Summary
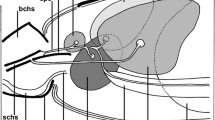
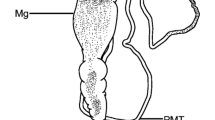
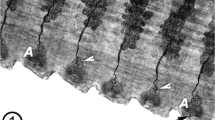
Type 2 cells, or mucocytes, are present in both inferior and superior Malpighian tubules ofCarausius morosus and are concentrated towards the distal ends of the main urine-secreting parts. They are absent from the proximal few millimetres of the main part and from the distal specialised regions of the tubules. They possess numerous Golgi bodies and abundant granular E. R., which is consistent with the hypothesis that they secrete mucus. However, they possess basal infoldings and apical microvilli suggesting that they may transport substances across the tubule wall. It is suggested that they perform both functions. Reabsorption of ions or water could precipitate solid components of the urine (e.g., uric acid). Mucus may be important in nucleation of crystalline material and also prevent abrasion of the brush border.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja, S. K.: Chloride cell and mucous cell response to chloride and sulphate enriched media in the gills ofGambusia affinis affinis (Baird and Girard) andCatla catla (Hamilton). J. exp. Zool.173, 231–250 (1970).
Berkaloff, A.: Contribution à l'étude des tubes de Malpighi et de l'excrétion chez les Insectes. Observations au microscope électronique. Ann. Sci. Nat. Zool. XII Ser.2, 869–947 (1960a).
—: Le glycogène des tubes de Malpighi deGryllus domesticus (Orthoptère, Gryllidae). C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris)250, 2061–2063 (1960b).
Berridge, M. J.: Urine formation by the Malpighian tubules ofCalliphora. I. Cations. J. exp. Biol.48, 159–174 (1968).
—, Oschman, J. L.: A structural basis for fluid secretion by Malpighian tubules. Tissue and Cell1, 247–272 (1969).
Diamond, J. M., Bossert, W. H.: Standing-gradient osmotic flow: a mechanism for coupling water and solute transport in epithelia. J. gen. Physiol.50, 2061–2083 (1967).
— —: Functional consequences of ultrastructural geometry in “backwards” fluid-transporting epithelia. J. Cell Biol.37, 694–702 (1968).
Downing, S. W., Novales, R. R.: The fine structure of lamprey epidermis. 1. Introduction and mucous cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res.35, 282–294 (1971).
Fawcett, D. W.: Physiologically significant specialisations of the cell surface. Circulation26, 1105–1125 (1962).
Freeman, J. A.: Goblet cell fine structure. Anat. Rec.154, 121–148 (1966).
Gabe, M.: In: Handbuch der Histochemie, Bd. II/I, Ed. Graumann W., Neumann, K. G. Stuttgart: Fischer 1962.
Gallagher, J. T., Marsden, J. C., Robards, A. W.: The effects of an inhibitor of Na+-K+-active transport on the secretory activity of the rat submaxillary gland cell cultures. Z. Zellforsch.117, 314–321 (1971).
Henrikson, R. C., Matoltsy, A. G.: The fine structure of teleost epidermis. II. Mucous cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res.21, 213–221 (1968).
Jordon, B. M., Baker, J. R.: A simple pyronine/methyl green technique. Quart. J. micr. Sci.96, 177–179 (1955).
Marshall, A. T.: Histochemical studies on a muco-complex in the Malpighian tubules of cecropid larvae. J. Insect Physiol.12, 925–932 (1966).
Martoja, R.: Mise en évidence d'une secrétion muqueuse dans les tubes de Malpighi de quelques Orthoptères et d'un Phasmoptère. Bull. Soc. Zool. France81, 172–173 (1956).
—: Données cytologiques et histochimiques sur les tubes de Malpighi et leurs secrétions muqueuses chezLocusta migratoria. R. et F. (Orth., Acrid.) Acta. histochem. (Jena)6, 185–217 (1959).
—: Characteristiques histologiques du segment muqueux de l'appareil excréteur des Orthoptères. C. R. Acad, Sci. (Paris)253, 3063–3065 (1961).
Mazzi, V., Baccetti, B.: Prime ricerche istochimique comparative sui tubi Malpighiani degli insetti. Redia42, 383–392 (1957).
Miles, P.: A modification of Wigglesworth's model for the excretion of uric acid in insects in the light of modern hypotheses of ion transport. J. theor. Biol.12, 130–132 (1966).
Neutra, M., Leblond, C. P.: Synthesis of the carbohydrate of mucus in the Golgi complex as shown by electron microscope radioautography of goblet cells from rats injected with glucose-3H. J. Cell Biol.30, 119–136 (1966).
Pease, D. C.: Infolded basal plasma membranes found in epithelia noted for their transport. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.2, (Suppl.) 203–208 (1956).
Ramsay, J. A.: The excretion of sodium and potassium by the Malpighian tubules ofRhodnius. J. exp. Biol.29, 110–126 (1952).
—: Active transport of water by the Malpighian tubules of the stick insect,Dixippus morosus (Orthoptera, Phasmidae). J. exp. Biol.31, 104–113 (1954).
—: The excretory system of the stick insectDixippus morosus (Orthoptera, Phasmidae). J. exp. Biol.32, 183–199 (1955a).
—: The excretion of sodium, potassium and water by the Malpighian tubules of the stick insect,Dixippus morosus (Orthoptera, Phasmidae). J. exp. Biol.32, 200–216 (1955b).
Taylor, H. H.: Ultrastructural studies on the Malpighian tubules of the stick insect. Ph. D. Thesis. University of Newcastle upon Tyne (1970).
—: Water and solute transport by the Malpighian tubules of the stick insect,Carausius morosus. The normal ultrastructure of the type 1 cells. Z. Zellforsch.118, 333–368 (1971).
Wigglesworth, V. B.: The physiology of excretion in a blood-sucking insect,Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). III. The mechanism of uric acid excretion. J. exp. Biol.8, 443–451 (1931).
—: The principles of insect physiology, 6th ed. London: Methuen and Co. Ltd. 1965.
—, Salpeter, M. M.: Histology of the Malpighian tubules inRhodnius prolixus Stål. (Hemiptera) J. Insect Physiol.8, 299–307 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation formed part of a thesis for the degree of Ph.D. in the University of Newcastle upon Tyne. It is a pleasure to thank Professor J. Shaw for his advice and encouragement and the Science Research Council for financial support.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, H.H. The fine structure of the type 2 cells in the Malpighian tubules of the stick insect,Carausius morosus . Z.Zellforsch 122, 411–424 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936077
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936077