Abstract
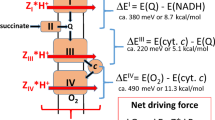
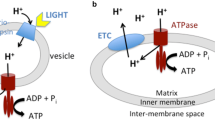
A minimum model of adenine nucleotide exchange through the inner membrane of mitochondria is presented. The model is based on a sequential mechanism, which presumes ternary complexes formed by binding of metabolites from both sides of the membrane. The model explains the asymmetric kinetics of ADP-ATP exchange as a consequence of its electrogenic character. In energized mitochondria, a part of the membrane potential suppresses the binding of extramitochondrial ATP in competition with ADP. The remaining part of the potential difference inhibits the back exchange of internal ADP for external ATP. The assumption of particular energy-dependent conformational states of the translocator is not necessary. The model is not only compatible with the kinetic properties reported in the literature about the adenine nucleotide exchange, but it also correctly describes the response of mitochondrial respiration to the extramitochondrial ATP/ADP ratio under different conditions. The model computations reveal that the translocation step requires some loss of free energy as driving force. The size of the driving force depends on the flux rate as well as on the extra- and intramitochondrial ATP/ADP quotients. By both quotients the translocator controls the export of ATP formed by oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böhme, G., Hartung, K. J., and Kunz, W. (1978). InBioenergetics at Mitochondrial and Cellular Levels (Wojtczak, L., Lenartowicz, E., and Zborowski, J., eds.), Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Warsaw, pp. 79–102.
Bohnensack, R. (1981).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 634 203–218.
Cleland, W. W. (1963).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 67 104–137.
Davis, E. J., and Davis-van-Thienen, W. F. A. (1978).Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 83 1260–1266.
Duyckaerts, C., Sluse-Goffart, C. M., Fux, J.-P., Sluse, F. E., and Liebecq, C. (1980).Eur. J. Biochem. 106 1–6.
Erecinska, M., Kula, T., and Wilson, D. F. (1978).FEBS Lett. 87 139–144.
Klingenberg, M. (1970). InEssays in Biochemistry (Campbell, S. N., and Dickens, F., eds.), Vol. 6, Academic Press, New York, pp. 120–159.
Klingenberg, M. (1972). InMitochondria/Biomembranes (Van den Berg, S. G., Borst, F., Van Deenen, L. L. M., Riemersma, J. C., Slater, E. C., and Tager, J. M., eds.), North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp. 147–162.
Klingenberg, M. (1979).Trends Biochem. Sci. 4 249–252.
Klingenberg, M. (1980).J. Membr. Biol. 56 97–105.
Klingenberg, M., and Rottenberg, H. (1977).Eur. J. Biochem. 73 126–130.
Krämer, R., and Klingenberg, M. (1980a).Biochemistry 19 556–560.
Krämer, R., and Klingenberg, M. (1980b). First European Bioenergetics Conference, Short Reports, Patron Editore, Bologna, pp. 271–272.
Kunz, W., Bohnensack, R., Böhme, G., Küster, U., Letko, G., and Schönfeld, P. (1981).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 209 219–229.
Kunz, W., Bohnensack, R., Küster, U., Letko, G., and Schönfeld, P. (1979). InFunctions and Molecular Aspects of Biomembranes (Quagliariello, E., Palmieri, F., Papa, S., and Klingenberg, M., eds.) Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp. 313–316.
Küster, U., Letko, G., Kunz, W., Duszynski, J., Bogucka, K., and Wojtczak, L. (1981).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 636 32–38.
La Noue, K., Mizani, S. M., and Klingenberg, M. (1978).J. Biol. Chem. 253 191–198.
Letko, G., and Küster, U. (1979).Acta Biol. Med. Germ. 38 1379–1385.
Pfaff, E., Heldt, H. W., and Klingenberg, M. (1969).Eur. J. Biochem. 10 484–493.
Souverijn, J. H. M., Huisman, L. A., Rosing, J., and Kemp, A., Jr. (1973).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 305 185–198.
Stubbs, M., Vignais, P. V., and Krebs, H. A. (1978).Biochem. J. 172 333–342.
Van der Meer, R., Akerboom, T. P. M., Groen, A. K., and Tager, J. M. (1978).Eur. J. Biochem. 84 421–428.
Vignais, P. V. (1976).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 456 1–38.
Vignais, P. V., Vignais, P. M., and Doussiére, J. (1975).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 376 219–230.
Vignais, P. V., Vignais, P. M., Lauquin, G., and Morel, F. (1973).Biochemie 55 763–778.
Villiers, C., Michejda, J. W., Block, M., Lauquin, G. J. M., and Vignais, P. V. (1979).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 546 157–170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bohnensack, R. The role of the adenine nucleotide translocator in oxidative phosphorylation. A theoretical investigation on the basis of a comprehensive rate law of the translocator. J Bioenerg Biomembr 14, 45–61 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00744078
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00744078