Abstract
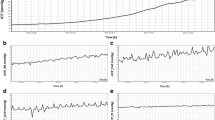
Because of its noninvasive and repeatable nature, Doppler ultrasound has been increasingly used to assess changes in cerebral haemodynamics in infants and children with hydrocephalus. There is general agreement that a direct correlation exists between the intracranial pressure (from experimental, fontanometric and direct measurement evidence) and the resistance index. In addition, this increasing index has been predominantly due to a reduction in the end-diastolic velocity. Stable ventriculomegaly is associated with normal pulsatility. The cerebral blood flow velocity parameters change significantly following CSF drainage by tapping or shunting. The measurement of intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow velocity are currently the best ways of assessing the need for CSF diversion and monitoring subsequent shunt function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvisi C, Marziano C, Giulioni M, Monari P, Salvioli GP, Sandri F, Lippi C, Bovicelli L, Gianluigi P (1985) Evaluation of cerebral blood flow changes by transfontanelle Doppler ultrasound in infantile hydrocephalus. Child's Nerv Syst 1:244–247
Anderson JC, Mawk JR (1991) Intracranial arterial duplex Doppler wave-form analysis in infants. Child's Nerv Syst 4:144–148
Chadduck WM, Seibert JJ (1989) Intracranial duplex Doppler: practical uses in paediatric neurology and neurosurgery. J Child Neurol 4:S77-S86
Chadduck WM, Crabtree HM, Blankenship JB, Adametz J (1991) Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography for the evaluation of shunt malfunction in pediatric patients. Child's Nerv Syst 7:27–30
Deeg KH, Paul J, Rupprecht T, Harms D, Mang C (1988) Pulsed Doppler sonographic determination of absolute flow velocities in the anterior cerebral artery in infants with hydrocephalus in comparison with a healthy patient sample. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 136:85–94
Drayton MR, Skidmore R (1986) Doppler ultrasound in the neonate. Ultrasound Med Biol 12:761–772
Finn JP, Quinn MW, Hall-Craggs MA, Kendall BE (1990) Impact of vessel distortion on transcranial Doppler velocity measurements: correlation with magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 73:572–575
Goh D, Minns RA, Pye SD, Steers AJW (1991) Cerebral blood flow velocity changes after ventricular taps and ventriculoperitoneal shunting. Child's Nerv Syst 7:452–457
Goh D, Minns RA, Pye SD (1991) Transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound as a noninvasive means of monitoring cerebrohemodynamic change in hydrocephalus. Eur J Pediatr Surg 1 [Suppl 1]:14–17
Goh D, Minns RA, Pye SD, Steers AJW (1992) Cerebral blood-flow velocity and intermittent intracranial pressure elevation during sleep in hydrocephalic children. Dev Med Child Neurol 34:676–689
Goh D, Minns RA, Hendry GMA, Thambyayah M, Steers AJW (1992) Cerebrovascular resistive index assessed by duplex Doppler sonography and its relationship to intracranial pressure in infantile hydrocephalus. Pediatr Radiol 22:246–250
Grant EG, White EM, Schellinger D, Choyke PL, Sarcone AL (1987) Cranial duplex sonography of the infant. Radiology 163:177–185
Hanlo PW (1990) Fontanelle pressure measurements and transcranial pulsed Doppler (TCD) in childhood hydrocephalus. Z Kinderchir 45 [Suppl 1]:31
Hill A, Volpe JJ (1982) Decrease in pulsatile flow in the anterior cerebral arteries in infantile hydrocephalus. Pediatrics 69:4–7
Horikawa M (1991) Usefulness of Doppler method for evaluating intracranial haemodynamics in infantile hydrocephalus. No-To-Hattatsu 23:222–261
Huang CC, Chio CC (1991) Duplex color ultrasound study of infantile progressive hydrocephalus. Child's Nerv Syst 7:251–256
Kirkpatrick M, Engelman H, Minns RA (1989) Signs and symptoms of progressive hydrocephalus. Arch Dis Child 64:124–128
Lui K, Hellmann L, Springg A, Daneman A (1990) Cerebral blood-flow velocity patterns in post-haemorrhagic ventricular dilatation. Child's Nerv Syst 6:250–253
Minns RA, Goh D, Pye SD, Steers AJW (1991) A volume-blood flow velocity response (VFR) relationship derived from CSF compartment challenge as an index of progression of infantile hydrocephalus. In: Matsumoto S, Tamaki N (eds) Hydrocephalus —pathogenesis and treatment. Springer, Tokyo Berlin Heidelberg, pp 270–278
Nishimaki S, Kawakami T, Akamatsu H, Iwasaki Y (1991) Cerebral blood flow velocities in the anterior cerebral arteries and basilar artery. III. Investigation in hydrocephalus (part 2). NoTo-Hattatsu 23:560–566
Norelle A, Fischer AQ, Flannery AM (1989) Transcranial Doppler: a noninvasive method to monitor hydrocephalus. J Child Neurol 4:S87-S90
Pople IK, Quinn MW, Bayston R, Hayward RD (1991) The Doppler pulsatility index as a screening test for blocked ventriculo-peritoneal shunts. Eur J Pediatr Surg 1 [Suppl 1]:27–29
Quinn MW, Ando Y, Levene MI (1991) Cerebral venous velocity changes in posthaemorrhagic hydrocephalus (abstract). Eur J Pediatr Surg 1 [Suppl 1]:4
Seibert JJ, McCowan TC, Chadduck WM, Adametz JR, Glasier CM, Williamson SL, Taylor BJ, Leithiser RE, McConnell JR, Stansell CA, Rodgers AB, Corbitt SL (1989) Duplex pulsed Doppler US versus intracranial pressure in the neonate. Radiology 171:155–159
Van Bel F, Van de Bor M, Baan J, Stijnen T, Ruys JH (1988) Blood flow velocity pattern of the anterior cerebral arteries — before and after drainage of posthaaemorrhagic hydrocephalus in the newborn. J Ultrasound Med 7:553–559
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goh, D., Minns, R.A. Intracranial pressure and cerebral arterial flow velocity indices in childhood hydrocephalus: current review. Child's Nerv Syst 11, 392–396 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00717403
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00717403