Abstract
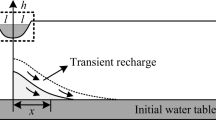
Recharging of aquifers due to irrigation, seepage from canal beds and other sources leads to the growth of water table near to the ground surface causing problems like water logging and increase of salinity in top soils in many regions of the world. This problem can be alleviated if proper knowledge of the spatio — temporal variation of the water table is available. In this paper an analytical solution for the water table fluctuation is presented for a 2-D aquifer system having inclined impervious base with a small slope in one — direction and receiving time varying vertical recharge. Application of the solution in estimation of water table fluctuation is demonstrated with the help of an example problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
length of the aquifer [L]
- B :
-
width of the aquifer [L]
- D :
-
mean depth of saturation [L]
- e :
-
specific yields
- h :
-
variable water table height [L]
- K :
-
hydraulic conductivity [LT −1]
- P(t) :
-
transient recharge rate [LT −1]
- P 1+P o :
-
initial rate of transient recharge [LT −1]
- P 1 :
-
final rate of transient recharge [LT −1]
- q :
-
slope of the aquifer base in percentage
- r :
-
decay constant [T −1]
- t :
-
time of observation [T]
- x, y :
-
coordinate axes
- x 2−x 1 :
-
length of the recharge basin [L]
- y 2−y 1 :
-
width of the recharge basin [L]
References
Agarwal, M. C., Goel, A. C., and Malik, R. K.: 1986, Consequences of irrigated agriculture in arid and semi-arid areas on groundwater, in G. Castary, E. Groba and E. Ramijn (eds.),Impact of agricultural activities on groundwater, IAH Publ.5, 233–242.
Abdulrazzak, M. J. and Morel-Seytoux, H. J.: 1983, Recharge from an ephemeral stream following wetting front arrival.Water Resour. Res. 19(1), 194–200.
Baumann, P.: 1952, Groundwater movements controlled through spreading.Trans. ASCE 117, 1024–1060.
Bear, J.: 1979, Hydraulics of Groundwater, McGraw-Hill, 569 pp.
Dagan, G.: 1967, Linearized solutions of free surface ground water flow with uniform recharge,J. Geophys. Res. 72(4), 1183–1193.
Glover, R. E.: 1961, Mathematical derivations as pertain to groundwater recharge,Agr. Res. Serv., USDA, Ft. Collins, Colo., 81 pp (mimeo).
Hantush, M. S.: 1967, Growth and decay of groundwater mounds in response to uniform percolation,Water Resour. Res. 3(1), 227–234.
Khanna, S. P. and Rai, J. N.: 1991, Groundwater management in parts of the Sarda sahayak canal command, Utter Pradesh,Bhujal-News, 39–45.
Morel-Seytoux, H. J.: 1984, From excess infiltration to aquifer recharge: A derivation based on the theory of flow of water in unsaturated soils,Water Resour. Res. 20(9), 1230–1240.
Ozisik, M. N.: 1980, Heat Conduction, John Wiley, 687 pp.
Rai, S. N. and Singh, R. N.: 1981, A mathematical model of water table fluctuations in a semi-infinite aquifer induced by localised transient recharge,Water Resour. Res. 17(4), 1028–1032.
Rai, S. N. and Singh, R. N.: 1985, Water table fluctuations in response to time varying recharge, in M. Diskin (ed.),Scientific Basis for Water Resources Management, IAHS Publ. No.,153, 287–294.
Rai, S. N. and Singh, R. N.: 1992, Water table fluctuations in an aquifer system owing to time varying surface infiltration and canal recharge,J. Hydrol. 136, 381–387.
Rai, S. N., Manglik, A. and Singh, R. N.: 1994, Water table fluctuations in response to transient recharge from a rectangular basin,Water Resour. Manag. 8(1), 1–10.
Ram, S. and Chauhan, H. S.: 1987, Analytical and experimental solutions for drainage of sloping lands with time varying recharge.Water Resour. Res. 23(6), 1090–1095.
Rao, N. H. and Sarma, P. B. S.: 1981, Recharge from rectangular areas to finite aquifers.J. Hydrol. 53, 269–275.
Rastogi, A. K. and Prasad, B.: 1992, FEM modelling to investigate seepage losses from the lined Nadiad branch canal, India,138, 153–168.
Singh, R. N. and Rai, S. N.: 1980, On subsurface drainage of transient recharge,J. Hydrol. 48, 303–311.
Singh, R. N., Rai, S. N., and Ramana, D. V.: 1991, Water table fluctuations in a sloping aquifer with transient recharge,J. Hydrol., 315–326.
Zomorodi, K.: 1991, Evaluation of the response of a water table to a variable recharge rate,Hydrol. Sci. J. 36, 67–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramana, D.V., Rai, S.N. & Singh, R.N. Water table fluctuation due to transient recharge in a 2-D aquifer system with inclined base. Water Resour Manage 9, 127–138 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00872464
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00872464