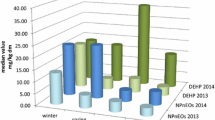
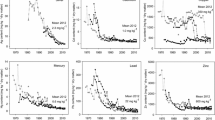
Abstract
The European Community is producing annually about 300 × 106 tons of sewage sludges as well as about 150, 950,160 and 200 tons of domestic, agricultural, industrial and other wastes (street litter, dead leaves etc.). About 20–25% of the German sewage sludges, which contain in average about 3.8,1.6, 0.4, 0.6, 5.3% DM−1 N, P, K, Mg and Ca, 202, 5, 131, 349, 53, 3 and 1446 mg kg−1 DM Pb, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Hg, Zn as well as ca. 37 and 5 mg kg−1 Dm polychlorinated hydrocarbons and biphenyls, are recycled annually as fertilizer. In addition environmental impacts on the arable land of Germany may derive from 76,19.2, 64.7, 33.6, 7.8 and 0.1 kg ha−1 a−1 of N, P, K, Ca, Mg and Cu added as animal manures. Besides heavy metals and hazardous organics pathogens are disseminated with organic wastes.
Crop production and soil fertility generally profit from the considerable amounts of plant nutrients and carbon in sewage sludges, animal slurries and manures, but the physicochemical soil properties, the composition of microbial, faunal and plant communities as well as the metabolic processes in the soil-, rhizo- and phyllosphere are changed by organic manuring. Consequences for the soil carbon-, nitrogen-and phosphorus-cycle are discussed. Impacts of heavy metals and hazardous organics on the soil biomass and its habitat as well as on transport mechanisms and surival times of disseminated pathogens in soils are reviewed with emphasis on the German situation. A proposal for future strategies (landscape recycling) is made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou Seada MNI and Ottow JCG (1988) Einfluß chemischer Bodeneigenschaften auf Ausmaß und Zusammensetzung der Denitrifikationsverluste drei verschiedener Bakterien. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 151: 109–115
Acea MJ and Carballas T (1988) The influence of cattle slurry on soil microbial population and nitrogen cycle micro-organisms. Biol Wastes 23: 229–241
Addiscott TM, Whitmore AP and Powlson DS (1991) Farming, fertilizers and the nitrate problem. CAB International, Wallingford, UK. 170 p
Aldag R (1991) Stickstoffverluste durch Ammoniakentbindun. In: Deutsche Landwirtschaftsgesellschaft (DLG, ed), Stoffeinträge aus der Landwirtschaft in die Atmosphäre, pp 67–75. Arbeitsunterlagen der DLG, Frankfurt.
ApSimon HM, Kruse M and Bell JNP (1987) Ammonia emissions and their role in acid deposition. Atmos Environ 21: 1939–1946
Arbeitskreis “Eutrophierung gestauter und frei fließender Gewässer” (1991) In: Hamm A (ed) Studie über Wirkungen und Qualitätsziele von Nährstoffen in Fließgewässern, pp 331–446, Academia-Verlag, Sankt Augustin.
Artiola JF and Pepper IL (1992) Denitrification in the root zone of a sludge-amended desert soil. Biol Fertil Soils 13: 200–205
Barriuso E, Baer U and Calvet A (1992) Dissolved organic matter and adsorption-desorption of Dimefuron, Atrazine, and Carbetamide by soils. J Environ Qual 21: 359–367
Bauchhenß J (1983) Die Bedeutung der Bodentiere für die Bodenfruchtbarkeit und die Auswirkung landwirtschaftlicher Maßnahmen auf die Bodenfauna. Kali-Briefe 16: 529–548
Becker R, Bach M und Frede H-G (1993) Stickstoffzufuhr aus organischer Düngung. In:Wendland F, Albert H, Bach M und Schmidt R (eds), Atlas zum Nitratstrom in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland, pp 82–83, Springer, Berlin.
Bellin CA and Rao PSC (1993) Impact of bacterial biomass on contaminant sorption and transport in a subsurface soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 59: 1813–1820
Benckiser G and Simarmata T (1993) Relationships between field-measured denitrification losses, CO2 formation, and diffusional constraints. Soil Biol Biochem
Benckiser G, Gaus G, Syring KM, Haider K and Sauerbeck D (1987) Denitrification losses from an Inceptisol field treated with mineral fertilizer or sewage sludge. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkund 150: 241–248
Benckiser G, Santiago S, Neue HU, Watanabe I and Ottow JCG (1984) Effect of fertilization on exudation, dehydrogenase activity, iron-reducing populations and Fe2+ formation in the rhizophere of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in relation to iron toxicity. Plant Soil 79: 305–316
Bender M and Conrad A (1992) Kinetics of CH4 oxidation in oxic soils exposed to ambient air or high CH4 mixing ratios. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 101: 261–270
Bernal MP and Kirchmann H (1992) Carbon and nitrogen mineralization and ammonia volatilization from fresh, aerobically and anaerobically treated pig manure during incubation with soil. Biol Fertil Soils 13: 135–141
Bingemer HG and Crutzen P (1987) The production of methane from solid wastes. Geophys Res 92: 2181–2187
BMFT (1992) Nitratumsatz unterhalb der Wurzelzone in einem landwirtschaftlich genutzten Trinkwassereinzugsgebiet. Endbericht des vom Bundesministerium für Forschung und Technologie (BMFT) geförderten Forschungsvorhaben 0339250. Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH (ed). 222 p
Born M, Dörr H and Levin I (1990) Methane consumption in aerated soils of the temperate zone. Tellus 42: 2–8
Bouwman AF (1990) Soils and the greenhouse effect, pp 25–167, Wiley and Sons, New York
Boyle M and Paul EA (1989a) Carbon and nitrogen mineralization kinetics in soil previously amended with sewage sludge. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53: 99–103
Boyle M and Paul EA (1989b) Nitrogen transformations in soil previously amended with sewage sludge. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53: 740–744
Carrington EG (1978) The contribution of sewage sludges to the dissemination of pathogenic micro-organisms in the environment. Techn. Report 71, Water Research Center, Medmenham Laboratory, Medmenham, Great Britain. 31p
Chander K and Brookes PC (1991) Plant inputs of carbon to metal-contaminated soil and effects on the soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem 23: 1169–1177
Chaudri AM, McGrath SP and Giller KE (1992) Metal tolerance of isolates ofRhizobium leguminosarum BiovarTrifolii from soil contaminated by past applications of sewage sludges. Soil Biol Biochem 24: 83–88
Collins YE and Stotzky G (1992) Heavy metals alter the electrokinetic properties of bacteria yeasts and clay minerals. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 1592–1600
Comfort SD, Kelling KA, Keeney DR and Converse JC (1990) Nitrous oxide production from injected liquid dairy manure. Soil Sci Soc Am J 54: 421–427
Conrad R (1987) Der Kreislauf des Methans - Grundlagen und Bedeutung. Forum Mikrobiol 9: 320–329
Costa F, Moreno JI, Hernandez T, Lax A, Cegarra J and Roig A (1989) Mineralization of organic materials in a calcareous soil. Biol Wastes 28: 189–201
Crill PM, Harrisson RC and Bartlett KB (1991) Methane fluxes from terrestrial wetland environments. In: Rogers JE and Whitman WB (eds), Microbial production and consumption of greenhouse gases: methane, nitrogen oxides, and halomethanes. pp 7–38, Am Soc Microbiol, Washington DC
Daniel P, Opitz von Boberfeld W, Obermüler P, Benckiser G und Ottow JCG (1993) Einfluß von Gülledüngung auf Mikroflora, Gäreigenschaften, Gärqualität und Futterwert von Deutschem Weidelgras (Lolium perenne L.). VDLUFA-Schriftenreihe 37, 465–468
Dias S, Grime JP and McPherson E (1993) Evidence of a feedback mechanism limiting plant response to elevated carbon dioxide. Nature 364: 616–617
Dindal DL (1990) Soil biology guide. Wiley, New York. 1349 p
Doelman P, Haanstra, H, Loonen H and Vos A (1990) Decomposition ofα- andβ-hexachlorocyclohexane in soil under field conditions in a temperate climate. Soil Biol Biochem 22: 629–634
Douglas BF and Magdoff FR (1991) An evaluation of nitrogen mineralization indices for organic residues. J Environ Qual 20: 368–372
Driel W van and Smilde KW (1990) Micronutrients and heavy metals in Dutch agriculture. Fertil Res 25: 115–126
Ehrlich HL (1993) Mineralization of organic carbon under anaerobic conditions. In: Bollag JM and Stotzky G (eds), Soil Biochemistry Volume 8, pp 341–407, Marcel Dekker, New York
Eichner MJ (1990) Nitrous oxide emissions from fertilized soils: summary of available data. J Environ Qual 19: 272–280
Elsas JD van, Trevors JT and Overbeek LS van (1991) Influence of soil properties on the vertical movement of genetically-markedPseudomonas fluorescens through large soil microcosms. Biol Fertil Soils 10: 249–255
Fließbach A und Reber H (1991) Auswirkungen einer langjährigen Zufuhr von Klärschlamm auf Bodenmikroorganismen und ihre Leistungen. In: Sauerbeck D und Lübben S (eds) Berichte aus der ökologischen Forschung (Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH), Band 6 “Auswirkungen von Siedlungsabfällen auf Böden, Bodenorganismen und Pflanzen”, pp 327–359
Focht DD (1993) Microbial degradation of chlorinated biphenyls. In: Bollag JM and Stotzky G (eds), Soil Biochemistry Volume 8, pp 341–407. Marcel Dekker, New York
Folorunso CA and Rolston DE (1984) Spatial variability of field-measured denitrification gas fluxes. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48: 1214–1219
Frank V, Tamova G and Takacsova (1993) Effects of cadmium and mercury on growth and differentiation ofTrichoderma viride. Zentralbl Mikrobiol 148: 229–232
Fu MH and Tabatabai MA (1989) Nitrate reductase activity in soils: effects of trace elements. Soil Biol Biochem 21: 943–946
Führ F (1991) Stofftransporte in Böden. Mitt Dtsch Bodenkundl Ges 63: 27–30
Gannon JT, Mingelgrin U, Alexander M and Wagenet RJ (1991) Bacterial transport through homogeneous soil. Soil Biol Biochem 23: 1155–1160
Gannon JT, Manilal VB and Alexander M (1991) Relationship between cell surface properties and transport of bacteria through soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 57: 190–193
Green M (1980) Cytokinin production by microorganisms. Bot Rev 46: 25–74
Guo L, Bicki, TJ, Felsot AS and Hinesly TD (1991) Phytotoxicity of atrazine and alachlor in soil amended with sludge, manure and activated carbon. J Environ Sci. Health 26: 513–527
Haimi J, Salminen J, Huhta V, Knuutinen J and Palm H (1992) Bioaccumulation of organochlorine compounds in earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 24: 1699–1703
Hansen S, Mehlum JE and Bakken LR (1993) N2O and CH4 fluxes in soil influenced by fertilization and tractor traffic. Soil Biol Biochem 25, 621–630
Hiller DA und Brümmer G W (1991) Mikrosondenuntersuchung zur Bestimmung von Bindungsformen von Schwermetallen in Böden. In: Sauerbeck D und Lübben S (eds) Berichte aus der ökologischen Forschung (Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH), Band 6 “Auswirkungen von SiedIungsabfällen auf Böden, Bodenorganismen und Pflanzen”. pp 34–61
Hooda PS and Alloway BJ (1993) Effects of time and temperature on the bioavailability of Cd and Pb from sludgeamended soils. J Soil Sci 44: 97–110
Hue NV (1992) Correcting soil acidity of a highly weathered Ultisol with chicken manure and sewage sludge. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 23: 241–264
Hurst CJ, Gerba CP and Cech J (1980) Effects of environmental variables and soil characteristics on virus survival in soil. App Environ Microbiol 40: 1067–1079
Hütsch B and Webster CP (1993) Effect of nitrogen fertilization on methane oxidation in the Broadbalk Wheat experiment. Mitt Dtsch Bodenkundl Ges 69: 227–230
Huysman F and Verstraete W (1993) Water faciliated transport of bacteria in unsaturated soil columns: influence of cell surface hydrophobicity and soil properties. Soil Biol Biochem 25: 83–90
Isermann K (1990a) Die Stickstoff- und Phosphoreinträge in die Oberflächengewässer der Bundesrepublik Deutschland durch verschiedene Wirtschaftsbereiche unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Stickstoff- und Phosphorbilanz der Landwirtschaft und der Humanernährung. Schriftenr Akad Tiergesundheit 1: 358–413
Isermann K (1990b) Share of agriculture in nitrogen and phosphorus emissions into the surface waters of Western Europe against the background of their eutrophication. Fertil Res 26: 253–269
Isermann K (1993) Territorial, continental and global aspects of C, N, P and S emissions from agricultural ecosystems. In: Wollast R, Mackenzie FT and Chou L (eds) NATO ASI Series 14, Interactions of C, N, P and S biogeochemical cycles and global change, pp 79–121, Springer-Verlag Heidelberg.
Jones KS, Stratford JA, Waterhouse KS, Turlong ET, Giger W, Hites RA, Schaffner C and Johnston AE (1989) Increases in the polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons content of an agricultural soil over the last century. Environ Sci Technol 23: 95–101
Joshi DK and Gold MH (1993) Degradation of 2,4,5,-Trichlorophenol by the lignin-degrading basidiomycetePhanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 59: 1779–1785
Kausik CP (1991) Persistence and metabolism of HCH and DDT in soil under subtropical conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 23: 131–134
Kautenburger R und Müller P (1993) Polyzyklische aromatische Kohlenwasserstoffe auf Pappelblättern (Populus nigra “Italica”) im Stadtgebiet von Bonn. Forum Städte-Hyg 44: 22–27
Kick H (1984) Anforderungen des Landbaus an die Beschaffenheit der Abwasserklärschlämme. Gewässerschutz-Wasser-Abwasser 65: 9–31
Kiehl JT and Dickinson RE (1987) A study on the radiative effects of enhanced CO2 and CH4 on early earth surface temperatures. J Geophys Res 92: 2991–2998
Kirchmann H and Lundvall A (1993) Relationship between N immobilization and volatile fatty acids after application of pig and cattle slurry. Biol Fertil Soils 15: 161–164
Ko WH and Lockwood JL (1968) Accumulation and concentration of chlorinated hydrocarbon pesticides by microorganisms in soil. Can J Microbiol 14: 1075–1078
Körner R, Benckiser G und Ottow JCG (1993) Quantifizierung der Lachgas (N2O)-Freisetzung aus Kläranlagen unterschiedlicher Verfahrensführung. Korresp Abw 40: 514–525
Kula H and Kokta C (1992) Side effects of selected pesticides on earthworms under laboratory and field conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 24: 1711–1714
Krämer M, Baumgärtner M, Bender M and Conrad R (1990) Consumption of NO by methanotrophic bacteria in pure culture and in soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73: 345–350
Kuntze H (1991) Böden als Produktions- und Lebensräume. Mitt Dtsch Bodenkundl Ges 63: 9–17
Klärschlammverordnung (1992) In: Hösel G. und Freiherr H, von Lersner (eds) Berlin, Recht der Abfallbeseitigung; Erich Schmitt Verlag.
Kutschera L and Sobotik M (1981) Gülleflora - Unterschiede durch Klima und Boden. In: Bericht über die 7. Arbeitstagung “Fragen der Güllerei” Bundesversuchsanstalt für alpenländische Landwirtschaft (ed). Gumpenstein, Austria
Lambert DH and Weidensaul TC (1991) Element uptake by mycorrhizal soybean from sewage-sludge-treated soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55: 393–398
Lampkin N (1990) Organic farming. Farming Press Books, Ipswich. 763 p
Lee RB (1977) Effects of organic acids on the loss of ions from barley roots. J Exp Bot 28: 578–587
Lehmann DL and Wallis PM (1982) Literature review -occurrence and survival of pathogenic bacteria in sludge and on soil. In: Wallis PM and Lehmann DL (eds) Biological hazards associated with the terrestrial disposal of sewage sludge in cold climates. Kananaskis Centre of Environ Res, Univ of Calgary, Biosci 100: 115–145
Leschber R (1991) Organohalogen compounds in sewage sludges and their determination as cumulative parameters. Intern J Environ Anal Chem 44: 233–241
Lockyer DR and Whitehead DC (1990) Volatilization of ammonia from cattle urine applied to grassland. Soil Biol Biochem 22: 1137–1142
Lorenz SE, McGrath SP and Giller KE (1992) Assessment of free-living nitrogen fixation activity as a biological indicator of heavy metal toxicity in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 24: 601–606
Lovely DR, Phillips EJP and Caccavo F (1992) Acetate oxidation by dissimilatory Fe (II) reducers. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 3205–3208
Madariaga GM and Angle JS (1992) Sludge-borne salt effects on survival ofBradyrhizobium japonicum. J Environ Qual 21: 276–280
Madsen T and Licht D (1992) Isolation and characterization of an anaerobic chlorophenol transforming bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 2874–2878
Makeschin F (1990) Die Regenwurmfauna forstlich und landwirtschaftlich genutzter Böden und deren Beeinflussung durch Düngung. Kali-Briefe 20: 49–63
Marschner H (1986) Mineral nutrition in higher plants. Academic press, London. 674 p
Martens DA, Johanson JB and Frankenberger WT (1992) Production and persistence of soil enzymes with repeated addition of organic residues. Soil Sci 153: 53–61
Mbagwu JSC and Piccolo A (1990) Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in aggregates of organic waste-amended soils. Biol Wastes 31: 97–111
Megraw SR and Knowles R (1987a) Active methanotrophs suppress nitrification in a humisol. Biol Fertil Soils 4: 205–212
Megraw SR and Knowles R (1987b) Methane production and consumption in a cultivated humisol. Biol Fertil Soils 5: 56–60
Mehnert DU and Stewien KE (1993) Detection and distribution of Rotavirus in raw sewage and creeks in Soa Paulo, Brazil. Appl Environ Microbiol 59: 140–143
Mehrer I and Mohr H (1989) Ammoniumtoxicity: description of the syndrome inSinapis alba and the search for its causation. Physiol Plant 77: 545–550
Mohr H (1990) Der Stickstoff - ein kritisches Element der Biossphäre. In: Sitzungsberichte der Heidelberger Akademie der Wissenschaften, Mathematischnaturwissenschaftliche Klasse, 5. Abhandlung, Springer, Heidelberg, pp 296–330
Morgan JE and Morgan AJ (1992) Heavy metal concentrations in the tissues, ingesta and faeces of ecophysiologically different earthworm species. Soil Biol Biochem 24: 1691–1697
Müller U, Hennings V und Horn A (1991) Untersuchungen zur PCB- und Dioxinverbreitung in Böden. Mitt Dtsch Bodenk Gesellsch 66: 365–368
Munch JC und Dominik HP (1991) Verhalten und Versickerung von fäkalen Organismen nach Gülleausbringung auf typische Böden des Langenauer Donaurieds. VDLUFA-Schriftenreihe 33: 613–618
Munch JC und Ottow JCG (1977) Modelluntersuchungen zum Mechanismus der bakteriellen Eisenreduktion in hydromorphen Böden. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 140: 549–562
Nieto KF and Frankenberger WT (1990) Microbial production of cytokinins. In: Bollag JM and Stotzky G (eds) Soil Biochemistry Vol. 6, Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 191–245
Neetson JJ and Wadman WP (1990) Ammonia volatization and nitrate leaching after animal manure to agricultural crops. Proc. Sixth Int. Symp. Agric. Food Process Wastes Am. Soc. Agric. Eng., Chicago. pp 327–334
Nüßlein K, Maris D, Timmis K and Dwyer DF (1992) Expression and transfer of engineered catabolic pathways harbored byPseudomonas spp. introduced into activated sludge microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 3380–3386
Oppermann MH, Cherrett CP, Wood M and Harris PJ (1989) Responses of soil micro-organisms to the addition of cattle slurry. In: Hansen JAA and Henriksen K (eds). Nitrogen in organic wastes applied to soils, Academic Press, London. pp 47–58
Oppermann MH, Wood M, Harris PJ and Cherrett CP (1993) Nematode and nitrate dynamics in soils treated with cattle slurry. Soil Biol Biochem 25: 19–24
Ottow JCG (1985) Einfluß von Pflanzenschutzmitteln auf die Mikroflora von Böden. Naturw Rundsch 38: 181–189
Ottow JCG (1990) Bedeutung des Abbaus chemischorganischer Stoffe in Böden. Techn Lab 1: 91–97
Ottow JCG (1994) Abbaukinetik und Persitenz von Fremdstoffen in Böden. In: Ottow und Bidlingsmaier (eds), Umweltbiotechnologie, Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart (In press)
Pain BF, Thompson RB, Rees YJ and Skinner JH (1990) Reducing gaseous losses of nitrogen from cattle slurry applied to grassland by use of additives. J Sci Food Agric 50: 141–153
Pastene AJ and Corey RB (1980) Forms and availibility of phosphorous in sewage sludge amended soil. In: Proc. Ann. Conf. Appl. Res. Pract. Munic. Ind. Waste, 3rd, Madison, WI. 10–12 Sept. 1980. Univ; of Wis Ext., Madison. pp 163–74
Paterson E, Kemp JS, Gammack SM, FitzPatrick EA, Cresser MS, Mullins CE and Killham K (1993) Leaching of genetically modifiedPseudomonas fiuorescens through intact soil microcosms: Influence of soil type. Biol Fertil Soils 15: 308–314
Patrick ZA (1971) Phytotoxic substances associated with the decomposition in soil of plant residues. Soil Sci 111: 13–18
Paul JW and Beauchamp EG (1989) Biochemical changes in soil beneath dairy cattle slurry layer: The effect of volatile fatty acid oxidation on denitrification and soil pH. In: Hansen JAA and Henriksen K (eds). Nitrogen in organic wastes applied to soils, Academic Press, London. pp 261–270
Philipp W, Gresser R, Michels E und Strauch D (1990) Vorkommen von Salmonellen in Gülle, Jauche und Stallmist landwirtschaftlicher Betriebe in einem Wasserschutzgebiet. Forum Städte-Hyg 41: 209–212
Pietz RI, Peterson JR, Prater JE and Zenz DR (1984) Metal concentrations in earthworms from sewage sludgeamended soils at a strip mine reclamation site. J Environ Qual 13: 651–654
Reber HH (1992) Simultanous estimates of the diversity and the degradative capability of heavy-metal affected soil bacterial communities. Biol Fertil Soils 13: 181–186
Recous S, Mary B and Faurie G (1990) Microbial immobilization of ammonium and nitrate in cultivated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 22: 913–922
Reinsch K, Gülden A, Deneke J und Zaiß U (1989) Untersuchungen zur Elimination von Salmonellen und Fäkalindikatoren bei der Klärschlammbehandlung. Forum Städte-Hyg 40: 364–367
Romanowski G, Lorenz MG, Sayler G and Wackernagel G (1992) Persistence of free plasmid DNA in soil monitored by various methods, including a transformation assay. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 3012–3019
Russell TH, Knight IT, Anikis MS and Colwell RR (1993) Benthic distribution of sewage sludge indicated byClostridium perfringens at a deep-ocean dump site. Appl Environ Microbiol 59: 47–51
Sauerbeck D and Lübben S (1991) Auswirkungen von Siedlungsabfällen auf Böden, Bodenorganismen und Pflanzen. In: Berichte aus Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH (ed) Zentralbibliothek, Jülich. 416 p
Sawyer JE and Hoeft RG (1990) Greenhouse evaluation of simulated injected liquid beef manure. Agron J 82: 613–618
Sawyer JE, Schmitt MA and Hoeft RG (1990) lnorganic nitrogen distribution and soil chemical transformations associated with injected liquid beef manure. Agron J 82: 963–969
Schäffer A (1993) Pesticide effects on enzyme activities in the soil ecosystem. In: Bollag JM and Stotzky G (eds), Soil Biochemistry Volume 8, Marcel Dekker, New York. pp 341–407
Schechtner H (1981) Nährstoffwirkung und Sonderwirkungen der Gülle auf dem Günland. In: Bericht über die 7. Arbeitstagung “Fragen der Güllerei” Bundesversuchsanstalt für alpenländische Landwirtschaft (ed) Gumpenstein, Austria
Schilke-Gartley KL and Sims JT (1993) Ammonia volatilization from poultry manure-amended soil. Biol Fertil Soils 16: 5–10
Schipper LA, Dyck WJ, Barton PG and Hodgkiss PD (1989) Nitrogen renovation by denitrification in forest sewage irrigation systems. Biol Wastes 29: 181–187
Schröder J (1992) Legislation on animal manure in Europe. Meststoffen 14: 69–74
Schulten H R and Leinweber P (1991) Influence of longterm fertilization with farmyard manure on soil organic matter: Characteristics of particle-size fractions. Biol Fertil Soils 12: 81–88
Schuster E and Schröder D (1990) Side effects of sequentially-applied pesticides on nontarget soil microorganisms: Field experiments. Soil Biol Biochem 22: 367–373
Serna M D and Pomares F (1991) Comparison of biological and chemical methods to predict nitrogen mineralization in animal wastes. Biol Fertil Soils 12: 89–94
Serna M D and Pomares F (1992) Nitrogen mineralization of sludge-amended soil. Bioresource Tech 39: 285–290
Sharp R, O'Donnell AG, Gilbert HG and Hazelwood GP (1992) Growth and survival of genetically manipulatedLactobacillus plantarum in silage. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 2517–2522
Srikanth S and Reddy SRP (1991) Lead, cadmium and chromium levels in vegetables grown in urban sewage sludge - Hyderabad, India. Food Chem 40: 229–234
Srikumar TS and Ockerman PA (1990) The effect of fertilization and manuring on the content of some nutrients in potatoes (var Provita). Food Chem 37: 47–53
Steudler PA, Bowden LO, Melille SM and Aker JD (1989). Influence of nitrogen fertilization on methane uptake in temperate forest soils. Nature 341: 314–316
Stevenson FJ (1982) Humus chemistry. Wiley, New York pp 55–92
Stevens RJ and Cornforth IS (1974) The effect of pig slurry applied to a soil surface on the composition of the soil atmosphere. J Sci Food Agr 25: 1263–1272
Straub TM, Pepper IL and Gerba CP (1992) Persistence of viruses in desert soils amended with anaerobically digested sewage sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 636–641
Tebaay RH, Welp G and Brümmer G W (1991) Gehalte an polycyclischen aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffen in Böden unterschiedlicher Belastung. Mitt Dtsch Bodenk Gesellsch 63: 157–160
Thauer RK, Jungermann K and Decker K (1977) Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bact Rev 41: 100–180
Thompson RB and Pain BF (1989) Denitrification from cattle slurry applied to grassland. In: Hansen JAA and Henriksen K (eds). Nitrogen in organic wastes applied to soils, Academic Press, London. pp 247–260
Trösch W (1993) Bereitstellung von Energie und Massenrohstoffen für eine den stationären, biogenen Stoffkreisläufen nachempfundene, umweltkompatible Stoffwirtschaft. Eine Herausforderung für die Biotechnik. Bio-Eng 9: 20–28
Tunney H, Molloy S and Codd F (1980) Effects of cattle slurry, pig slurry and fertiliser on yield and quality of grass silage. In: Grasser JKR, Hawkins JC, O'Callaghan JR and Pain BF (eds), Effluents from livestock, Appl. Sci. Publ., London. pp 28–37
Tsai YL, Palmer CJ and Sangermano LR (1993) Detection ofEscherichia coli in sewage and sludge by polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol 59: 353–357
Tyler SC (1991) The global methane budget. In: Rogers JE and Whitman WB (eds) Microbiol production and consumption of greenhouse gases: methane, nitrogen oxides, and halomethanes pp 7–38. Am Soc. Microbiol., Washington DC.
Tyler G, Balsberg PM, Bengtsson G, Baath E and Tranvik L (1989) Heavy metal ecology of terrestrial plants, microorganisms and invertebrates. A review. Water Air Soil Pollut 47: 189–216
Umweltbundesamt (1992) Daten zu Umwelt 1990/1991. Erich Schmidt Verlag, Berlin. 675 p
Unken R (1987) Nähr- und Schadstoffgehalte in Klär- und Flußschlämmen, Müll und Müllkomposten - Datensammlung und Bewertung - VDLUFA-Projekt 1985. VDLUFA-Schriftenreihe 22. 95p
Unwin RJ, Pain BF and Whinham WN (1986) The effect of rate and time of application of nitrogen in cow slurry on grass cut for silage. Agric Wastes: 253–268
Vandevivere P and Baveye P (1992) Relationship between transport of bacteria and their clogging efficiency in sand columns. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 2523–2530
Varadarajan K, Paliwal K, Rajamanickam C, Manickaval K, Jeyapaul G and Logasundari S (1991) Impact of sewage disposal on the hematological and biochemical parameters of dairy cows. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 47: 653–659
VDLUFA (1990) Datensammlung und statistische Auswertung über Gehalte an chlorierten Kohlenwasserstoffen und polychlorierten Biphenylen in Klärschlämmen, Böden, Pflanzen und tierischen Produkten. VDLUFA-Schrifetnreihe 31. 243 p
Verhagen FJM and Laanbroek HJ (1992) Effects of grazing flagellates on competition for ammonium between nitrifying and heterotrophic bacteria in chemostats. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 1962–1969
Vetter und Steffens (1986) Wirtschaftseigene Düngung. Verlagsunion Agrar, Frankfurt Main. 235 p
Vivekanandan M and Fixen PE (1990) Effect of large manure applications on soil P intensity. Commun Soil Plant Anal 21: 287–293
Walsh JL, Valentine GE and Ross CC (1991) Agricultural wastes. Res J WPCF 66: 452–458
Weiss B and Larink O (1991) Influence of sewage sludge and heavy metals on nematodes in an arable soil. Biol Fertil Soils 12: 5–9
Whitehead DC and Raistrick N (1991) Effects of some environmental factors on ammonia volatilization from simulated livestock urine applied to soil. Biol Fertil Soils 11: 279–284
Wild SR and Jones KC (1992) Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon uptake by carrots grown in sludge-amended soil. J Environ Qual 21: 217–225
Wild SR, Berrow ML, McGrath SP and Jones K C (1992) Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in crops from longterm field experiments amended with sewage sludge. Environ Pollut 76: 25–32
Woldendorp JW and Laanbroek HJ (1989) Activity of nitrifiers in relation to nitrogen nutrition of plants in natural ecosystems. Plant Soil 115: 217–228
Wong MFT, Wild A and Juo ASR (1987) Retarded leaching of nitrate measured in monolith lysimeters in south-east Nigeria. J Soil Sci 38: 511–518
Yokoyama K, Kai H and Tsuchyama H (1991) Paracoprid dung beetles and gaseous loss of nitrogen from cow dung. Soil Biol Biochem 23: 643–647
Yates MV and Ouyang Y (1992) VIRTUS, a model of virus transport in unsaturated soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 1609–1616
Young CS and Burns RG (1993) Survival and activity of bacteria added to soil. In: Bollag JM and Stotzky G (eds). Soil Biochemistry Volume 8, Marcel Dekker, New York. pp 341–407
Zeien H und Brümmer G W (1991) Chemische Extraktion zur Bestimmung von Bindungsformen von Schwermetallen in Böden. In: Sauerbeck D und Lübben S (eds). Berichte aus der ökologischen Forschung (Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH), Band 6 “Auswirkungen von Siedlungsabfällen auf Böden, Bodenorganismen und Pflanzen” pp 62–91
Zusammenfassender Endbericht zum BMFT-Forschungsvorhaben 0339250 (1992) Nitratumsatz unterhalb der Wurzelzone in einem landwirtschaftlich genutzten Trinkwassereinzugsgebiet. Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH (ed) 222p
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benckiser, G., Simarmata, T. Environmental impact of fertilizing soils by using sewage and animal wastes. Fertilizer Research 37, 1–22 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00750669
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00750669