Abstract
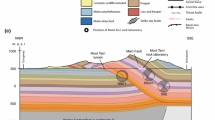
Analysis of stope convergence measurements in a burst-prone lead-zinc-silver mine is being used by the U.S. Bureau of Mines to study rock burst processes. Three convergence gages were installed in a 3-m wide stope of the Galena Mine with an inter-gage distance of approximately 8 m. The two-month period immediately after installation, during which the subsequent cut of the pillar was made, is the subject of the analysis described in this paper. Microseismicity rates and locations (local magnitude −5 and above) were also recorded during this period. Coseismic convergence steps within the 10-minute sample interval are observed at various times on all three gages. The convergences of the three gages do not track one another, indicating the blocky nature of deformation in this stope at a 10 meter or smaller size scale. The behavior of the three gages is different with respect to coseismic and interseismic convergence during the study period. For one of the gages, 82% of total closure occurs coseismically. The other two gages show much smaller percentages of coseismic convergence (30% and 35%), and proportionately higher percentages of interseismic steady creep. This heterogeneous convergence behavior may be indicative of the relative stability of the faults in the vicinity of each gage. An examination of stability models shows that the mine-geometry-related spatial variation in normal stress, acting on an existing set of faults, may explain the observed behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boler, F. M., andSwanson, P. L.,Computer-automated Measurement-and Control-based Workstation for Microseismic and Acoustic Emission Research (U.S. Bureau of Mines Information Circular 9262, Washington, D.C. 1990).
Brace, W. F., andByerlee, J. D. (1966),Stick-slip as a Mechanism for Earthquakes, Science153, 990–992.
Byerlee, J. D. (1970),The Mechanics of Stick-slip, Tectonophys.9, 475–486.
Dieterich, J. H.,Constitutive properties of faults with simulated gouge. InMechanical Behavior of Crustal Rocks (Am. Geophys. Union Monograph24, Washington, D.C. 1981) pp. 103–120.
Hodgson, K., andCook, N. G. W. The mechanism, energy content and radiation efficiency of seismic waves generated by rockbursts in deep-level mining. InDynamic Elastic Waves in Civil Engineering (eds. Howells D. A., et al.) (Wiley-Interscience, New York 1971) pp. 121–133.
McGarr, A. (1976),Seismic Moments and Volume Changes, J. Geophys. Res.81, 1487–1494.
McGarr, A., andWeibols, G. A. (1977),Influence of Mine Geometry and Closure Volume on Seismicity in a Deep-level Mine, Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. and Geomech Abstr.14, 139–145.
McGarr, A. (1971),Stable Deformation of Rock Near Deep-level Tabular Excavations, J. Geophys. Res.76, 7088–7106.
McMahon, T.,Rock Burst Research and the Coeur d'Alene District (U.S. Bureau of Mines Information Circular 9186, Washington, D.C. 1988).
Rice, J. R.,Shear instability in relation to the constitutive description of fault slip. InProceedings of the Ist International Congress on Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (eds. Gay, N. C., and Wainwright, E. H.) (SAIMM, Johannesburg 1984) pp. 57–62.
Scholz, C. H.,The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York 1990).
Steblay, B. J., Brady, B. T., andSwendseid, T.,Innovative microseismic monitoring system. InRockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (ed. Fairhurst, C.) (Balkema, Rotterman 1990) pp. 259–262.
Swanson, P. L. (1993),Mining-induced Seismicity in Faulted Geologic Structures: An Analysis of Seismicity-induced Slip Potential, Pure and Appl. Geophys.139, 657–676.
Tullis, T. E., andWeeks, J. D. (1986),Constitutive Behavior and Stability of Frictional Sliding of Granite, Pure and Appl. Geophys.124, 383–414.
Zipf, K.,Analysis of stable and unstable pillar failure using a local mine stiffness method. InProceedings of the Workshop on Coal Pillar Mechanics and Design (U.S. Bureau of Mines Information Circular 9315, Washington, D.C. 1992) pp. 138–143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boler, F.M., Swanson, P.L. Observations of heterogeneous stope convergence behavior and implications for induced seismicity. PAGEOPH 139, 639–656 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879956
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879956