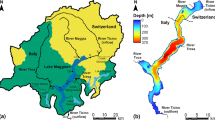
Abstract
Vertical mixing in Überlingersee is studied by releasing sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) as a tracer at a central hypolimnic depth of 60 m and measuring its subsequent vertical dispersion over a period of three months. The experiment started with a streaky tracer injection of 1 liter gaseous SF6 (STP) in August 1990. At that time the lake showed a typical strong summer stratification which in a weakened form lasts until November. From the SF6 profiles of fifteen surveys at three sampling sites vertical diffusivitiesK z are calculated compensating internal seiche displacement and horizontal tracer loss. Except of the bottom region no sampling site or time period is marked by significant differences in the hypolimnicK z profile. So vertical mixing in the whole Überlingersee is described by mean diffusivities decreasing from 1.7 cm2/s at 120 m depth to 0.4 cm2/s in 30 m. The minimal value of 0.3 cm2/s in the thermocline region at 20 m depth is only based on observations in autumn. For a strong summer stratification it is certainly lower. The gradient-flux-method for heat was applied to compute a meanK z (T) profile from continuously measured temperature profiles. Significant differences resulting from the two tracers showed, that theK z (T) values are underestimated by up to a factor of 5 if cooling by lateral exchange is neglected. Particularly, internal seiche pumping of colder water from the adjacent Lake Obersee over the separating sill of Mainau into the deep Überlingersee basin is observed in 1990 from August onward, obviously controlling the heat budget below the sill level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton, J.T., R.A. Dawe, K.W. Miller, E.B. Smith, and B.J. Stickings, 1968. The solubility of certain gaseous fluorine compounds in water. J. Chem. Soc. (A):1793–1796.
Bührer, H., and H. Ambühl, 1975. Die Einleitung von gereinigtem Abwasser in Seen. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 27:347–369.
Farmer, D.M., and L. Armi, 1986. Maximal two-layer exchange over a sill and through the combination of a sill and contraction with barotropic flow. J. Fluid Mech. 164:53–76.
Gargett, A.E., and G. Holloway, 1984. Dissipation and diffusion by internal wave breaking. J. Mar. Res. 42:15–27.
Heinz, G., 1990. Mischungs- und Strömungsverhältnisse im Westteil des Bodensees. Ph. D. Thesis, Institut für Umweltphysik, University of Heidelberg, 146 pp.
Heinz, G., J. Ilmberger, and M. Schimmele, 1990. Vertical mixing in Überlinger See, western part of Lake Constance, Aquatic Sciences 52/3:256–268.
Imboden, D.M., U. Lemmin, T. Joller, and M. Schurter, 1983. Mixing processes in lakes: mechanisms and ecological relevance. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 45/1:11–44.
Jassby, A., and T. Powell, 1975. Vertical patterns of eddy diffusion during stratification in Castle Lake, California. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20:530–543.
Ledwell, J.R., and A.J. Watson, 1991. The Santa Monica Basin tracer experiment: A study of diapycnal and isopycnal mixing. J. geophys. Res. 96:8695–8718.
Ledwell, J.R., A.J. Watson, and C.S. Law, 1993. Evidence for slow mixing across the pycnocline from an open-ocean tracer-release experiment. Nature 364:701–703.
Lerman, A., and M. Stiller, 1969. Vertical eddy diffusion in Lake Tiberias. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 17:323–333.
Li, Y.H., 1973. Vertical eddy diffusion coefficient in Lake Zürich. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 35:1–7.
Maiss, M., 1992. Schwefelhexafluorid (SF6) als Tracer für Mischungsprozesse im westlichen Bodensee. Ph. D. Thesis, Institut für Umweltphysik, University of Heidelberg, 219 pp.
Maiss, M., and I. Levin, 1994. Global increase of SF6 observed in the atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21:569–572.
Maiss, M., J. Ilmberger, A. Zenger, and K.O. Münnich, 1994. A SF6 tracer study of horizontal mixing in Lake Constance. Aquatic Sciences, this issue.
Mortimer, C.H., 1942. The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. J. of Ecology 30:147–201.
Quay, P.D., W.S. Broecker, R.H., Hesslein, and D.W. Schindler, 1980. Vertical diffusion rates determined by tritium tracer experiments in the thermocline and hypolimnion of two lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25:201–218.
Schimmele, M., 1993. Anregung interner Seiches im Bodensee durch den Wind. Ph. D. Thesis, Institut für Umweltphysik, University of Heidelberg, 161 pp.
Schlatter, J., M. Hofer, and D.M. Imboden, 1990. Die Verwendung von Schwefelhexafluorid zum Studium von Transportprozessen in Seen. Gas-Wasser-Abwasser 70/1:36–42.
Van Senden, D.C., and D.M. Imboden, 1989. Internal seiche pumping between sill-separated basins. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dynamics 48:135–150.
Ward, P.R.B., 1977. Diffusion in lake hypolimnia. Proc. 17th Cong. Int. Assoc. Hydraul. Res., Baden Baden, Germany: 103–110.
Weiss, W., K.H. Fischer, B. Kromer, W. Roether, H. Lehn, W.B. Clarke, and Z. Top, 1978. Gas exchange with the atmosphere and internal mixing of Lake Constance (Obersee). Verh. Gesell. Ökol., Kiel 1977:153–161.
Weiss, W., H. Lehn, K.O. Münnich, and K.H. Fischer, 1979. On the deep-water turnover of Lake Constance. Arch. Hydrobiol. 86:405–422.
Weiss, W., T. Zapf, M. Baitter, B. Kromer, K.H. Fischer, P. Schlosser, W. Roether, and K.O. Münnich, 1984. Subsurface horizontal water transport and vertical mixing in Lake Constance traced by Radon-222, Tritium, and other physical and chemical tracers, in: “Isotope Hydrology 1983”, IAEA-SM-270/7, Vienna 1984:43–54.
Welander, P., 1968. Theoretical forms for vertical exchange coefficients in a stratified fluid with application to lakes and seas. Acta R. Soc. Sci. Litt. Gothob. Geophys. 1:27.
Wilhelm, E., R. Battino, and R.J. Wilcock, 1977. Low-pressure solubility of gases in liquid water. Chemical Reviews 77/2:219–262.
Zenger, A., J. Ilmberger, G. Heinz, M. Schimmele, and K.O. Münnich, 1989. Untersuchungen zur Struktur der internen Seiches des Bodensees. Wasserwirtschaft 79:616–624.
Zenger A., J. Ilmberger, G. Heinz, M. Schimmele, P. Schlosser, D. Ilmboden, and K.O. Münnich, 1990(a). Behavior of a medium-sized basin connected to a large lake. In: M.M. Tilzer, and C. Serruya (eds.), “Large Lakes — Ecological Structure and Function”, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg:133–155.
Zenger, A., J. Ilmberger, P. Schlosser, and K.O. Münnich, 1990 (b). Winterliche vertikale Mischung im Bodensee. Wasser und Boden 9:577–582.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maiss, M., Ilmberger, J. & Münnich, K.O. Vertical mixing in Überlingersee (Lake Constance) traced by SF6 and heat. Aquatic Science 56, 329–347 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00877180
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00877180