Abstract
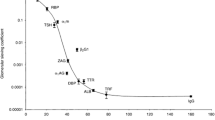
Low molecular weight proteins are of interest in children because their increased urinary excretion is a sign of renal tubular disease and their increased plasma concentration is inversely related to glomerular filtration rate. These proteins include β2-microglobulin (B2M), retinolbinding protein (RBP), α1-microgloulin (A1M) and lysozyme. B2M is unstable in acid urine, in contrast to RBP and A1M which are more stable. Any increase in the urinary excretion of B2M or RBP is highly specific for tubular disease, whereas increased excretion of A1M may be seen with glomerular proteinuria. Areas of clinical application include tubular and glomerular diseases, detection of drug toxicity, reflux nephropathy, birth asphyxia and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Methods of sample collection and analysis of these proteins are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butler EA, Flynn FV (1958) The proteinuria of renal tubular disorders. Lancet II: 978–980
Friberg L (1948) Proteinuria and kidney injury among workmen exposed to cadmium and nickel dust. J. Ind Hyg Toxicol 30: 32–36
Flynn FV, Platt HS (1968) The origin of the proteins excreted in tubular proteinuria. Clin Chim Acta 21: 377–399
Sumpio BE, Maack T, (1982) Kinetics, competition, and selectivity of tubular absorption of proteins. Am J Physiol 243: F379-F392
Maack T, Johnson V, Kau ST, Figueiredo J, Sigulem D (1979) Renal filtration, transport, and metabolism of low-molecular-weight proteins: a review. Kidney Int 16: 251–270
Trollfors B, Norrby R (1981) Estimation of glomerular filtration rate by serum creatinine and serum β2-microglobulin. Nephron 28: 196–199
Brocklebank T, Cooper EH, Richmond K (1991) Sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis patterns of proteinuria in various renal diseases of childhood. Pediatr Nephrol 5: 371–375
Berggard I, Bearn AG (1968) Isolation and properties of a low molecular weight β2-globulin occurring in human biological fluids. J Biol Chem 243: 4095–4103
Berggard I, Bjorck L, Cigen R, Logdberg L (1980) β2-Microglobulin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 40 [Suppl 154]: 13–25
Karlsson FA, Wibell L, Evrin PE (1980). β2-Microglobulin in clinical medicine. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 40 [Suppl 154]: 27–37
Kanai M, Raz A, Goodman DS (1968) Retinol-binding protein: the transport protein for vitamin A in human plasma. J Clin Invest 47: 2025–2044
Peterson PA, Berggard I (1971) Isolation and properties of a human retinol-transporting protein. J Biol Chem 246: 25–33
Rask L, Anundi H, Bohme J, Eriksson U, Frederiksson A, Nilsson SF, Ronne H, Vahlquist A, Peterson PA (1980) The retinol-binding protein. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 40 [Suppl 154]: 45–61
Ingenbleek Y, Van Den Schrieck H-G, De Nayer P, De Visscher M (1975) Albumin, transferrin and the thyroxine-binding prealbumin/retinol-binding protein (TBPA-RBP) complex in assessment of malnutrition. Clin Chim Acta 63 61–67
Ekstrom B, Peterson PA, Berggard I (1975) A urinary and plasma α1-glycoprotein of low molecular weight: isolation and some properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 65: 1427–1433
Berggard B, Ekstrom B, Akerstrom B (1980) α1-microglobulin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 40 [Suppl 154]: 63–71
Grubb A, Lopez C, Tejler L, Mendez E (1983) Isolation of human complex-forming glycoprotein, heterogeneous in charge (protein HC) and its IgA complex from plasma. J Biol Chem 258: 14698–14707
Hayslett JP, Perillie PE, Finch SC (1968) Urinary muramidase and renal disease. N Engl J Med 279: 506–512
Houser MT (1983) Improved turbidimetric assay for lysozyme in urine. Clin Chem 29: 1488–1493
Evrin P-E, Peterson PA, Wide L, Berggard I (1971) Radioimmunoassay of β2-microglobulin in human biological fluids. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 28: 439–443
Beetham R, Dawnay A, Landon J, Cattell WR (1985) A radioimmunoassay for retinol-binding protein in serum and urine. Clin Chem 31: 1364–1367
Shima K, Hirota M, Fukuda M, Tanaka A (1986) Determination of urinary lysozyme for potential detection of tubular dysfunction in diabetic nephropathy. Clin Chem 32: 1818–1822
Tomlinson PA, Dalton RN, Turner C, Chantler C (1990) Measurement of β2-microglobulin, retinol-binding protein, α1-microglobulin and urine protein 1 in healthy children using enzyme-linked immunosorvent assay. Clin Chim Acta 192: 99–106
Fernandez-Luna JL, Moneo I, Grubb A, Mendez E (1985) A sensitive and rapid enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using monoclonal antibodies for simultaneous quantitation of free and IgA-complexed protein HC. J Immunol Methods 82: 101–110
Bernard AM, Vyskocil A, Lauwerys RR (1981) Determination of β2microglobulin in human urine and serum by latex immunoassay. Clin Chem 27: 832–837
Bernard AM, Moreau D, Lauwerys RR (1982) Latex immunoassay of retinol-binding protein. Clin Chem 28: 1167–1171
Aperia A, Broberger O, Elinder G, Herin P, Zetterstrom R (1981) Postnatal development of renal function in pre-term and full-term infants. Acta Paediatr Scand 70: 183–187
Nolte S, Mueller B, Pringsheim W (1991) Serum α2-microglobulin and β2-microglobulin for the estimation of fetal glomerular renal function. Pediatr Nephrol 5: 573–577
Roberts DS, Haycock GB, Dalton RN, Turner C, Tomlinson PA, Stimmler L, Scopes JW (1990) Prediction of acute renal failure after birth asphyxia. Arch Dis Child 65: 1021–1028
Bernard AM, Lauwerys RR, Noel A, Vandeleene B, Lambert A (1989) Urine protein 1: a sex-dependent marker of tubular or glomerular dysfunction. Clin Chem 35: 2141–2142
Itoh Y, Kawai T (1991) Sex differences in urinary alpha-1-microglobulin value in normal individuals. Nephron 57: 121–122
Houser MT (1987) Characterization of recumbent, ambulatory, and postexercise proteinuria in the adolescent. Pediatr Res 21: 442–446
Bernard, A, Vyskocyl A, Mahieu P, Lauwerys R (1988) Effect of renal insufficiency on the concentration of free retinol-binding protein in urine and serum. Clin Chim Acta 171: 85–94
Evrin P-E, Wibell L (1972) The serum levels and urinary excretion of β2-microglobulin in apparently healthy subjects. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 29: 69–74
Bernard AM, Moreau D, Lauwerys R (1982) Comparison of retinol-binding protein and β2-microglobulin determination in urine for the early detection of tubular proteinuria. Clin Chim Acta 126: 1–7
Davey PG, Gosling P (1982) β2-Microglobulin instability in pathological urine. Clin Chem 28: 1330–1333
Schardijn G, Statius van Eps LW, Swaak AJG, Kager JCGM, Persijn JP (1979) Urinary β2-microglobulin in upper and lower urinarytract infections. Lancet I: 805–807
Donaldson MDC, Chambers RE, Woolridge MW, Whicher JT (1989) Stability of alpha1-microglobulin, beta2-microglobulin and retinol-binding protein in urine. Clin Chim Acta 179: 73–78
Pergande M, Jung K, Porstmann B, Evers U, Porstmann T (1986) Urinary osmolarity and pH and lysozyme stability. Clin Chem 32: 404–405
Jung K, Pergande M, Porstmann B, Porstmann T (1988) Diuresis-dependent excretions of low-molecular mass proteins in urine: β2-microglobulin, lysozyme, and ribonuclease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 48: 33–37
Peterson PA, Evrin P-E, Berggard I (1969) Differentiation of glomerular, tubular, and normal proteinuria: determinations of urinary excretion of β2-microglobulin, albumin, and total protein. J Clin Invest 48: 1189–1198
Bernard A, Viau C, Ouled A, Lauwerys R (1987) Competition between low- and high-molecular-weight proteins for renal tubular uptake. Nephron 45: 115–118
Tomlinson PA, Dalton RN, Chantler C (1989) A comparison of markers of renal tubular dysfunction in glomerular disease (abstract). Pediatr Nephrol 3: C233
Robson AM, Giangiacomo J, Kienstra RA, Naqvi ST, Ingelfinger JR (1974) Normal glomerular permeability and its modification by minimal change nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest 54: 1190–1199
Johansson BG, Ravnskov U (1972) The serum level and urinary excretion of α2-microglobulin, β2-microglobulin and lysozyme in renal disease. Scand J urol Nephrol 6: 249–256
Risdon RA, Sloper JC, de Wardener HE (1968) Relationship between renal function and histological changes found in renal-biopsy specimens from patients with persistent glomerular nephritis. Lancet II: 363–366
Mogensen CE, Solling K (1977) Studies on renal tubular protein reabsorption: partial and near complete inhibition by certain amino acids. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 37: 477–486
Bernard AM, Vyskocil AA, Mahieu P, Lauwerys RR (1987) Assessment of urinary retinol-binding protein as an index of proximal tubular injury. Clin Chem 33: 775–779
Yu H, Yanagisawa Y, Forbes MA Cooper EH, Crockson RA (1983) Alpha-1-microglobulin: an indicator protein for renal tubular function. J Clin Pathol 36: 253–259
Barratt TM, Crawford R (1970) Lysozyme excretion as a measure of renal tubular dysfunction in children. Clin Sci 39: 457–465
Brenton DP, Isenberg DA, Cusworth DC, Garrod P, Krywawych S, Stamp TCB (1981) The adult presenting idiopathic Fanconi syndrome. J Inherited Metab Dis 4: 211–215
Portman RJ, Kissane JM, Robson AM (1986) Use of β2-microglobulin to diagnose tubulo-interstitial renal lesions in children. Kidney Int 30: 91–98
Suzuki Y, Okada T, Higuchi A, Mase D, Kobayashi O (1985) Asymptomatic low molecular weight proteinuria: a report on 5 cases. Clin Nephrol 23: 249–254
Rybak MJ, Frankowski JJ, Edwards DJ, Albrecht LM (1987) Alanine aminopeptidase and β2-microglobulin excretion in patients receiving vancomycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 31: 1461–1464
Heney D, Wheeldon J, Rushworth P, Chapman C, Lewis IJ, Bailey CC (1991) Progressive renal toxicity due to ifosfamide. Arch Dis Child 66: 966–970
Hall PW, Vasiljevic M (1972) Beta2-microglobulin excretion as an index of renal tubular disorders with special reference to endemic Balkan nephropathy. J Lab Clin Med 81: 897–904
Chantler C, Carter JE, Bewick M, Counahan R, Cameron JS, Ogg CS, Williams DG, Winder E (1980) 10 years, experience with regular haemodialysis and renal transplantation. Arch Dis Child 55: 435–445
Torres VE, Velosa JA, Holley KE, Kelalis PP, Stickler GB, Kurtz SB (1980) The progression of vesicoureteral reflux nephropathy. Ann Intern Med 92: 776–784
Schardijn GHC, Statius ann Eps LW (1987) β2-Microglobulin: its significance in the evaluation of renal function. Kidney Int 32: 635–641
Sandberg T, Cooper EH, Lidin-Janson G, Yu H (1985) Fever and proximal tubular function in acute pyelonephritis. Nephron 41: 39–44
Bell FG, Wilkin TJ, Atwell JD (1986) Microproteinuria in children with vesicoureteric reflux. Br J Urol 58: 605–609
Ginevri F, Mutti A, Ghiggeri GM, Alinovi R, Ciardi MR, Bergamaschi E, Verrina E, Gusmano R (1992) Urinary excretion of brush border antigens and other proteins in children with vesico-ureteric reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 6: 30–32
Shalev A, Abeliovich D, Lieberman J (1984) β2-Microglobulin levels in amniotic fluids of abnormal fetuses. Isr J Med Sci 20: 1205–1206
Tack ED, Perlman JM, Robson AM, Hausel C, Chang CCT (1988) Renal injury in sick newborn infants: a prospective evaluation using urinary β2-microglobulin concentrations. Pediatrics 81: 432–440
Woo J, Floyd M, Cannon DC (1981) Albumin and β2-microglobulin radioimmunoassays applied to monitoring of renal allograft function and in differentiating glomerular and tubular diseases. Clin Chem 27: 709–713
Ravnskov U (1974) Proteinuria after human renal transplantation. I. Urinary excretion of α2-microglobulin (retinol binding protein), β2-microglobulin, lysozyme and albumin. Scand J Urol Nephrol 8: 37–44
Miller P, Varghese Z (1986) Measurement of retinol-binding protein in the assessment of renal allograft function. Med Lab Sci 43: 335–339
Prischl F, Gremmel F, Schwabe M, Schindler J, Balcke P, Kopsa H, Pinter G, Schwarzmeier J, Zazgornik J (1989) Beta-2-microglobulin for differentiation between ciclosporin A nephrotoxicity and graft rejection in renal transplant recipients. Nephron 51: 330–337
Viberti GC, Jarrett RJ, Mahmud U, Hill RD, Argyropoulos A, Keen H (1982) Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet I: 1430–1432
Davies AG, Price DA, Postlethwaite RJ, Addison GM, Burn JL, Fielding BA (1985) Renal function in diabetes mellitus. Arch Dis Child 60: 299–304
Walton C, Bodansky HJ, Wales JK, Forbes MA, Cooper EH (1988) Tubular dysfunction and microalbuminuria in insulin dependent diabetes. Arch Dis Child 63: 244–249
Gibb DM, Tomlinson PA, Dalton RN, Turner C, Shah V, Barratt TM (1989) Renal tubular proteinuria and microalbuminuria in diabetic patients. Arch Dis Child 64: 129–134
Rowe DJF, Anthony F, Polak A, Shaw K, Ward CD, Watts GF (1987) Retinol binding proteins as a small molecular weight marker of renal tubular function in diabetes mellitus. Ann Clin Biochem 24: 477–482
Watts GF, Powell M, Rowe DJF, Shaw KM (1989) Low-molecular-weight proteinuria in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a study of the urinary excretion of β2-microglobulin and retinol-binding protein in alkalinized patients with and without microalbuminuria. Diabetes Res 12: 31–36
Abrass CK (1984) Diabetic proteinuria: glomerular or tubular in origin?. Am J Nephrol 4: 337–346
Grillenberger A, Weninger M, Lubec G (1987) Determination of urinary low molecular weight proteins for the diagnosis of tubular damage. Padiatr Padol 22: 229–234
Donaldson MDC, Chambers RE, Woolridge MW, Whicher JT (1990) Alpha1-microglobulin, beta2-microglobulin and retinol binding protein in childhood febrile illness and renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 4: 314–318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomlinson, P.A. Low molecular weight proteins in children with renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 6, 565–571 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00866510
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00866510