Abstract
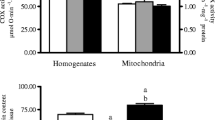
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) treatment of rats decreases gain of body weight without affecting food intake; simultaneously, the activities of liver malic enzyme and cytosolic glycerol-3-P dehydrogenase are increased. In the present study experiments were conducted to test the possibility that DHEA enhances thermogenesis and decreases metabolic efficiency via trans-hydrogenation of cytosolic NADPH into mitochondrial FADH2 with a consequent loss of energy as heat. The following results provide evidence which supports the proposed hypothesis: (a) the activities of cytosolic enzymes involved in NADPH production (malic enzyme, cytosolic isocitrate dehydrogenase, and aconitase) are increased after DHEA treatment; (b) cytosolic glycerol-3-P dehydrogenase may use both NAD+ and NADP+ as coenzymes; (c) activities of both cytosolic and mitochondrial forms of glycerol-3-P dehydrogenase are increased by DHEA treatment; (d) cytosol obtained from DHEA-treated rats synthesizes more glycerol-3-P during incubation with fructose-1,6-P2 (used as source of dihydroxyacetone phosphate) and NADP+; the addition of citratein vitro further increases this difference; (e) mitochondria prepared from DHEA-treated rats more rapidly consume glycerol-3-P added exogenously or formed endogenously in the cytosol in the presence of fructose-1,6-P2 and NADP+.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adinolfi, A., Guarriero-Bobyleva, V., Olezza, S., and Ruffo, A. (1971).Biochem. J. 15, 557–562.
Anfinsen, C. B. (1955).Methods Enzymol. 1, 695–698.
Beisenherz, G., Boltze, H. J., Bucher, T., Czok, R., Garbade, K. M., Meyer-Arendt, E., and Pfleiderer, G. (1953).Z. Naturforsch. 8B, 555–577.
Belli, M., Battelli, D., Fornieri, C., Mori, G., Muscatello, U., Lardy, H. A., and Bobyleva, V. (1992).J. Nutr. 122, 967–976.
Bergmeyer, H. U. (ed.) (1974).Methoden der Enzymatischen Analyse, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim/Bergstr.
Bobyleva-Guarriero, V., Ceccarelli-Stanzani, D., Masini, A., and Muscatello, U. (1982).J. Submicrosc. Cytol. 14, 461–470.
Borrebaek, B., Abraham, S., and Chaikoff, I. L. (1965).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 96, 237–247.
Casazza, J. P., Schaffer, W. T., and Veech, R. L. (1986).J. Nutr. 116, 304–310.
Cleary, M. P., Shepherd, A., Zisk, J., and Schwartz, A. G. (1983).Nutr. Behav. 1, 127–136.
Cleary, M. P., Shepherd, A., and Jenks, B. (1984).J. Nutr. 114, 1242–1251.
Cottam, G. L., Miller, B. C., and Matsunaga, A. M. (1989).J. Cell Biol. 107, 122a (abstract No 684).
Frenkel, R. A., Slaughter, C. A., Orth, K., Moomaw, C. R., Hicks S. H., Snyder, J. M., Bennet, M., Prough, R. A., Putnam, R. S., and Milewich, L. (1990).J. Steroid Biochem. 35, 333–342.
Gale, C. C. (1973).Annu. Rev. Physiol. 35, 391–430.
Gardner, R. S. (1974).Anal. Biochem. 59, 272–276.
Gerhard, M., and Lang, G. (1974). InMethoden der Enzymatischen Analyse (Bergmeyer, H. U., ed), Band II, Verlag Chemie, Weiheim/Bergstr, pp. 1460–1463.
Goglia, F., Liverini, G., Lanni, A., Iossa, S., and Barletta, A. (1988).Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 151, 1241–1249.
Gordon, G. B., Shantz, L. M., and Talalay, P. (1987).Adv. Enzyme Regul. 26, 355–382.
Guernsey, D. L., and Don Stevens, E. (1977).Science 196, 908–910.
Guernsey, D. L., and Edelman, I. S. (1983) InMolecular Basis of Thyroid Hormone Action (Oppenheimer, J. H., and Samuels, H. H., eds.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 293–324.
Kneer, N. M., Wagner, M. J., and Lardy, H. A. (1979).J. Biol. Chem. 254, 12160–12168.
Lardy, H. A., Paetkau, V., and Walter, P. (1965).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 53, 1410–1415.
Lardy, H. A., Su, C-Y., Kneer, N., and Wielgus, S. (1989). InHormones, Thermogenesis, and Obesity (Lardy, H. A., and Stratman, F. W., eds.), Elsevier, New York, pp. 415–426.
Launay, A. N., Michejda, I. W., and Vignais, P. V. (1974).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 347, 60–76.
Layne, E. (1957).Methods Enzymol. 3, 447–454.
Lee, Y-P., and Lardy, H. A. (1965).J. Biol. Chem. 240, 1427–1436.
Lee, Y-P., Takemori, A. E., and Lardy, H. A. (1959).J. Biol. Chem. 234, 3051–3054.
Leighton, B., Tagliaferro, A. R., and Newsholme, E. A. (1987).J. Nutr. 117, 1287–1290.
McIntosh, M. K., and Berdanier, C. D. (1991).J. Nutr. 121, 2037–2043.
Miller, B. C., Lau, H-W., Tyler, N. E., and Cottam, G. L. (1988).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 962, 25–36.
Mohn, R., and Berdanier, C. D. (1984).Nutr. Rep. Int. 30, 1255–1260.
Mohan, P. F., and Cleary, M. P. (1988).Am. J. Physiol. 255, E1-E8.
Mohan, P. F., and Cleary, M. P. (1989).J. Nutr. 119, 496–501.
Mohan, P. F., and Cleary, M. P. (1991).J. Nutr. 121, 240–250.
Mohan, P. F., Ihnen, J. S., Levin, B. E., and Cleary, M. P. (1990).J. Nutr. 120, 1103–1114.
Richert, D. A., and Westerfeld, W. W. (1970).Endocrinology 87, 1274–1281.
Rothwell, N. J., and Stock, M. J. (1988).J. Nutr. 118, 925–928.
Ruffo, A., and Adinolfi, A. (1963).Biochem. J. 89, 50P.
Shepherd, A., and Cleary, M. P. (1984).Am. J. Physiol. 248, E123-E129.
Su, C.-H. and Lardy, H. A. (1991).J. Biochem. 110, 207–213.
Tagliaferro, A., Davis, J. R., Truchon, S., and Van Hamont, N. (1986).J. Nutr. 116, 1977–1983.
Tepperman, H.M., and Tepperman, J. (1964) Am. J. Physiol. 206, 357–361.
Tepperman, H. M., De La Garza, S. A., and Tepperman, J. (1968).Am. J. Physiol. 214, 1126–1132.
Veech, R., Eggleston, L., and Krebs, H. (1969).Biochem. J. 115, 609–619.
Walsh, D. A., and Sallach, H. J. (1965).Biochemistry 4, 1076–1085.
Wernette, M. E., Ochs, R. S., and Lardy, H. A. (1981).J. Biol. Chem. 256, 12767–12771.
Yen, T. T., Allen, J. A., Pearson, D. V., Acton, J., and Greenberg, M. M. (1977).Lipids 12, 409–413.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bobyleva, V., Kneer, N., Bellei, M. et al. Concerning the mechanism of increased thermogenesis in rats treated with dehydroepiandrosterone. J Bioenerg Biomembr 25, 313–321 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00762592
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00762592