Abstract
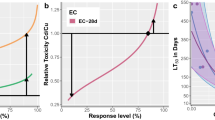
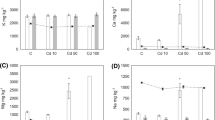
Chronic cadmium toxicity tests were carried out withChironomus riparius Meigen using a static-with-replacement exposure procedure. Significant reductions in larval development, survival and production were detected at 0.15 mg Cd l−1 a value approximately 5000 times lower than the 48 h LC50 for fourth instar larvae. The first instar appears to be the most critical stage in terms of sensitivity, with the number of adults eventually emerging reflecting first instar mortality. Male emergence was slightly delayed at 0.15 mg Cd l−1. The results of this study illustrate the importance of chronic toxicity tests in identifying sensitive life cycle stages and explaining pollutant-induced stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. L., C. T. Walbridge & J. J. Fiandt, 1980. Survival and growth of Tanytarsus dissimilis (Chironomidae) exposed to Copper, Cadmium, Zinc and Lead. Arch. Envir. Contam. Toxicol. 9: 329–335.
Beattie, J. H. & D. Pascoe, 1978. Cadmium uptake by rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri eggs and alevins. J. Fish. Biol. 13: 631–637.
Borgmann, U., O. Kramar & C. Loveridge, 1978. Rates of mortality, growth and biomass production ofLymnaea palustris during chronic exposure to lead. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 35: 1109–1115.
Credland, P. F., 1973. A new method for establishing a permanent laboratory culture of Chironomus riparius Meigen (Diptera: Chironomidae). Freshwat. Biol. 3: 45–51.
Derr, S. K. & M. J. Zabik, 1972. Biologically active compounds in the aquatic environment: The effect of DDE on the egg viability ofChironomus tentans. Bull. Envir. Contam. Toxicol. 7: 366–368.
Flannagan, J. F., 1974. Influence of trisodium nitrilotriacetate on the mortality, growth and fecundity of the freshwater snail (Helisoma trivolvis) through four generations. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 31: 155–161.
Gauss, J. D., P. E. Woods, R. W. Winner & J. H. Skillings, 1985. Acute toxicity of copper to three life stages ofChironomus tentans as affected by water hardness-alkalinity. Env. Pollut. (Ser A) 37: 149–157.
Holloway, M. T. P., 1983. Factors controlling the productivity of a benthic detritivore (Chironomus riparius). Unpublished PhD thesis, University of Wales Institute of Science and Technology.
Learner, M. A. & R. W. Edwards, 1966. The distribution of the midgeChironomus riparius in a polluted river system and its environs. Air. Water. Pollut. Int. J. 10: 757–768.
Macek, K. J., K. S. Buxton, S. K. Derr, J. W. Dean & S. Sauter, 1976. Chronic toxicity of lindane to selected aquatic invertebrates and fishes. US Environmental Protection Agency. Ecol. Res. Ser. EPA-600/3–76–046.
Marshall, J. S., 1978. Population dynamics ofDaphnia galeata mendotae as modified by chronic cadmium stress. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 35: 461–469.
Powlesland, C. & J. George, 1986. Acute and chronic toxicity of nickel to larvae ofChironomus riparius (Meigen). Env. Pollut. (Ser. A) 42: 47–64.
Thienemann, A., 1954.Chironomus. Leben, Verbreitung und wirtschaftliche Bedeutung der Chironomiden. Binnengewässer 20: 1–834.
Thornton, K. W. & J. L. Wilhm, 1975. The use of life tables in demonstrating the effects of pH, phenol and NaCl onChironomus attenuatus populations. Envir. Ent. 4: 325–328.
Wentsel, R., A. McIntosh & G. Atchison, 1977. Sublethal effects of heavy metal contaminated sediment on midge larvae (Chironomus tentans). Hydrobiologia 56: 153–156.
Wentsel, R., A. McIntosh & W. P. McCafferty, 1978. Emergence of the midgeChironomus tentans when exposed to heavy metal contaminated sediments. Hydrobiologia 57: 195–196.
Williams, K. A., 1981. Population Dynamics of Epiphytic Chironomid larvae in a Chalk Stream. Unpublished PhD thesis, University of Reading.
Williams, K. A., D. W. J. Green & D. Pascoe, 1984. Toxicity testing with freshwater macroinvertebrates: Methods and application in environmental management. In Pascoe, D. & Edwards, R. W. (eds) Freshwater Biological Monitoring. Advances in Water Pollution Control. Pergamon London: 81–91.
Williams, K. A., D. W. J. Green & D. Pascoe, 1985. Studies on the acute toxicity of pollutants to freshwater macroinvertebrates. 1 Cadmium. Arch. Hydrobiol. 102: 461–471.
Williams, K. A., D. W. J. Green, D. Pascoe & D. E. Gower, 1986. The acute toxicity of cadmium to different larval stages ofChironomus riparius (Diptera: Chironomidae) and its ecological significance for pollution control. Oecolog. 70: 362–366.
Williams, K. A., D. W. J. Green, D. Pascoe & D. E. Gower, 1987. Effect of cadmium on oviposition and egg viability inChironomus riparius (Diptera: Chironomidae). Bull. Envir. Contam. Toxicol. 38: 86–90.
Winner, R. W. & M. P. Farrell, 1976. Acute and chronic toxicity of copper to four species of Daphnia. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 33: 1685–1691.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pascoe, D., Williams, K.A. & Green, D.W.J. Chronic toxicity of cadmium toChironomus riparius Meigen — effects upon larval development and adult emergence. Hydrobiologia 175, 109–115 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00765121
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00765121