Abstract
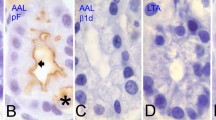
Using immunochemical and immunohistochemical methods, the binding site ofAnguilla anguilla agglutinin (AAA) was characterized and compared with the related fucose-specific lectin fromUlex europaeus (UEA-I). In solid-phase enzyme-linked immunoassays, the two lectins recognized Fucα1-2Galβ-HSA. AAA additionally cross-reacted with neoglycolipids bearing lacto-N-fucopentaose (LNFP) I [H type 1] and II [Lea] and lactodifucotetraose (LDFT) as glycan moieties. UEA-I, on the other hand, bound to a LDFT-derived neoglycolipid but not to the other neoglycolipids tested. Binding of AAA to gastric mucin was competitively neutralized by Lea-specific monoclonal antibodies. UEA-I binding, on the other hand, was reduced after co-incubation with H type 2- and Ley-specific monoclonal antibodies. According to our results, AAA reacts with fucosylated type 1 chain antigens, whereas UEA-I binds only to the α1-2-fucosylated LDFT-derived neoglycolipid. In immunohistochemical studies, the reactivity of AAA and UEA-I in normal pyloric mucosa from individuals with known Lewis and secretor status was analysed. AAA showed a broad reaction in the superficial pyloric mucosa from secretors and non-secretors, but AAA reactivity was more pronounced in Le(a+b-) individuals. On the other hand, UEA-I stained the superficial pyloric mucosa only from secretor individuals. A staining of deep mucous glands by the lectins was found in all specimens. Both reacted with most human carcinomas of different origin. Slight differences in their binding pattern were observed and may be explained by the different fine-specificities of the lectins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liener IE, Sharon N, Goldstein IJ (1986)The Lectins. Orlando: Academic Press.
Damjanov I (1987)Lab Invest 57: 5–20.
Walker RA (1989)Path Res Pract 185: 826–35.
Watkins WM, Morgan WTJ (1952)Nature 169: 825–26.
Springer GF, Desai PR, Kolecki BJ (1964)Biochemistry 3: 1076–85.
Springer GF, Desai PR (1970)Vox Sang 18: 551–54.
Springer GF, Desai PR (1971)Biochemistry 10: 3749–61.
Baldo BA, Uhlenbruck G (1973)Immunology 25: 649–61.
Cazal P, Lalaurie M (1952)Acta Haematol 8: 73–80.
Matsumoto I, Osawa T (1969)Biochim Biophys Acta 194: 180–89.
Pereira MEA, Kisailus EC, Gruezo F, Kabat EA (1978)Arch Biochem Biophys 185: 108–15.
Hindsgaul O, Norberg T, LePendu J, Lemieux RU (1982)Carbohydrate Res 109: 109–42.
Pereira MEA, Kabat EA (1974)Biochemistry 13: 3184–92.
Petryniak J, Goldstein IJ (1986)Biochemistry 25: 2829–38.
Baldus SE, Thiele J, Charles A, Hanisch FG, Fischer R (1994)Histochemistry 102: 205–11.
Ito M, Takata K, Saito S, Aoyagi T, Hirano H (1985)Histochemistry 83: 189–93.
Bara J, Mollicone R, Herrero-Zabaleta E, Gautier R, Daher N, Oriol R (1988)Int J Cancer 41: 683–89.
Bara J, Daher N, Mollicone R, Oriol R (1987)Rev Fr Transfus Hemobiol 30: 685–92.
Mollicone R, Cailleau A, Imberty A, Gane P, Perez S, Oriol R (1996)Glycoconjugate J, in press.
Rouger P, Anstee D, Salmon C (1987)Blood Transfus Immunohaematol 30: 355–720.
Hanisch FG, Auerbach B, Bosslet K, Kolbe K, Karsten U, Nakahara Y, Ogawa T, Uhlenbruck G (1993)Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 374: 1083–91.
Hanisch FG, Uhlenbruck G, Dienst C, Stottrop M, Hippauf E (1985)Eur J Biochem 149: 323–30.
Stoll MS, Hounsell EF, Lawson AM, Chai W, Feizi T (1990)Eur J Biochem 189: 499–507.
Cromer R, Spohr U, Khare DP, LePendu J, Lemieux RU (1991)Can J Chem 70: 1511–30.
Du MH, Spohr U, Lemieux RU (1994)Glycoconjugate J 11: 443–61.
Lemieux RU, LePendu J, Hindsgaul O (1979)Jpn J Antibiot 32(Suppl: S21-S31.
Mollicone R, Bara J, LePendu J, Oriol R (1985)Lab Invest 53: 219–27.
Mollicone R, Le Pendu J, Bara J, Oriol R (1986)Glycoconjugate J 3: 187–202.
Lloyd KO (1987)Am J Clin Pathol 87: 129–39.
Clausen H, Hakomori S (1989)Vox Sang 56: 1–20.
Singhal AK (1991)Sem Cancer Biol 2: 379–88.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldus, S.E., Thiele, J., Park, YO. et al. Characterization of the binding specificity ofAnguilla anguilla agglutinin (AAA) in comparison toUlex europaeus agglutinin I (UEA-I). Glycoconjugate J 13, 585–590 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00731446
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00731446