Abstract
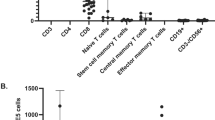
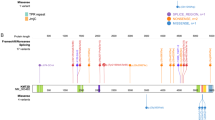
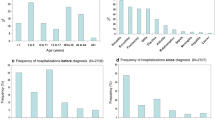
We have identified five patients with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) who developed multiple monoclonal serum immunoglobulin components (multiclonal gammopathy) following bone marrow transplantation. Four patients received haploidentical bone marrow stem cells depleted of T cells and other mature marrow cells by soy lectin agglutination and/or sheep erythrocyte rosetting. One patient received unfractionated HLA-identical bone marrow. Twenty-one distinct paraproteins were detected: 14 IgG, 5 IgM, and 2 IgA, all containing either kappa or lambda light chains. In the haploidentical stemcell recipients, these monoclonal immunoglobulins appeared immediately prior to, or concomitant with, a rise in T-cell numbers and function. Resolution or diminution of this multiclonal gammopathy occurred as T-cell function was established. Posttransplant karyotypic analyses revealed PHA-stimulated T cells to be of donor origin in all patients. Karyotyping of B-cell lines posttransplantation revealed them to be 100% donor in the patient receiving unfractionated HLA-identical marrow and 100% host (1/4), 100% donor (1/4), mixed (1/4), or not tested (1/4) in the patients receiving haploidentical marrow stem cells. There was no evidence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection in any of the patients. All patients are currently alive and well. Immunoglobulin synthesis is normal in the patient who received the HLA-identical marrow but remains below normal in the four patients who received T cell-depleted haploidentical stem cells. The posttransplantation development of monoclonal immunoglobulins in the absence of EBV infection did not adversely affect the outcome of either HLA-identical marrow or haploidentical stem-cell grafting. The development of these monoclonal components posttransplantation in SCID patients is a more common phenomenon than previously recognized (26% of 31 patients we have evaluated). The onset and resolution of multiclonal gammopathy in this patient population may have implications for the pathogenesis of other clonal B-cell and plasma disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bortin MM, Rimm AA: Severe combined immunodeficiency disease. Characterization of the disease and results of transplantation. JAMA 238:591, 1977
Buckley RH. Transplantation.In Immunologic Disorders in Infants and Children, ER Steihm (ed). Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 1989, pp 774–808
O'Reilly RJ, Brochstein J, Collins N, Keever C, Kapoor N, Kirkpatrick D, Kernan N, Dupont B, Burns J, Reisner Y: Evaluation of HLA-haplotype disparate parental marrow grafts depleted of T lymphocytes by differential agglutination with a soybean lectin and E-rosette depletion for the treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency. Vox Sang 51(S2):81–86, 1986
Buckley RH, Schiff S, Sampson HA, Schiff R, Markert ML, Knutsen A, Hershfield M, Huang A, Mickey G, Ward F: Development of immunity in human severe primary T cell deficiency following haploidentical bone marrow stem cell transplantation. J Immunol 136:2398, 1986
DeKoning J, Van Bekkum DW, Dicke HA, Dooren LH, Van Rood JJ, Radl J: Transplantation of bone marrow cells and fetal thymus in an infant with lymphopenic immunological deficiency. Lancet 1:1223–1227, 1969
Ghory P, Schiff SE, Buckley RH: Appearance of multiple benign paraproteins during early engraftment of soy lectin T cell-depleted haploidentical bone marrow cells in severe combined immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol 6:161–169, 1986
Buckley RH, Dees SC, O'Fallon WM: Serum immunoglobulins. I. Levels in normal children and in uncomplicated childhood allergy. Pediatrics 41:600–611, 1968
Buckley RH, Fiscus SA: Serum IgD and IgE concentrations in immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest 55:157–165, 1975
Buckley RH, Dees SC: Serum immunoglobulins. III. Abnormalities associated with chronic urticaria in children. Allergy 40:294–303, 1968
Schiff RI, Buckley RH, Gilbertsen RB, Metzgar RS: Membrane receptors and in vitro lymphocyte responsiveness in immunodeficiency. J Immunol 112:376–385, 1974
Haynes BF: Human T lymphocyte antigens as defined by monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Rev 57:127–161, 1981
Schiff SE, Kurtzberg J, Buckley RH: Studies of human bone marrow treated with soybean lectin and sheep erythrocytes: Stepwise analysis of cell morphology, phenotype and function. Clin Exp Immunol 68:685–693, 1987
Sindel LJ, Buckley RH, Schiff SE, Ward, FE, Mickey GH, Huang AT, Naspitz C, Koren H: Severe combined immunodeficiency with natural killer-cell predominance: Abrogation of graft-versus-host disease and immunologic reconstitution with HLA-identical bone marrow cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 73:829–36, 1984
Crawford J, Eye MK, Cohen HJ: Evaluation of monoclonal gammopathies in the “well” elderly. Am J Med 82:39–45, 1987
Hansen JA, Fu SM, Antonelli P, Kamoun M, Hurley JN, Winchester RJ, Dupont B, Kunkel HG: B-lymphoid cell lines derived from HLA-D homozygous donors. Immunogenetics 8:51, 1979
Barrett M, Buckley RH, Schiff SE, Kidd PC, Ward FE: Accelerated development of immunity following transplantation of maternal marrow stem cells into infants with severe combined immunodeficiency and transplacentally acquired lymphoid chimerism. Clin Exp Immunol 72:118–123, 1988
Gerritsen E, Vossen J, Tol M van, Zijde C jol-van der, Weijden-Ragas R van der, Radl J: Monoclonal gammopathies in children. J Clin Immunol 9(4):296–305, 1989
Harboe M, Pande H, Brandtzaeg P, Tveter K, Hjort P: Synthesis of donor type gamma G globulin following thymus transplantation in hypogammaglobulinemia with severe lymphocytopenia. Scand J Hematol 3:351–374, 1966
De Fazio SR, Criswell BS, Kimzey SL, South MA, Montgomery JR: A paraprotein in severe combined immunodeficiency disease detected by immunoelectrophoretic analysis of plasma. Clin Exp Immunol 19:563–570, 1975
Filipovich AH, Heinitz KJ, Robinson LL, Frizzera G: The immunodeficiency registry: A research resource. Am J Pediat Hematol Oncol 9:183–184, 1987
Shearer WT, Ritz J, Finegold MJ, Guerra IC,et al.: Epstein-Barr virus-associated B cell proliferations of diverse clonal origins after bone marrow transplantation in a 12 year old patient with severe combined immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med 312:1151–1159, 1985
Cleary ML, Sklar J: Lymphoproliferative disorders in cardiac transplant recipients are multiclonal lymphomas. Lancet 2:489–493, 1984
Starzl TE, Nalesnik MA, Porter KA,et al.: Reversibility of lymphomas and lymphoproliferative lesions developing under cyclosporin-steroid therapy. Lancet 1:583–587, 1984
Shirley LR, Buckley RH, Borowitz MJ, Welt SI, Kostyu DD: Monoclonal immunoglobulin-secreting lymphoma in a patient with severe combined immunodeficiency disease. Clin Exp Immunol 48:666–674, 1982
Roberts JL, Volkman DJ, Buckley RH: Modified major histocompatibility complex (MHC) restriction of donororigin T cells in humans with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) transplanted with haploidentical bone marrow stem cells. J Immunol 143:1575–1579, 1989
Nelson D: Cellular interactions in the human immune response.In Immunologic Disorders in Infants and Children, R Stiehm (ed). Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 1989, pp 1–28
Radl J, Valentijn RM, Haaijman JJ, Paul LC: Monoclonal gammopathies in patients undergoing immunosuppressive treatment after renal transplantation. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 37:98–102, 1985
Briault S, Courtois-Capella M, Duarte F, Anconturier, and Preud'homme JL: Isotypy of serum monoclonal immunoglobulins in human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults. Clin Exp Immunol 74:181–184, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kent, E.F., Crawford, J., Cohen, H.J. et al. Development of multiple monoclonal serum immunoglobulins (multiclonal gammopathy) following both HLA-identical unfractionated and T cell-depleted haploidentical bone marrow transplantation in severe combined immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol 10, 106–114 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00918192
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00918192