Summary
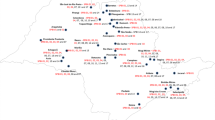
Pathogenicity patterns of 42Mycosphaerella graminicola (Septoria tritici) isolates secured from the major wheat growing regions in Israel, were assessed on seedlings of 16 bread and durum wheats. The spring bread wheat cultivar Titan (CI12615), the winter bread wheats Bezostaya 1, Kavkaz, NE7060 and the durum wheats Nursit 163 and Zenati Bouteille, all exhibited a high level of resistance. Significant cultivar × isolate interactions were recorded for isolates from the different regions in relation to the response of the 16 cultivars organized in 6 reponse classes to the test isolate ISR8036. Number of genes for resistance in the 16 cultivars was estimated, based on the assumption of a gene-for-gene relationship. Twelve complementary genes were hypothesized in the 42M. graminicola isolates × 16 wheat cultivars matrix. There was considerable variation in virulence frequencies between regions and between locations within the same region. The overall frequency of Bezostaya-Kavkaz virulence was low throughout the country (5–7%). The frequency of designated hypothesized virulence genes VST OLAF, VST COLOTANA, VST IAS 20 in Israel, was high in most locations. The reported analytical approach enables the identification of virulence hot-spots and assists in designing breeding for resistance strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AckermannM. D., 1983. Variabilidad patogenica deSeptoria tritici Rob, exDesm. Invest. Agronomicas 4: 46–50.
AoH. C. & E.Griffiths, 1976. Changes in virulence ofSeptoria nodorum andS. tritici after passage through alternative hosts. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc. 66: 219–224.
DanonT., J. M.Sacks & Z.Eyal, 1982. The relationships among plant stature, maturity class and susce susceptibility ofSeptoria leaf blotch of wheat. Phytopathology 72: 1037–1042.
EngelmanL. & J. A.Hartigan, 1981. K-means clustering. p. 464–473. In: W. J.Dixon (Ed.), BMDP-statistical software. University of California Press, Berkeley, California. 727 p.
EyalZ., 1981. Integrated control ofSeptoria diseases of wheat. Plant Disease 65: 763–768.
EyalZ. & M. B.Brown, 1976. A quantitative method for estimating density ofSeptoria tritici pycnidia on wheat leaves. Phytopathology 66: 11–14.
EyalZ., Z.Amiri & I.Wahl, 1973. Physiologic specialization ofSeptoria tritici. Phytopathology 63: 1087–1091.
EyalZ. & A. L.Scharen, 1977. A quantitative method for the inoculation of wheat seedlings with pycnidiospores ofSeptoria nodorum. Phytopathology 67: 712–714.
EyalZ., I.Wahl & J. M.Prescott, 1983. Evaluation of germplasm response toSeptoria leaf blotch of wheat. Euphytica 32: 439–446.
EyalZ., A. L.Scharen, M. D.Huffmann & J. M.Prescott, 1985. Global insights into virulence frequencies ofMycosphaerella graminicola. Phytopathology 75: 1456–1462.
FraneJ. W., 1987. All possible subsets regression-P9R. p. 264–277. In: W. J.Dixon (Ed.), BMDP-statistical software, University of California Press, Berkeley, California. 727 pp.
KampmeijerP., 1981. EPIDAT-Data analysis for disease nurseries. Report on a joint project CIMMYT, Mexico-The Research Institute of Plant Protection (IPO), and the Department of Phytopathology of the Agricultural University, Wageningen, the Netherlands. 33 pp.
KingJ. E., R. J.Cook & S. C.Melville, 1983. A review ofSeptoria diseases of wheat and barley. Ann. Appl. Biol. 103: 345–373.
ParlevlietJ. E., 1983. Models explaining the specificity and durability of host resistance derived from the observation on the barley-Puccinia hordei system. p. 57–78. In: F.Lamberti, J. M.Waller & N. A.Van derGraaff (Eds), Durable resistance in crops. Plenum Press, NY. 454pp.
RosielleA. A. & A. G. P.Brown, 1979. Inheritance, heritability and breeding behaviour of three sources of resistance toSeptoria tritici in wheat. Euphytica 28: 385–392.
SaariE. E. & R. D.Wilcoxson, 1974. Plant disease situation of high-yielding dwarf wheats in Asia and Africa. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 12: 49–48.
ScharenA. L. & Z.Eyal, 1983. Analysis of symptoms on spring and winter wheat cultivars inoculated with different isolates ofSeptoria nodorum. Phytopathology 73: 143–147.
ShanerG. & R. E.Finney, 1982. Resistance in soft red wheat toMycosphaerella graminicola. Phytopathology 72: 154–158.
ShiptonW. A., W. J. R.Boyd, A. A.Rosielle & B. L.Shearer, 1971. The commonSeptoria diseases of wheat. Bot. Rev. 37: 231–262.
Wilson, R. E., 1985. Inheritance of resistance toSeptoria tritici in wheat. p. 33–35. In:A. L. Scharen (Ed.), Septoria of cereals. Proc. Workshop at Montana State University, Bozeman, MT, August 2–4, 1983. USDA, ARS-12. 116 pp.
Yechilevich-AusterM., E.Levi & Z.Eyal, 1983. Assessment of interactions between cultivated and wild wheats andSeptoria tritici. Phytopathology 73: 1077–1083.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eyal, Z., Levy, E. Variations in pathogenicity patterns ofMycosphaerella graminicola withinTriticum spp. in Israel. Euphytica 36, 237–250 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00730670
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00730670