Summary
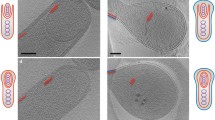
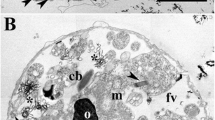
The formation and final structure of the oocyst wall ofEimeria acervulina is described, based on a detailed electron microscope study of the maturing oocysts. After fertilization of the macrogametocyte the wallforming bodies of type I progressively undergo disaggregation into smaller bodies and eventually move into spaces left by the pellicular membranes of the zygote, which simultaneously separate and elevate away from the zygote cytoplasm to form the outer layer of the oocyst wall. A newly formed membrane separates this layer from the cytoplasm. Following the formation of the outer layer, another membrane separates and elevates away from the cytoplasm, and the wall-forming bodies of type II, which by now have migrated to the periphery, move into the spaces and fuse together to form the inner layer of the oocyst wall. A newly formed membrane separates this layer from the cytoplasm. The wall of the young oocyst thus consists of two membrane-bound layers of approximately similar thickness; the outer layer being osmiophilic whilst the inner one is paler. An overlying membrane covers the oocyst. The surface of the oocyst wall was smooth in appearance when viewed with the scanning electron microscope.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birch-Andersen, A., Ferguson, D.J.P., Pontefract, R.D.: A technique for obtaining thin sections of coccidian oocysts. Acta Pathol Microbiol. Scand. [B]84, 235–239 (1976)
Hammond, D.M.: Life cycles and development of coccidia. In: The coccidia, D.M. Hammond and P.L. Long, eds., pp. 45–79. Baltimore: University Park Press/London: Butterworths 1973a
Hammond, D.M.: Ultrastructure and development of coccidia. In: Proceedings of the symposium on coccidia and related organisms, pp. 11–43. University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario 1973b
Hirsch, J.H., Fedorko, M.E.: Ultrastructure of the human leucocytes after simultaneous fixation with glutaraldehyde/OsO4 and post-fixation in uranyl acetate. J. Cell Biol.38, 615–627 (1968)
Karnovsky, M.J.: A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolarity for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.27, 137A-138A (1965)
Lee, D.L., Millard, B.J.: The structure and development of the macrogamete and oocyst ofEimeria acervulina. Parasitology62, 31–34 (1971)
Madden, P.A., Vetterling, J.M.: Scanning electron microscopy ofEimeria tenella microgametogenesis and fertilization. J. Parasitol.63, 607–610 (1977)
McLaren, D.J.: Observations on the fine structural changes associated with schizogony and gametogony inEimeria tenella. Parasitology59, 563–574 (1969)
Nyberg, P.A., Knapp, S.E.: Scanning electron microscopy ofEimeria tenella oocysts. Proc Helminthol. Soc. Wash.37, 29–32 (1970)
Nyberg, P.A., Knapp, S.E.: Effect of sodium hypochloride on the oocyst wall ofEimeria tenella as shown by electron microscopy. Proc. Helminthol Soc. Wash.37, 32–36 (1970)
Roberts, W.L., Hammond, D.M.: Scanning electron microscope study of invasion of host cells byEimeria larimerensis sporozoites. Proc. Helminthol Soc. Wash.40, 118–122 (1973)
Roberts, W.L., Speer, C.A., Hammond, D.M.: Electron and light microscope studies of the oocyst walls, sporocysts, and excysting sporozoites ofEimeria callospermophili, andE. larimerensis. J. Parasitol.56, 918–926 (1970)
Scholtyseck, E.: Ultrastructure. In: The coccidia, D.M. Hammond and P.L. Long, eds., pp. 81–144. Baltimore: University Park Press, London: Butterworths 1973
Scholtyseck, E., Mehlhorn, H., Hammond, D.M.: Fine structure of macrogamonts and oocysts of coccidia and related organisms. Z. Parasitenkd.37, 1–43 (1971)
Scholtyseck, E., Weissenfels, N.: Electronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen von Sporozoen. I. Die Oocystenmembran des HühnercoccidsEimeria tenella. Arch. Protistenkd.101, 215–222 (1956)
Vetterling, J.M., Madden, P.A., Dittemore, N.S.: Scanning electron microscopy of poultry coccidia after in vitro excystation and penetration of cultured cells. Z. Parasitenkd.37, 136–147 (1971)
Witlock, D.R., Lushbaugh, W.B., Danforth, H.D., Ruff, M.D.: Scanning electron microscopy of the caecal mucosa inEimeria tenella-infected and uninfected chickens. Avian Dis.19, 293–304 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michael, E. The formation and final structure of the oocyst wall ofEimeria acervulina: A transmission and scanning electron microscope study. Z. Parasitenkd. 57, 221–228 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00928035
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00928035