Summary
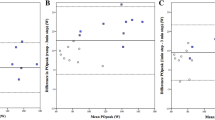
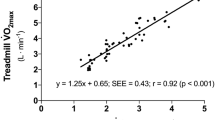
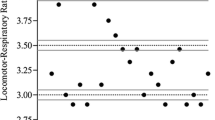
Twenty male subjects, age (± SD) 31.1±5.6 years and weight 74.3±12.7 kg participated in this study to compare the\(\dot V\)O2 peak values in arm cranking obtained using continuous (C) and discontinuous (D) protocols. Each subject performed a continuous (C) and discontinuous (D) protocol in random order on two separate days. Cranking was performed at 60 rev·min−1 with tests terminated when this fell below 50. Peak values for oxygen uptake ventilation and heart rate were determined during each test. The C protocol involved increasing power output each minute, while in the D protocol 2 min work bouts were separated by 1 min rest intervals. No significant differences (p>0.05) between the C and D protocols were shown on any measured variable. It was concluded that the use of C or D protocols for determining\(\dot V\)O2 peak in arm cranking provide comparable results with the C protocol being advantageous in terms of administration time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asmussen E, Hemmingsen I (1958) Determination of maximum working capacity at different ages in work with the legs or with the arms. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 10: 67–71
åstrand I (1960) Aerobic work capacity in men and women with special reference to age. Acta Physiol Scand 49: [Suppl 169]
åstrand PO, Ekblom P, Messin R, Saltin B, Stenberg J (1965) Intra-arterial blood pressure during exercise with different muscle groups. J Appl Physiol 20: 253–256
åstrand PO, Saltin B (1961) Maximal oxygen uptake and heart rate in various types of muscular activity. J Appl Physiol 16: 979–981
Bar-Or O, Zwiren LD (1975) Maximal oxygen consumption test during arm exercise-reliability and validity. J Appl Physiol 38: 424–426
Bevegard BS, Shepherd JT (1967) Regulation of circulation during exercise in man. Physiol Rev 47: 178–213
Christensen EH (1932) BeitrÄge zur Physiologie schwere körperlicher Arbeit. VI. Der Stoffwechsel und die respiratorischen Funktionen bei schwerer körperlicher Arbeit. Arbeitsphysiologie 5: 463–478
Davies CTM, Sargeant AJ (1974) Physiological responses to standardised arm work. Ergonomics 17: 41–49
Davis JA, Vodak P, Wilmore JH, Vodak J, Kurts P (1976) Anaerobic threshold and maximal aerobic power for three modes of exercise. J Appl Physiol 41: 544–550
Hays WL (1973) Statistics for the social sciences. Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York
Magel JR, McArdle WD, Toner M, Delio DJ (1978) Metabolic and cardiovascular adjustment to arm training. J Appl Physiol 45: 75–79
Seals DR, Mullin JP (1982)\(\dot V\)O2 max in variable type exercise among well trained upper body athletes. Res Q Ex Sport 53: 58–63
Stamford BA, Cuddihee RW, Moffatt RJ, Rowland R (1978) Specific changes in maximal oxygen uptake resulting from arm versus leg training. Ergonomics 21: 1–9
Vodac Z, Bell H, Bautz-Holter E, Rodahl K (1975) Oxygen uptake heart rate relationship in leg and arm exercise, sitting and standing. J Appl Physiol 39: 54–59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Washburn, R.A., Seals, D.R. Comparison of continuous and discontinuous protocols for the determination of peak oxygen uptake in arm cranking. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 51, 3–6 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00952531
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00952531