Abstract
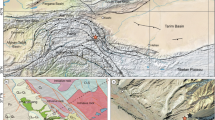
Recent investigations in and along the mountains south of the Loess Plateau (Central China) give no evidence of Pleistocene glaciations below 2800 m asl. Reliable Late-Pleistocene glacial landforms and till only occur in the Qinling Shan (3767 m). The paleosnowline in altitudes of 3250–3300 m was more than 1000 m lower than at present. A Late-Pleistocene periglacial region has been descended to about 2300 m asl, resulting an increase of the sediment yield of the rivers and intensified sediment aggradation in the valleys in and along the Qinling Shan. The Late-Pleistocene descend of the coniferous forest was comparable to the snowline depression. A spruce-fir forest dominated along the northern flank of the mountain range during the time 30-20 ka BP. Towards the end of the Pleistocene glacial periods respectively at the beginning of the following interglacial phase, dissection of alluvial deposits and terracing began in the mountain valleys and in the northern foreland. The replacement of forest vegetation by a more steppe-like vegetation as well as the loess accumulation along the northern Qinling Shan indicates increasing aridity as the climate warmed at the end of the last glacial period and during the Early Holocene. The widespread occurrence of Mid-Holocene paleosols within the loess proves a more moist and warm interval, which is followed by a drier and cooler Late Holocene period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, Z. S.; Ho, C. K.: New Magnetostratigraphic Dates of LantianHomo erectus. Quaternary Research 32, 213–221 (1989)
An, Z. S.; Kukla, G. J.; Porter, S.; Xiao, J.: Magnetic susceptibility evidence of monsoon variation on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the last 130,000 years. Quaternary Research 36, 29–36 (1991)
Cao, J. D.; Shao S. X.: Neotectonic Movements in China. In: Zhang Z. H. (ed.): The Quaternary of China, pp. 9–41, China Ocean Press, Beijing 1991.
Chen, C.: Standörtliche, vegetationskundliche und waldbauliche Analyse chinesischer Gebirgsnadelwälder und Anwendung alpiner Gebirgswaldbau-Methoden im chinesischen fichtenreichen Gebirgsnadelwald. Dissertation Universität f. Bodenkultur Wien (VWGÖ) 30, 1987.
Derbyshire, E.: A History of Glacial Stratigraphy in China. Quaternary Science Review 6, 301–314 (1987)
Fenzel, G.: Das Taipei-Massiv im Tschinlingschan, Nordchina. Petermanns Geographische Mitteilungen 83, 203–206 (1937)
Kozarski, S.: Problem of Pleistocene Glaciations in the Mountains of East China. Zeitschrift f. Geomorphologie, N. F. 7, 48–70 (1963)
Kukla, G.; Heller, F.; Liu, X.; Xu, T. C.; Liu, T. S.; An, Z. S.: Pleistocene climate in China dated by magnetic susceptibility. Geology 16, 811–814 (1988)
Kukla, G.; An, Z. S.: Loess stratigraphy in central China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 72, 203–223 (1989)
Lee, J. S.: The Geology of China. London 1939.
Lee, J. S.: Quaternary glaciations in the Lushan area, central China. Memoirs of the Institute of Geology, Academia Sinica 2, 1–70 (1947)
Lehmkuhl, F.: Breitböden als glaziale Erosionsformen — Ein Bericht über Vergletscherungstypen im Qilian Shan und im Kunlun Shan (China). Zeitschrift für Gletscherkunde und Glazialgeologie 27/28, 51–62 (1991/92)
Lehmkuhl, F.; Rost, K. T.: Zur pleistozänen Vergletscherung Ostchinas und Nordosttibets. Petermanns Geographische Mitteilungen 137, 67–78 (1993)
Limprecht, W.: Botanische Reisen in den Hochgebirgen Chinas und Ost-Tibets. Repertorium specierum novarum regni vegetabilis, Beihefte 12 (1922).
Liu, K. B.: Quaternary History of the Temperate Forests of China. Quaternary Science Reviews 7, 1–20 (1988)
Liu, T. S. et al. (eds): Loess and environment. China Ocean Press, Beijing 1985.
Liu T. S.; Zhang, S. X.; Han, J. M.: Stratigraphy and Paleoenvironmental Changes in the Loess of Central China. Quaternary Science Reviews 5, 498–495 (1986)
Liu, Y. M.; Wang, J. H.; Chen, J. G.: On the Number of Times and Character of Glaciations in the Qinling Range. Bulletin Tianjin Institute Geology and Mineral Ressources 9, 87–98 (1984)
Peltzer, G.; Tapponnier, P.; Zhang Z. T.; Xu Z. Q.: Neogene and Quaternary Faulting in and along the Qinling Shan. Nature 317, 500–505 (1985)
Porter, S. C.; An, Z. S.; Zheng, H. B.: Cyclic Quaternary Alluviation and Terracing in a Nonglaciated Drainage Basin on the North Flank of the Qinling Shan, Central China. Quaternary Research 38, 157–169 (1992)
Pu, Q. Y.: Quaternary Glaciers in China. In: Zhang Z. H. (ed.): The Quaternary of China, pp. 240–273, China Ocean Press, Beijing, 1991.
Qi, C. H.; Gan, Z. M.; Xi, Z.; Zhao, G.; Chen, W.: Basic characteristics of the glacial landforms on the Mount Tai-bai and its near areas. Journal of Shaanxi Teachers University 4, 53–70 (1985)
Rost, K. T.: Geomorphologische Höhenstufen im Qinling Shan (VR China) unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der jungpleistozänen Vergletscherungen. Göttinger Geographische Abhandlungen 97 (1992)
Rost, K. T.: Die jungpleistozäne Vergletscherung des Qinling Shan (Provinz Shaanxi). Erdkunde 47, 131–142, (1993)
Rost, K. T.: Geomorphological investigations on former and recent glacial and periglacial features in central Qinling Shan (PR China). Journal of Xian College of Geology 16(2) (1994)
Rost, K. T.; Ma, Z. M.: Glacial Relics and its Survey in Taibai Shan (Shaanxi). In: Wang, W. Y. (ed.), Collected Papers of Survey and Draw, pp. 159–174, Xian Cartographical Publishing House, Xian 1991.
Shi, Y. F.: Glaciers and glacial geomorphology in China. Zeitschrift f. Geomorphologie N. F., Suppl.-Bd. 86, 51–63 (1992)
Sun, J. Z. et al. (eds.): Quaternary of Loess Plateau in China. Science Press, Beijing 1991.
Sun, T. C.: Beobachtungen von quartären Vereisungsspuren in der Volksrepublik China. Berichte d. Geologischen Gesellschaft i.d. DDR 6, 181–193 (1961)
Wang, G. Z.: A Sketch of Quaternary Glaciation in Eastern Qinling. Geology of Shaanxi 2, 47–62 (1984).
Wang, S. F.; Chen, M.; Duan, W.; Cao, Z. Y.: Demand of Quaternary Glaciation Relics in Lantian District, Shaanxi. In: Institute of Palaeontology, Academia Sinica (ed.), Reports on Neozoic Geology in Lantian Area, Shaanxi. Reports on a Conference (Nov. 1964), pp. 124–135. Science Press Publishing House, Beijing 1966.
Zhou, M. F.; Zhou, W. J.; Head, J.: Stratigraphy and 14C datings of Beizhuancun profile during the last 30,000 years. In: Liu Tungsheng (ed.), Loess, Quaternary Geology and Global Change Part I, pp. 12–19, Beijing 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rost, K.T. Paleoclimatic field studies in and along the Qinling Shan (Central China). GeoJournal 34, 107–120 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00813974
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00813974