Abstract
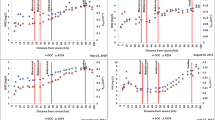
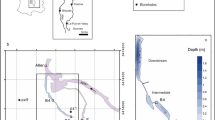
To detect temporal changes and the origin of the refractory dissolved organic matter in the Upper Rhône River, UV light absorbance (A) at 285 nm and quantitative dissolved organic carbon (DOC) measurements were carried out. Data from 63 visits to the main channel over a period of two years and from visits to different waterbodies in the alluvial plain before and after a flood are presented. There was a good correlation between A (0.019–0.160) and the DOC content (1.40–9.81 mg/L) for the waterbodies, but not for the river axis with lower A (0.013–0.044) and DOC content (1.13–2.20 mg/L). Due to this good correlation, the DOC content could be quantified for the waterbodies by absorbance measurements only. For the river water this indirect determination of the DOC content was not possible. However, the A/DOC ratio showed changes in the composition of DOC of river water and provided indications about the origin of the dissolved organic matter in the Upper Rhône River.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoros, C., 1991. Changes in side-arms connectivity and implications for river system management. Rivers 2:105–112.
Amoros, C., A.L. Roux and J.L. Reygrobellet, 1987. A method for applied ecological studies of fluvial hydrosystems. Regulated Rivers 1:17–36.
Amoros, C. and A.L. Roux, 1988. Interaction between waterbodies within the floodplains of large rivers: function and development of connectivity. Münst. Geogr. Arbeit. 29:125–130.
Benner, R., M.A. Moran and R.E. Hodson, 1986. Biochemical cycling of lignocellulosic carbon in marine and freshwater ecosystems: relative contributions of procaryotes and eucaryotes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 31:89–100.
Bornette, G., C. Amoros and D. Chessel, 1994. Effect of allogenic processes on the successional rates in the former river channels. J. Veg. Sci. 5:237–246.
Bravard, J.P., C. Amoros and G. Pautou, 1986. Impacts of civil engineering works on succession of communities in a fluvial system: a methodological and predictive approach applied to a section of the upper Rhône River. Oïkos 47:92–111.
Buffle, J., P. Deladoey, J. Zumstein and W. Haerdi, 1982. Analysis and characterization of natural organic matters in freshwaters. I. Study of analytical techniques. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 44:325–362.
Buffle, J. and P. Deladoey, 1982. Analysis and characterization of natural organic matters in freshwaters. II. Comparison of the properties of waters of various origins and their annual trend. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 44:363–391.
Cellot, B., A. Berly, H. Tachet and M. Bournaud, 1991. Composition and dynamics of suspended matter in the Upper Rhône, upstream from Lyon. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 24:1789–1794.
Cellot, B. and J.C. Rostan, 1993. Dissolved organic carbon dynamics in the French Upper Rhône: the influence of the side-arms? Regulated Rivers: Research & Management 8:391–397.
Geller, A., 1986. Comparison of mechanisms enhancing biodegrability of refractory lake water constituents. Limnol. Oceanogr. 31:755–764.
Grubaugh, J.W. and R.V. Anderson, 1989. Upper Mississippi River: seasonal and floodplain forest influences on organic matter transport. Hydrobiologia 174:235–244.
Kieber, R.J., X. Zhou and H. Mopper, 1990. Formation of carbonyl compounds from U.V. induced photodegradation of humic substances in natural waters: fate of riverine carbon in the sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35:1503–1515.
Mc Dowel, W.H. and G.E. Likens, 1988. Origin composition and flux of dissolved organic carbon in the Hubbard Brook Valley. Ecol. Monogr. 58:177–195.
Moore, T.R., 1987. An assessment of a simple spectrophotometric method for the determination of dissolved organic carbon in freshwaters. New Zealand J. Mar. and Freshwat. Res. 21:585–589.
Moran, M.A. and R.E. Hodson, 1989. Formation and bacterial utilization of dissolved organic carbon from derived from detrital lignocellulose. Limnol. Oceanogr. 34:1034–1047.
Naïman, R.J., H. Décamps, J. Pastor and C.A. Johnston, 1988. The potential importance of boundaries to fluvial ecosystems. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 7:289–306.
Pautou, G. and H. Décamps, 1985. Ecological interactions between the alluvial forests and hydrology of the Upper Rhône. Arch. Hydrobiol. 104:13–37.
Pautou, G., H. Décamps, C. Amoros and J.P. Bravard, 1985. Successions végétales dans les couloirs fluviaux: l'exemple de la plaine alluviale du Haut Rhône français. Bull. Ecol. 16:203–212.
Rostan, J.C. and C. Mouvet, 1986. Apport de la spectrophotométrie UV et de la matière organique dissoute à l'étude du fonctionnement des écosystèmes dulcicoles. Sciences de l'Eau 5:9–28.
Rostan, J.C., C. Amoros and J. Juget, 1987. The organic content of the surficial sediment: a method for the study of ecosystems development in abandoned river channels. Hydrobiologia 184:45–62.
Roux, A.L., J.P. Bravard, C. Amoros and G. Pautou, 1989. Ecological changes of the French Upper Rhône River since 1750. In: G.E. Petts (ed.), Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester (UK): Historical changes of large alluvial rivers: Western Europe, pp. 323–350.
Rutherford, J.E. and H.B.N. Hynes, 1987. Dissolved organic carbon in streams and groundwater. Hydrobiologia 154:33–48.
Wainright, S.C., C.A. Couch and J.L. Meyer, 1992. Fluxes of bacteria and organic matter into a blackwater river from river sediment and floodplain soils. Fresh. Biol. 28:37–48.
Ward, J.V., 1989. The four dimensional nature of lotic ecosystem. J.N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 8:2–8.
Zumstein, J. and J. Buffle, 1989. Circulation of pedogenic and aquagenic organic matter in an eutrophic lake. Wat. Res. 23:229–230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rostan, J.C., Cellot, B. On the use of UV spectrophotometry to assess dissolved organic carbon origin variations in the Upper Rhône River. Aquatic Science 57, 70–80 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878027
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878027