Summary
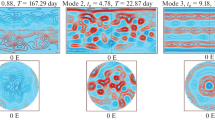
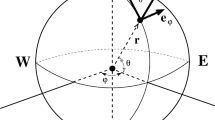
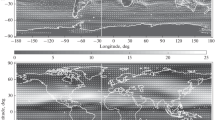
By means of highly truncated spherical harmonic expansions, an extended four-level quasi-geostrophic model with variable Coriolis parameter is transformed into a set of ordinary non-linear differential equations. Non-adiabatic effects, frictional dissipation, and boundary effects are approximately included in the equations. A numerical experiment made with the equations succeeds in producing many realistic statistical gross features, especially in the lower stratosphere, e. g., a poleward temperature incrase, the up-gradient horizontal transports of heat and momentum due to large-scale eddies, the upward energy flux of extra-long waves, and the trapping of the upward energy flux of tropospheric unstable waves near the tropopause. The mean energy flow in the lower stratosphere and in the troposphere are analyzed and compared with each other, indicating very clearly the baroclinical activness of the troposphere and the passiveness of the lower stratosphere. The dynamics in the lower stratosphere are discussed. the mean meridional circulation is also studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. G. Charney andP. G. Drazin,Propagation of planetary-scale disturbances from the lower into the upper atmosphere, J. Geoph. Res.66 (1961), 83.
J. G. Charney andA. Eliassen,A numerical method for predicting the perturbations of the middle latitude westerlies, Tellus1 (1949), 38.
P. F. Clapp,Normal heat sources and sinks in the lower troposphere in winter, Mon. Wea. Rev.89 (1961), 147.
E. T. Eady,Long waves and cyclone waves, Tellus1 (1949), 33.
A. Eliassen andE. Palm,On the transfer of energy in stationary mountain waves, Geofysiske Publikasjoner, Geophys. Norvegica12 (1961), 1.
J. S. A. Green,A problem in baroclinic instability, Quart. J. R. Meteor. Soc.86 (1960), 237.
H. G. Houghton,On the annual heat balance of northern hemisphere, J. Meteor.11 (1954), 1.
W. Jones,Energetics of the solar semidiurnal tide in the atmosphere, Ph. D. dissertation, Dept. of Meteor., Mass. Inst. of Tech. (1963), 161 pp.
H. L. Kuo,Energy-releasing processes and stability of thermally driven motions in a rotating fluid, J. Meteor.13 (1956), 82.
E. N. Lorenz,Energy and numerical weather production, Tellus12 (1960), 364.
E. N. Lorenz,Deterministic nonperiodic flow, J. Atmos. Sci.20 (1963), 130.
S. Manabe andF. Möller,On the radiative equilibrium and heat balance of the atmosphere, Mon. Wea. Rev.89 (1961), 509.
A. C. Molla andC. J. Loisel,On the hemispheric correlation of vertical and meridional wind components, Geofis. pura e appl.51 (1962), 166.
T. Murakami,Stratospheric wind temperature and isobaric height conditions during the IGY period, Part I, Report No. 5, Planetary Circulation Project, Dept. of Meteor., Mass. Inst. of Tech. (1962), 213 pp.
R. E. Newell,The general circulation of the atmosphere and its effects on the movement of trace substances, J. Geophys. Res.68 (1963), 3949.
G. Ohring,The radiation budget of the stratosphere, J. Meteor.15 (1958), 440.
A. H. Oort,On estimates of the atmospheric energy cycle, Mon. Wea. Rev.92 (1964), 483.
A. H. Oort,On the energetics of the mean and eddy circulations in the lower stratosphere, Tellus16 (1964), 309.
J. P. Peixoto,Hemispheric temperature conditions during the year 1950, Sci. Rept. No. 4, Planetary Circulation Project. Dept. of Meteor., Mass. Inst. of Tech. (1960), 211 pp.
L. Peng,Stratospheric wind temperature and isobaric height conditions during the IGY period, Part II, Report No. 10, Planetary Circulation Project, Dept. of Meteor., Mass. Inst. of Tech. (1963), 208 pp.
B. Saltzman andA. Fleisher,The exchange of kinetic energy between larger scales of atmospheric motion. Tellus12 (1960), 347.
V. P. Starr andJ. M. Wallace,Mechanics of eddy processes in the tropical troposphere, Pure and Appl. Geophys.58 (1964), 138.
S. Teweles,Spectral aspects of the stratospheric circulation during the IGY, Report No. 8, Planetary Circulation Project, Dept. of Meteor., Mass. Inst. of Tech. (1963), 191 pp.
M. V. Wilkes,Oscillations of the earth's atmosphere, Cambridge Univ. Press (New York and London 1949).
R. M. White,The counter-gradient flux of sensible heat in the lower stratosphere, Tellus6 (1954), 177.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, L. A simple numerical experiment concerning the general circulation in the lower stratosphere. PAGEOPH 61, 191–218 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00875777
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00875777