Abstract
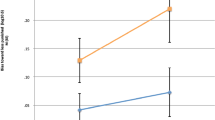
The optimal stimulation theory proposes that hyperactive children are less tolerant of lower levels of arousal than nonhyperactive children and should thus derive greater gains from stimulation added to repetitive copying tasks than do comparisons. To test this hypothesis, 16 adolescents, rating high on attention and behavior problems, were matched on the basis of age and poor handwriting performance to 16 controls. Matched pairs were randomly assigned to treatment order (high-stimulation colored letters followed in 2 weeks by low-stimulation black letters or the reverse order) and to level of information (color added to difficult letter parts or added to randomly selected letters), counterbalanced for treatment order and level of information within each order. Errors and activity were subjected to a mixed-design analysis of covariance, with IQ the covariate. The major findings indicated that attention-problem adolescents performed better with high-stimulation task stimuli than with low, relative to the opposite performance pattern of controls. Different responding was significant for experimental but not for control children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aman, M. G. (1980). Psychotropic drugs and learning problems — A selective review.Journal of Learning Disabilities, 13, 87–97.
Barkley, A. (1977). A review of stimulant drug research with hyperactive children.Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 18, 137–165.
Berlyne, D. E. (1960).Conflict, arousal and curiosity. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Brown, F. (1977). The hobbyist. In J. B. Hogins (Ed.),Literature: A collection of mythology and folklore, short-stories, poetry, and drama (2nd ed., pp. 309–310). Chicago: Science Research Associates.
Conners, C. K. (1973). Rating scales for use in drug studies with children.Psychopharmacology Bulletin (Special Issue: Pharmacotherapy of children), 24–84.
Douglas, V. (1974). Sustained attention and impulse control: Implications for the handicapped child. In J. A. Swets & L. L. Elliot (Eds.),Psychology of the handicapped child (pp. 149–168). Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Douglas, V. I., & Peters, K. G. (1979). Toward a clearer definition of the attentional deficit of hyperactive children. In G. A. Hale & M. Lewis (Eds.),Attention and the development of cognitive skills (pp. 173–247). New York: Plenum Press.
Hammill, D., & Larsen, S. (1978).Test of written language. Austin, Texas: Pro-Ed.
Hockey, G. R. J. (1970). Effects of loud noise on attentional selectivity.Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 22, 28–36.
Hopkins, B. L., Schutte, R. C., & Garton, K. L. (1971). The effects of access to a playroom on the rate and quality of printing and writing of first and second grade students.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 4, 77–87.
Hoy, E., Weiss, G., Minde, K., & Cohen, N. (1978). The hyperactive child at adolescence: Cognitive, emotional, and social functioning.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 6, 311–324.
Knights, R. M., & Hinton, G. G. (1969). The effects of methylphenidate (Ritalin) on the motor skills and behavior of children with learning problems.Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 148, 643–653.
Lerer, R. J., Artner, J., & Lerer, M. P. (1979). Handwriting deficits in children with minimal brain dysfunction: Effects of methylphenidate and placebo.Journal of Learning Disabilities, 12, 450–455.
Lerer, R. J., Lerer, M. P., & Artner, J. (1977). The effects of methylphenidate on the handwriting of children with minimal brain dysfunction.Journal of Pediatrics, 91, 128–136.
Lockhead, G., & Crist, W. (1980). Making letters distinctive.Journal of Educational Psychology, 72, 483–493.
Newland, E. (1932). An analytic study of the development of illegibilities in handwriting from the lower grades to adulthood.Journal of Educational Research, 26, 249–258.
Olmedo, E. L., Kirk, R. E., & Suarez, E. M. (1973). Effects of environmental variation on arousal during vigilance performance.Perceptual and Motor Skills, 36, 1251–1257.
Rugel, R. P., Cheatam, D., & Mitchell, A. (1978). Body movement and inattention in learningdisabled and normal children.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 6, 325–337.
Schain, R. J., & Reynard, C. L. (1975). Observations on the effects of a central stimulant drug (methylphenidate) in children with hyperactive behavior.Pediatrics, 55, 709–716.
Townsend, R. M. (1978).Looking ahead, imaginary line handwriting. Austin, Texas: Steck-Vaughn.
Swanson, J. M., Barlow, A., & Kinsbourne, M. (1979). Task specificity of responses to stimulant drugs in laboratory tests.International Journal of Mental Health, 8, 67–82.
Whalen, C. K., Henker, B., & Finck, D. (1981). Medication effects in the classroom: Three naturalistic indicators.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 9, 419–433.
Zentall, S. S. (1975). Optimal stimulation as theoretical basis of hyperactivity.American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 45, 549–563.
Zentall, S. S. (in press). Effects of color stimulation on performance and activity of hyperactive and nonhyperactive children.Journal of Educational Psychology.
Zentall, S. S., & Barack, R. S. (1979). Rating scales for hyperactivity: Concurrent validity, reliability, and decisions to label for the Conners and Davids abbreviated scales.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 7, 179–190.
Zentall, R. S., Gohs, D. E., & Culatta, B. (1983). Language and activity of hyperactive and comparison preschoolers in a listening task.Exceptional Children, 50, 255–266.
Zentall, S. S., & Zentall, T. R. (1983). Optimal stimulation: A model of disordered activity and performance in normal and deviant children.Psychological Bulletin, 94, 446–471.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by National Institute of Mental Health Grant MH32282 to the first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zentall, S.S., Falkenberg, S.D. & Smith, L.B. Effects of color stimulation and information on the copying performance of attention-problem adolescents. J Abnorm Child Psychol 13, 501–511 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00923137
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00923137