Abstract
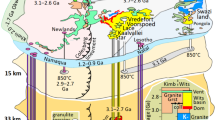
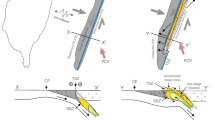
Cataclasites and mylonites, and the brittle-ductile processes that produce them, were studied at exposures along the northern rim of the Grong culmination, a transverse basement antiform in the central Scandinavian Caledonides. The rock suite studied is composed of gneisses, mylonites, and cataclasites which have a granodioritic composition. The microstructure of the rocks appears to be the result of repeated alternations of brittle faulting (associated with hydrothermal mineral growth) and ductile deformation of the crystallization products. During brittle faulting K-feldspar-chlorite veins are formed, probably by incongruent pressure solution of micas. During plastic deformation of the rocks the mineral association is transformed to white mica and green biotite, according to the reaction.
During this reaction plagioclase is overgrown by mica and epidote, and K-feldspar crystals are replaced by albite. The reactions which involve K-feldspars are cyclic: K-feldspar that is generated in cracks tends to be removed by albitization during ductile deformation. It is concluded that the mylonites studied represent a movement zone in the Earth's crust in which seismic and aseismic slip alternated during a large part of the deformation history.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, J. Barnett, R. L. andKerrich, R. (1979),Superplastic flow and changes in crystal chemistry of feldspars, Tectonophys.53, T41–46.
Augevin, C. L., Turcotte, D. L. andFurnish, M. D. (1982),Pressure solution lithification as a mechanism for the stick-slip behaviour of faults. Tectonics1, 151–160.
Aukes, P. G., Reymer, A. P. S., de Ruiter, G. W. M., Stel, H. andZwart, H. J. (1979),The geology of the Lierne district, north-east of the Grong culmination, central Norway. Norges Geol. Unders. Publ.354, 115–129.
Beach, A. (1979),Pressure solution as a metamorphic process in deformed terrigenous sedimentary rocks. Lithos12, 51–58.
Beach, A. (1980),Retrogressive metamorphic processes in shear zones with special reference to the Lewesian complex. J. Struct. Geol.2, 257–263.
Bell, T. H. andEtheridge, M. A. (1973),Microstructure of mylonites and their descriptive terminology. Lithos6, 337–348.
Boullier, A. M. (1980),A preliminary study of the behaviour of brittle minerals in a ductile matrix. J. Struct. Geol.,2, 211–217.
Ferry, J. M. (1983),Regional metamorphism of the Vassalboro formation, South Central Maine, USA: A case study of the role of fluid in metamorphic petrogenesis. J. Geol. Soc. London140, 551–576.
Frey, M., Hunziker, J. C., O'Neill, J. R. andSchander, H. W. (1976),Equilibrium disequilibrium relations in the Monte Rosa granite, western Alps: Petrological, Rb−Sr and stable isotope data. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol.55, 147–179.
Fyfe, W. S., Price, N. J. andThompson, A. B. (1978),Fluids in the Earth's Crust. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 383 pp.
Gee, D. G. (1975),A geotraverse through the Scandinavian Caledonides-Ostersund to Trondheim. SGUC717, 66 pp.
Graham, C. M., Greig, K. M., Sheppard, S. M. andTuri, B. (1983),Genesis and mobility of the H2O−CO2 fluid phase during regional greenschist and epidote amphibolite facies metamorphism: Petrological and stable isotope study in the Scottish Dalradian. J. Geol. Soc. London140, 577–599.
Hanmer, S. K. (1982),Microstructure and geochemistry of plagioclase and microcline in naturally deformed granite. J. Struc. Geol.4, 197–215.
Heimann, R. B. (1979),Hydrothermale Verdrängungsreaktionen an Alkalifeldspäte der Zusammensetzungen Or93Ab7 und Ab9Or4. Neues Jahrb. Min. Abh.137, 1–19.
Hobbs, B. E., Means, W. D. andWilliams, P. F. (1976),An Outline of Structural Geology. Wiley, New York, 571 pp.
Hosckek, G. (1973),Zur Stabilität metamorpher Biotit Paragenesen. Tschermaks Mineral. Petrol. Mitt.20, 48–58.
Kerrich, R., Allison, I., Barnett, R. L., Moss, S. andStarkey, J. (1980),Microstructural and chemical transformations accompanying deformation of granite in a shear zone at Miéville, Switzerland; with implications for stress corrosion cracking and superplastic flow. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol.73, 221–242.
Meyer, C. andHemley, J. J. (1967), ‘Wall rock alteration,’ in L. Barnes (ed.),Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. Holt, Rinehart, New York, 166–235.
Mitra, G. (1978),Ductile deformation zones and mylonites, the mechanical processes involved in the deformation of crystalline basement rocks. Am J. Sci.278, No. 8, 1057–1084.
Miyashiro, A. (1973),Metamorphism and Metamorphic Belts, Allen and Unwin, London, 492 pp.
Nicolas, A. andPoirier, J. P. (1976),Crystalline Plasticity and Solid State Flow in Metamorphic Rocks. Wiley, London, 444 pp.
Oftedahl, C. (1956),Om Grongkulminasjonen og Grongsfeltet skyvedekken. Norges Geol. Unders.195, 57–64.
Orville, P. M. (1963),Alkali metasomatism and feldspars. Norsk Geol. Tidskr.42, 283–316.
Passchier, C. W. (1982),Mylonitic deformation in the Saint Barthélemy Massif, French Pyrenees, with emphasis on the genetic relationship between ultramylonite and pseudotachylyte, GUA Papers Geol., Ser. 1, No. 16, 171 pp.
Petrovic, R. (1974), ‘Diffusion of alkali ions in alkalifeldspars,’ in W. S. McKenzie and J. Zussman, (eds.),The Feldspars. Manchester Univ. Press,Manchester, p. 174–182.
Poirier, J. P. andGuilloppé, M. (1979),Deformation induced recrystallization of minerals, Bull. Minéral.,102, 67–74.
Ramsay, J. G. (1980),The crack-seal mechanism of rock deformation. Nature284, 135–139.
Ramsay, J. G. andGraham, R. H. (1979),Strain variations in shear belts. Canad. J. Earth Sci.7, 786–813.
Spry, A. (1969),Metamorphic Textures, Pergamon, Oxford, 350 pp.
Stel, H. (1981),Crystal growth in cataclasites: Diagnostic microstructures and implications. Tectonophys.78, 585–600.
Stel, H. (1984),Hydrothermal processes in mylonitic rocks at the NW edge of the Grong culmination, Central Norway. Geologica Ultraiectina, No. 27.
Vernon, R. H. (1974),Metamorphic Processes. Allen and Unwin, London, 247 pp.
White, S. (1976),The effect of strain on the microstructures, fabrics and deformation mechanisms in quartzites. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. A,3283,69–86.
Wintch, R. P. (1975), Solid-fluid equilibria in the system KAISi3O8−NaAISI3O8−Al2Si2O5−HCl, J. Petrol.16, 57–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stel, H. The effect of cyclic operation of brittle and ductile deformation on the metamorphic assemblage in cataclasites and mylonites. PAGEOPH 124, 289–307 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00875729
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00875729