Summary
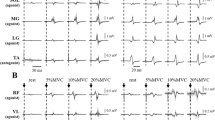
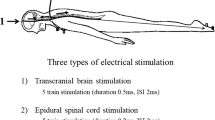
Magnetic stimulation of the brain and cervical and lumbar spinal roots was performed on 50 healthy volunteers. Compound muscle action potentials (CMAPs) were recorded from biceps brachii, abductor digiti minimi (ADM), rectus femoris and tibiahs anterior (TA). We assessed central conduction times by subtraction of peripheral from central latencies and compared results using either spinal root stimulation or the F-wave method. Side-to-side differences of total conduction time, peripheral conduction time and central conduction time (CCT) were measured and the effect of clockwise vs counterclockwise stimulations on latencies and sizes of CMAPs is emphasized. Amplitudes and areas of CMAPs were expressed as a percentage of the peripheral M response for ADM and TA. There was a positive correlation between CCT to the lumbosacral region and height, but not between the cervical region and height. No correlation was observed between genders and central conduction times, amplitudes or areas of CMAPs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amassian VE, Quirk GJ, Stewart M (1987) Magnetic coil versus electrical stimulation of monkey motor cortex. J Physiol (Loud) 394:119P
Barker AT, Jalinous R, Freeston IL (1985) Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet I:1106–1107
Barker AT, Freeston IL, Jalinous R, Jarratt JA (1987) Magnetic stimulation of the human brain and peripheral nervous system: an introduction and the results of an initial clinical evaluation. Neurosurgery 20:100–109
Britton TC, Meyer BU, Herdmann J, Benecke R (1990) Clinical use of the magnetic stimulator in the investigation of peripheral conduction time. Muscle Nerve 13:396–406
Chokroverty S, Sachdeo R, Dilullo J, Duvoisin RC (1989) Magnetic stimulation in the diagnosis of lumbosacral radiculopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:767–772
Chu NS (1989) Motor evoked potentials with magnetic stimulation: correlations with height. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 74:481–485
Claus D, Harding AE, Hess CW, Mills KR, Murray NMF, Thomas PK (1988) Central motor conduction in degenerative ataxic disorders: a magnetic stimulation study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:790–795
Claus D, Murray NMF, Spitzer A, Flügel D (1990) The influence of stimulus type on the magnetic excitation of nerve structures. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 75:342–349
Comi G, Galardi G, Del Carro U, Picconi R (1990) Magnetic stimulation of motor pathways: normative data. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 75:15P
Day BL, Dressler D, Maertens De Noordhout A, Marsden CD, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD (1988) Magnetic stimulation of the human brain can activate different neuronal elements when magnetic field direction is reversed. J Physiol (Lond) 401:46P
Day BL, Dressler D, Maertens De Noordhout A, Marsden CD, Nakashima K, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD (1989) Electric and magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex: surface EMG and single motor unit responses. J Physiol (Lond) 412:449–473
Eisen A, Shytbel W, Murphy K, Hoirch M (1990) Cortical magnetic stimulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 13:146–151
Eisen A, Shtybel W, Siejka S, MacNeil M (1990) Effects of aging on the normal motor evoked potential (MEP). Neurology 40[Suppl 1]:287
Hess CW, Mills KR, Murray NMF (1986) Measurement of central motor conduction in multiple sclerosis by magnetic brain stimulation. Lancet I:355–358
Hess CW, Mills KR, Murray NMF (1987) Responses in small hand muscles from magnetic stimulation of the human brain. J Physiol (Lond) 388:397–419
Hess CW, Mills KR, Murray NMF, Schriefer TN (1987) Magnetic brain stimulation: central motor conduction studies in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 22:744–752
Hufnagel A, Jaeger M, Elger CE (1990) Transcranial magnetic stimulation: specific and non-specific facilitation of magnetic motor evoked potentials. J Neurol 237:416–419
Ingram DA, Thompson AJ, Swash M (1988) Central motor conduction in multiple sclerosis: evaluation of abnormalities revealed by transcutaneous magnetic stimulation of the brain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:487–494
Jarratt JA (1986) Magnetic stimulation for motor conduction. In: International Symposium on New Concepts in Electrodiagnosis. American Association of Electromyography and Electrodiagnosis, Boston, Mass, pp 27–33
Kimura J (1974) F-wave velocity in central segment of the median and ulnar nerves. A study in normal subjects and in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Neurology 24:539–546
Maertens De Noordhout A, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Delwaide PJ, Marsden CD (1989) La stimulation percutanée électrique et magnétique du cortex moteur chez l'homme. Rev Neurol (Paris) 145:1–15
Mills KR, Murray NMF, Hess CW (1987) Magnetic and electrical transcranial brain stimulation: physiological mechanisms and clinical applications. Neurosurgery 20:164–168
Rossini PM, Caramia MD, Zarola F (1987) Mechanisms of nervous propagation along central motor pathways: noninvasive evaluation in healthy subjects and in patients with neurological disease. Neurosurgery 20:183–191
Rothwell JC, Thompson PD, Day BL, Dick JPR, Kachi T, Cowan JMA, Marsden CD (1987) Motor cortex stimulation in intact man. I. General characteristics of EMG responses in different muscles. Brain 110:1173–1190
Schriefer TN, Hess CW, Mills KR, Murray NMF (1989) Central motor conduction studies in motor neurone disease using magnetic brain stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 74:431–437
Tabaraud F, Hugon J, Salle JY, Boulesteix JM, Vallat JM, Dumas M (1989) Etude de la voie motrice centrale par stimulation magnétique corticale et électrique spinale: résultats chez 20 sujects normaux. Rev Neurol (Paris) 145:690–695
Ugawa Y, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Marsden CD (1989) Magnetic stimulation over the spinal enlargements. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:1025–1032
Ugawa Y, Kohara N, Shimpo T, Mannen T (1990) Magnetoelectrical stimulation of central motor pathways compared with percutaneous electrical stimulation. Eur Neurol 30:14–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furby, A., Bourriez, J.L., Jacquesson, J.M. et al. Motor evoked potentials to magnetic stimulation: technical considerations and normative data from 50 subjects. J Neurol 239, 152–156 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00833916
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00833916