Abstract
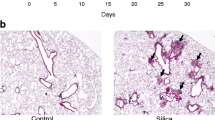
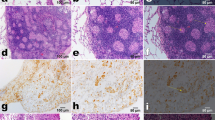
Prolonged asbestos and silica inhalation is associated with pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Several studies suggest that TNF may play a rolc in the development of inflammation and fibrosis. We studied TNF production in a murine model of asbestosis and silicosis. Asbestos fibers caused a significant inflammatory response at two weeks and pulmonary fibrosis beginning at one month. Pulmonary inflammation was principally caused by an accumulation of neutrophils (0.88 × 105 neutrophils/compared to 0.05×105 in controls). TNF production by bronchoalveolar cells was higher in asbestos-instilled mice at two weeks, but was significantly diminished in older mice. Pulmonary inflammation was observed until six months in silica-instilled mice. Neutrophils were also the principal protagonists of the inflammation. In this group, severe fibrosis was observed at two weeks. TNF production in silica-instilled mice was similar to controis, possibly due to the presence of large numbers of neutrophils (3.3 × 105/lavage) that could adsorb TNF. In vitro experiments showed an augmentation of TNF production by bronchoalveolar cells in the presence of silica. Taken together, our data suggest that asbestos and silica stimulate alveolar macrophages to produce TNF, which can be involved in pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carswell, E. A., L. J. Old, R. L. Kassel, S. Green, N. Fiore, andB. Williamson. 1975. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72:3666–3670.
Helson, L., S. Green, A. Carswell, andL. J. Old. 1975. Effect of tumor necrosis factor on cultured human melanoma cells.Nature 258:731–732.
Sugarman, B. J., B. B. Agoarwal, P. E. Hass, I. S. Figari, M. A. Palladino, andH. M. Shepard. 1985. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factorα: Effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro.Science 230:943–945.
Creasy, A. A., L. V. Doyle, M. T. Reynolds, T. Jung, L. S. Lin, andC. R. Vitt. 1987. Biological effects of recombinant human tumor necrosis factors and its novel muteins on tumor and normal cells lines.Cancer Res. 47:145–149.
Mannel, D. N., R. N. Moore, andS. E. Mergenhagen. 1980. Macrophages as a source of tumoricidal activity (tumor necrosis factor).Infea. Immunol. 30:523–530.
Kelker, H. C., J. D. Oppenheim, D. Stone-Wolff, D. Henrjksen-DeStefano.B. B. Aggarwal, H. C. Stevenson, andJ. Vilcek. 1985. Characterization of human tumor necrosis factor produced by peripheral blood monocytes and its separation from lymphotoxin.Int. J. Cancer 36:69–73.
Old, L. J. 1985. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF).Science 230:630–632.
Degliantoni, G., M. Murphy, M. Kobayashi, M. K. Francis, B. Perussia, andG. Trinchieri. 1985. NK cell-derived hematopoietic colony-inhibiting activity and NK cytotoxic factor: Relationship with tumor necrosis factor and synergism with immune Interferon.J. Exp. Med. 162:1512–1530.
Aderka, D., H. Holtmann, L. Toker, T. Hahn, andD. Wallach. 1986. Tumor necrosis factor induction by Sendai virus.J. Immunol. 136:2938–2942.
Movat, H. Z. 1987. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 role in acute inflammation and microvascular injury.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 110:668–681.
Smith, R. J., S. C. Speziak, andB. J. Bowman. 1985. Properties of interleukin 1 as a complete secretagogne for human neutrophils.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 130:1233–1240.
Gamble, J. R., J. M. Harlan, S. J. Klebanoff, A. F. Lopez, andM. A. Vadas. 1986. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophlis to umbilical vein endotheliurn by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82:8667–8671.
Klebanoff, S. J., M. A. Vadas, J. M. Harlan, L. H. Sparks, J. R. Gamble, J. M. Agosti, andA. M. Waltersdorph. 1986. Stimulation of neutrophiis by tumor necrosis factor.J. Immunol. 136:4220–4225.
Dayer, J. M., B. Beutler, andA. Cerami. 1985. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal flbroblasts.J. Exp. Med. 162:2163–2168.
Bertolini, D. R., G. E. Nedwin, T. S. Bringman, D. D. Smith, andG. R. Mundy. 1986. Stimulation of bone resorption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumor necrosis factors.Nature 319:516–518.
Silberstein, D. S., andJ. R. David. 1986. Tumor necrosis factor enhances eosinophil toxicity toSchistosoma mansoni larvae.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83:1055–1059.
Dinarello, C. A., J. G. Cannon, S. M. Wolff, H. A. Bernheim, B. Beutler, A. Cerami, I. S. Figari, M. A. Palladino, andJ. V. O'Connor. 1986. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1.J. Exp. Med. 163:1433–1450.
Nawroth, P. P., I. Bank, D. Handley, J. Cassimeris, L. Chess, andD. Stern. 1986. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1.J. Exp. Med. 163:1363–1375.
Vilcek, J., V. J. Palombella, D. Henriksen-DeStefano, C. Swenson, R. Feinman, M. Hirai, andM. Tsujimoto. 1986. Fibroblast growth-enhancing activity of tumor necrosis factor and its relationship to other polypeptide growth factors.J. Exp. Med. 163:632–643.
Austgulen, R., T. Esperik, andJ. Nissen-Meyer. 1987. Fibroblast growth-stimulatory activity released from human monocytes, the contribution of tumor necrosis factor.Scand. J. Immunol. 26:621–629.
Seite, A., L. Adorini, E. Mambini, andG. Doria. 1986. A microcomputer program for probit analysis of interleukin-2 (IL-2) titration data.J. Immunol. Methods 86:265–277.
Haslam, P. L., C. W. G. Turton, B. Heard, A. Lukoszek, J. V. Collins, A. J. Salsbury, andM. Turner-Warwick. 1988. Bronchoalveolar lavage in pulmonary fibrosis: Comparison of cells obtained with lung biopsy and clinical features.Thorax 35:9–18.
Bégin, R., M. Rola-Pleszczynski, S. Massé, D. Nadeau, andG. Drapeau. 1983. Assessment of progression of asbestosis in the sheep mode by bronchoalveolar lavage and pulmonary function tests.Thorax 38:449–457.
Semenzato, G., M. Chilosi, E. Ossi, L. Trentin, G. Pizzolo, A. Cipriani, C. Agostini, R. Zambello, G. Marcer, andG. Gasparotto. 1985. Bronchoalveolar lavage and lung histology. Comparative analysis of inflammatory and immunocompetent cells in patients with sarcoidosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis.Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 132:400–404.
Dauber, J. H., M. D. Rossman, G. G. Pietra, S. A. Jimenez, andR. P. Daniele. 1980. Experimental silicosis. Morphologic and biochemical abnormalities produced by intratracheal instillation of quartz into guinea pig lungs.Am. J. Pathol. 101:595–607.
Callis, A. H., P. G. Sohnle, G. S. Mandel, J. Wiessner, andN. S. Mandel. 1985. Kinetics of inflammatory and fibrotic pulmonary changes in a murine model of silicosis.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 105:547–553.
Davis, G. S. 1986. Pathogenesis of siiicosis: Current concepts and hypothesis.Lung 164:139–154.
Adamson, I. Y. R., andD. H. Bowden, 1984. Role of polymorphonuclear-leukocytes in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Am. J. Pathol. 117:37–43.
Lemaire, I. 1985. Characterization of the bronchoalveolar cellular response in experimental asbestosis. Different reactions depending on the fibrogenic potential.Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 131:144–149.
Shalaby, M. R., M. A. Palladino, S. E. Hirabayashi, T. E. Eessalu, G. D. Lewis, H. M. Shepard, andB. B. Aggarwal. 1987. Receptor binding and activation of polymorphonuclear neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor-alpha.J. Leukocyte Biol. 41:196–204.
Brieland, J. K., R. G. Kunkel, andJ. C. Fantone. 1987. Pulmonary alveolar macrophage function during acute inflammatory lung injury.Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 135:1300–1306.
Hoffman, M., andJ. B. Weinberg. 1987, Tumor necrosis factor-α induces increased hydrogen peroxide production and Fc receptor expression, but not increased Ia antigen expression by peritoneal macrophages.J. Leukocyte Biol. 42:704–707.
Tsujimoto, M., S. Yokota, J. Vilcek, andG. Weissmann. 1986. Tumor necrosis factor provokes superoxide anion generation from neutrophils.Biochen. Biophys. Res. Commun. 137:1094–1100.
Figari, S., N. A. Mori, andM. A. Palladino. 1987. Regulation of neutrophil migration and superoxide production by recombinanl tumor necrosis factors-α and B: Comparison to recombinant interferon-gamma and interleukin-lα.Blood 70:979–984.
Babior, B. M. 1984. Oxidants from phagocytes: Agents of defense and destruction.Blood 64:959–966.
Hedenborg, M., andM. Klockars. 1987. Production of reactive oxygen metabolites induced by asbestos fibers in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes.J. Clin. Pathol. 40:1189–1193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the Medical Research Council of Canada.
E. B. is a recipient of a Studentship from the Fonds de la Recherche en Santé du Québec.
M. R.-P. is a Scholar of the Fonds de la Recherche en Santé du Québec.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bissonnette, E., Rola-Pleszczynski, M. Pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in a murine model of asbestosis and silicosis. Inflammation 13, 329–339 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00914399
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00914399