Conclusions
-
1.
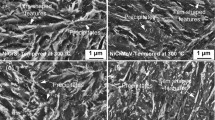
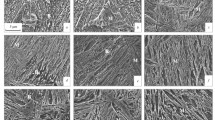
Low-carbon alloyed steels with a martensite structure differ from steels with a bainite structure (if they are compared at close values of σ0.2) by a considerably higher impact strength at test temperatures from +20 to −60°C. This is explained by a coarser bainite structure differentiation and formation of austenite-martensite islets during cooling from austenization temperatures in bainite steels.
-
2.
Of the investigated steels the 07Kh3GNM martensite class steel has the better properties; it requires no hardening in liquid media and has a packet structure of martensite in cross sections to 80 mm after cooling or austenization and cooling in air.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
M. A. Tylkin, V. I. Bol'shakov and P. D. Odesskii, Structure and Properties of Structural Steel [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1983).
F. B. Pickering, Physical Metallurgy and Processing of Steels [Russian translation], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1982).
Yoshiro Koyasu, Hiroshi Shinosaki, et al., "HSLA steel bar for hot forging and tempering," Nippon Steel Techn. Report, No. 30, 20–27 (1986).
G. V. Kudyumov, L. M. Ytevskii and R. I. Éntin, Transformation in Iron and Steel [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1977).
A. Yu. Kaletin, A. B. Kut'in, N. M. Gerbikh, et al., "Proloned High Tempering of 38KhN3MFA steel with bainite structure. 1. Carbide formation and structural transformations," Fiz. Met. Metalloved., No. 5, 915–921 (1986).
R. I. Éntin, L. I. Kogan, P. D. Odesskii, et al., "Strength properties of low-carbon martensitic 07Kh3GNM steel," Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Metally, No. 4, 86–90 (1982).
R. I. Éntin, L. M. Kleiner, L. I. Kogan and L. D. Pilkina, "Low-carbon martensitic steels," Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Metally, No. 3, 114–120 (1973).
L. I. Kogan, L. M. Kleiner and R. I. Éntin, "Special features of austenite transformation in a low-carbon alloyed steel," Fiz. Met. Metalloved.,41, No. 1, 118–124 (1976).
Additional information
I. P. Bardin Central Scientific-Research Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 6, pp. 31–33, June, 1991.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Éntin, R.I., Pankova, M.N., Uspenskaya, S.V. et al. Structure and properties of some low-carbon alloyed weldable steels. Met Sci Heat Treat 33, 463–466 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00775382
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00775382