Abstract
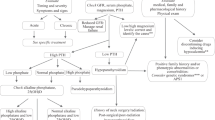
The main factors which regulate parathyroid hormone (PTH) production are calcium, phosphate, vitamin D, and estrogens. Hypocalcemia leads to increased PTH secretion in seconds and minutes, gene expression in hours, and parathyroid (PT) cell number in weeks and months. Hypercalcemia leads to a decrease in PTH secretion by its action on the PT cell calcium receptor and no decrease in PTH mRNA levels. There is now convincing evidence that phosphate regulates the PT, independent of its effect on serum calcium and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D3]. In vivo in rats hypophosphatemia markedly decreases PTH mRNA and serum intact PTH levels, independent of its effect on serum calcium and 1,25(OH)2D3. Clinical studies also indicate that phosphate regulates the PT independent of its effect on calcium and 1,25(OH)2D3; 1,25(OH)2D3 itself has a marked effect on the PT, where it decreases PTH gene transcrption by a direct action on the PT. The application of basic science findings of how calcium, phosphate, and 1,25(OH)2D3 regulate the PT has led to an efficient and safe prescription for the management of the secondary hyperparathyroidism of chronic renal failure, which is the maintenance of a normal serum calcium and phosphate and the careful use of 1,25(OH)2D3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi R, Lombardi M, Butters R, Kifor O, Sun A, Hediger MA, Lytton J, Hebert J (1993) Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature 366: 575–580
Naveh-Many T, Silver J (1990) Regulation of parathyroid hormone gene expression by hypocalcemia, hypercalcemia, and vitamin D in the rat. J Clin Invest 86: 1313–1319
Naveh-Many T, Kilav R, Moallem E, Silver J (1994) Post-transcriptional regulation of the PTH gene by calcium and phosphate in vivo (abstract). J Bone Miner Res 9: S338
Naveh-Many T, Raue F, Grauer A, Silver J (1992) Regulation of calcitonin gene expression by hypocalcemia, hypercalcemia, and vitamin D in the rat. J Bone Miner Res 7: 1233–1237
Mithal A, Kifor O, Kifor I, Vassilev P, Butters R, Krapcho K, Simin R, Fuller F, Hebert SC, Brown EM (1995) The reduced responsivenes of cultured bovine parathyroid cells to extracellular Ca2+ is associated with marked reduction in the expression in the expression of extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor messenger ribonucleic acid and protein. Endocrinology 136: 3087–3092
Okazaki T, Chung U, Nishishita T, Ebisu S, Usuda S, Mishiro S, Xanthoudakis S, Igarashi T, Ogata E (1994) A redox factor protein, refl, is involved in negative gene regulation by extracellular calcium. J Biol Chem 269: 2755–27862
Vadher S, Hawa NS, O'Riordan JLH, Farrow SM (1995) Translation of parathyroid hormone mRNA is regulated through the 3′-untranslated region (abstract). J Bone Miner Res 10: S278
Brown EM, Wilson RE, Thatcher JG, Marynick SP (1981) Abnormal calcium-regulated PTH release in normal parathyroid tissue from patients with adenoma. Am J Med 71: 565–570
Ramirez JA, Goodman WG, Gornbein J, Menezes C, Moulton L, Segre GV, Salusky IB (1993) Direct in vivo comparison of calcium-regulated parathyroid hormone secretion in normal volunteers and patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 76: 1489–1494
Naveh-Many T, Rahamimov R, Livni N, Silver J (1995) Parathyroid cell proliferation in normal and chronic renal failure rats: the effects of calcium, phosphate and vitamin D. J Clin Invest 96: 1786–1793
Arnold A, Brown MF, Urena P, Gaz RD, Sarfati E, Drueke TB (1995) Monoclonality of parathyroid tumors in chronic renal failure and in primary parathyroid hyperplasia. J Clin Invest 95: 2047–2053
Juppner H, Abou-Samra A-B, Freeman M, Kong XF, Schipani E, Richards J, Kolakowski LF, Hock J, Potts JT, Kronenberg HM, Segre GV (1991) A G-protein-linked receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide. Science 254: 1024–1026
Kilav R, Silver J, Naveh-Many T (1995) Parathyroid hormone gene expression in hypophosphatemic rats. J Clin Invest 96: 327–333
Lopez-Hilker S, Dusso AS, Rapp NS, Martin KJ, Slatopolsky E (1990) Phosphorus restriction reverses hyperparathyroidism in uremia independent of changes in calcium and calcitriol. Am J Physiol 259: F432-F437
Slatopolsky E, Bricker NS (1973) The role of phosphorus restriction in the prevention of secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic renal disease. Kidney Int 4: 141–145
Aparicio M, Combe C, Lafage MH, De Precigout V, Potaux L, Bouchet JL (1994) In advanced renal failure, dietary phosphorus restriction hyperparathyroidism independent of the levels of calcitriol. Nephron 63: 122–123
Lafage MH, Combe C, Fournier A, Aparicio M (1992) Ketodiet, physiological calcium intake and native vitamin D improve renal osteodystrophy. Kidney Int 42: 1217–1225
Combe C, Aparicio M (1994) Phosphorus and protein restriction and parathyroid function in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 46: 1381–1386
Tanaka Y, DeLuca HF (1973) The control of vitamin D by inorganic phosphorus. Arch Biochem Biophys 154: 566–570
Condamine L, Vztovsnik F, Friedlander G, Menaa C, Garabedian M (1994) Local action of phosphate depletion and insulin-like growth factor 1 on in vitro production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D by cultured mammalian kidney cells. J Clin Invest 94: 1673–1679
Escoubet B, Djabali K, Amiel C (1989) Adaptation to Pi deprivation of cell Na-dependent Pi uptake: a widespread process. Am J Physiol 256: C322-C328
Murer H (1992) Homer Smith award. Cellular mechanisms in proximal tubular Pi reabsorption: some answers and more questions. J Am Soc Nephrol 2: 1649–1665
Kilav R, Silver J, Biber J, Murer H, Naveh-Many T (1995) Co-ordinate regulation of the rat renal parathyroid hormone receptor mRNA and the Na−Pi cotransporter mRNA and protein. Am J Physiol 268: F1017-F1022
Werner A, Kempson SA, Biber J, Murer H (1994) Increase of Na/Pi-cotransport encoding mRNA in response to low Pi diet in rat kidney cortex. J Biol Chem 269: 6637–6639
Levi M, Arar M, Kaissling B, Murer H, Biber J (1994) Low-Pi diet increases the abundance of an apical protein in rat proximal-tubular S3 segments. Pflugers Arch 426: 5–11
Fraser DR (1980) Regulation of the metabolism of vitamin D. Physiol Rev 60: 551–613
Silver J, Russell J, Sherwood LM (1985) Regulation by vitamin D metabolites of messenger ribonucleic acid for preproparathyroid hormone in isolated bovine parathyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 4270–4273
Silver J, Naveh-Many T, Mayer H, Schmelzer HJ, Popovtzer MM (1986) Regulation by vitamin D metabolites of parathyroid hormone gene transcription in vivo in the rat. J Clin Invest 78: 1296–1301
Shvil Y, Naveh-Many T, Barach P, Silver J (1990) Regulation of parathyroid cell gene expression in experimental uremia. J Am Soc Nephrol 1: 99–104
Naveh-Many T, Silver J (1993) Effects of calcitriol, 22-oxacalcitriol and calcipotriol on serum calcium and parathyroid hormone gene expression. Endocrinology 133: 2724–2728
Kubrusly M, Gagne ER, Urena P, Hanrotel C, Chabanis S, Lacour B, Drueke TB (1993) Effect of 22-oxa-calcitriol on calcium metabolism in rats with severe secondary hyperparathyroidism. Kidney Int 44: 551–556
Quarles LD, Yohay DA, Carroll BA, Spritzer CE, Minda SA, Bartholomay D, Lobaugh BA (1994) Prospective trial of pulse oral versus intravenous calcitriol treatment of hyperparathyroidism in ESRD. Kidney Int 45: 1710–1721
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marks, K.H., Kilav, R., Naveh-Many, T. et al. Calcium, phosphate, vitamin D, and the parathyroid. Pediatr Nephrol 10, 364–367 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00866787
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00866787