986) Synaptic connections of cholecystokinin-immunoreactive neurons and terminals in the rat fascia dentata: a combined light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 254:51–63
Leranth C, Frotscher M, Tömböl T, Palkovits M (1984) Ultrastructure and synaptic connections of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-like immunoreactive non-pyramidal neurons and axon terminals in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 12:531–542
Leranth C, Frotscher M, Rakic P (1988) CCK-immunoreactive terminals form different types of synapses in the rat and monkey hippocampus. Histochemistry 88:343–352
Leranth C, Malcolm AJ, Frotscher M (1990) Afferent and efferent synaptic connections of somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons in the rat fascia dentata. J Comp Neurol 295:111–122
Lübbers K, Frotscher M (1987) Fine structure and synaptic connections of identified neurons in the rat fascia dentata. Anat Embryol 177:1–14
Lübbers K, Wolff JR, Frotscher M (1985) Neurogenesis of GABAergic neurons in the dentate gyrus: a combined autoradiographic and immunocytochemical study. Neurosci Lett 62:317–322
Nitsch R, Klauer G (1989) Cryostat sections for coexistence studies and pre-embedding electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of central and peripheral nervous system tissue. Histochemistry 92:459–465
Nitsch C, Scotti A, Sommacal A, Kalt G (1989) GABAergic hippocampal neurons resistant to ischemia-induced neuronal death contain the Ca2+-binding protein parvalbumin. Neurosci Lett 105:263–268
Nitsch R, Soriano E, Frotscher M (1990a) The parvalbumin-containing nonpyramidal neurons in the rat hippocampus. Anat Embryol 181:413–425
Nitsch R, Leranth C, Frotscher M (1990b) Most somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons in the rat fascia dentata do not contain the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin. Brain Res 528:327–329
Nitsch R, Bergmann I, Küppers K, Mueller G, Frotscher M (1990c) Late appearance of parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the development of GABAergic neurons in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 118:147–150
Ribak CE, Anderson L (1980) Ultrastructure of the pyramidal basket cells in the dentate gyrus of the rat. J Comp Neurol 192:903–916
Schlander M, Frotscher M (1986) Nonpyramidal neurons in the guinea-pig hippocampus: a combined Golgi-electron microscope study. Anat Embryol 174:35–47
Schlander M, Hoyer S, Frotscher M (1988) Glutamate decarboxylase immunoreactive neurons in the aging rat hippocampus are more resistant to ischemia than CA1 pyramidal cells. Neurosci Lett 91:241–246
Seress L, Ribak CE (1985) A combined Golgi-electron microscopic study of nonpryamidal neurons in the CA1 area of the hippocampus. J Neurocytol 14:717–730
Seress L, Ribak CE (1990) Postnatal development of the light and electron microscopic features of basket cells in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of the rat. Anat Embryol 181:547–565
Seress L, Frotscher M, Ribak CE (1989) Local circuit neurons in both the dentate gyrus and Ammon's horn establish synaptic connections with principal neurons in five day old rats: A morphological basis for inhibition in early development. Exp Brain Res 78:1–9
Seto-Ohshima A, Aoki E, Semba R, Emson PC, Heizmann CW (1990) Appearance of parvalbumin-specific immunoreactivity in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of the developing rat and gerbil brain. Histochemistry 94:579–589
Sloviter RS (1989) Calcium-binding protein (Calbindin-D28k) and parvalbumin immunocytochemistry: localization in the rat hippocampus with specific reference to the selective vulnerability of hippocampal neurons to seizure activity. J Comp Neurol 280:183–196
Sloviter RS, Nilaver G (1987) Immunocytochemical localization of GABA-, cholecystokinin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-, and somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the area dentata and hippocampus of the rat. J Comp Neurol 256:42–60
Soriano E, Cobas A, Fairén A (1989) Neurogenesis of glutamic acid decarboxylase immunoreactive cells in the hippocampus of the mouse. I: Regio superior and regio inferior. J Comp Neurol 281:586–602
Soriano E, Nitsch R, Frotscher M (1990) Axo-axonic chandelier cells in the rat fascia dentata: Golgi-EM and immunocytochemical studies. J Comp Neurol 293:1–25
Swann JW, Brady RJ, Martin DL (1989) Postnatal development of GABA-mediated synaptic inhibition in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 28:551–561
Tinner R, Oertle M, Heizmann CW, Bosshard HR (1990) Ca2+-binding site of carp parvalbumin recognized by monoclonal antibody. Cell Calcium 11:19–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
In partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Dr. med. at the University of Frankfurt/Main
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergmann, I., Nitsch, R. & Frotscher, M. Area-specific morphological and neurochemical maturation of non-pyramidal neurons in the rat hippocampus as revealed by parvalbumin immunocytochemistry. Anat Embryol 184, 403–409 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00957901
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00957901