Abstract
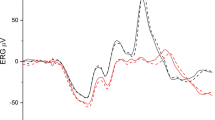
A male patient suffering from cone dystrophy was followed over 9 years. In addition to the typical clinical and electrophysiologic signs, supernormal b-waves were found in the dark-adapated electroretinogram. Our case is compared with 12 similar patients described in the literature. Our patient differed from the other patients in the following aspects: he was male and had a congenital stationary disease with a small pigment epithelial scar in the left eye only and no other fundus changes up to the age of 22 years. He did not complain of night blindness. The dark-adapted electroretinogram of our patient showed a normal b-wave threshold with increased b-wave amplitudes and markedly prolonged b-wave latencies and implicit times. This combination of signs has not been reported to date in any other patient and points towards a postreceptoral defect of the interneuronal connection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander KR, Fishman GA (1984) Supernormal scotopic ERG in cone dystrophy. Br J Ophthalmol 68:69–78
Berson EL, Gouras P, Gunkel RD (1968) Progressive cone degeneration, dominantly inherited. Arch Ophthalmol 80:77–83
Cavender JC, Ai E (1981) Hereditary macular dystrophies. In: Duane TD (ed) Clinical ophthalmology, vol 3, chap 9. Lippincott, Philadelphia
Fishman GA, Rhee AJ, Blair NP (1986) Blood-retinal barrier function in patients with cone or cone-rod dystrophy. Arch Ophthalmol 104:545–548
Francois J, De Rouck A, De Lacy JJ (1976) Progressive cone dystrophies. Ophthalmologica (Basel) 173:81–101
Gouras P, Eggers HM, MacKay CJ (1983) Cone dystrophy, nyctalopia, and supernormal rod responses. A new retinal degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol 101:718–724
Knave B, Nilsson SE, Lunt T (1973) The human electroretinogram: DC recordings at low and conventional stimulus intensities. Acta Ophthalmol 51:716–726
Krill AE (1977) Hereditary retinal and choriodal diseases, vol 2: Clinical characteristics. Harper and Row, Hagerstown, pp 359–370
Ripps H, Noble KG, Greenstein VC, Siegel IM, Carr RE (1987) Progressive cone dystrophy. Ophthalmology 94:1401–1409
Rohde N, Täumer R, Pernice D (1977) Vorschlag eines verbesserten klinischen EOG-Testes. Ber Dtsch Ophthalmol Ges 74:747–750
Yagasaki K, Miyake Y, Litao RE, Ichikawa K (1986) Two cases of retinal degeneration with an unusual form of electroretinogram. Doc Ophthalmol 63:73–82
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foerster, M.H., Kellner, U. & Wessing, A. Cone dystrophy and supernormal dark-adapted b-waves in the electroretinogram. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 228, 116–119 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00935718
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00935718