Summary
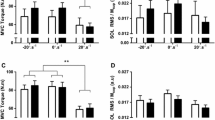
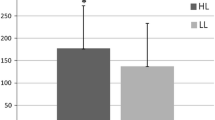
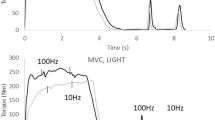
To investigate training-induced changes in neuromuscular performance under voluntary and reflex contractions, 11 male subjects went through heavy resistance (high loads of 70–120% of one maximum repetition) and 10 male subjects through explosive type (low loads with high contraction velocities) strength training three times a week for 24 weeks. A large increase (13.9%,p<0.01) in voluntary unilateral maximal knee extension strength with only slight and insignificant changes in time of isometric force production were observed during heavy resistance strength training. Explosive type strength training resulted in a small insignificant increase in maximal strength but in considerable shortening (p<0.05) in the time of force production. A significant increase (p<0.05) noted in the averaged maximal integrated electromyogram (IEMG) of the knee extensors during heavy resistance strength training correlated (p<0.01) with the increase in maximal strength. No changes were noted during training in reflex time components, but significant decreases (p<0.05) occurred in the peak-to-peak amplitudes of the reflex electromyograms (EMG) in both groups. The individual changes during training in the reflex EMG/force ratio were related (p<0.01) to the respective changes in IEMG/force ratio in voluntary contractions. The present observations support the concept of specificity of training, and suggest that specific training-induced adaptations in the neuromuscular system may be responsible for these changes in performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caiozzo V, Perinne J, Edgerton V (1981) Training-induced alternations of the in vivo force-velocity relationship of human muscle. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 51:750–754
Coyle E, Feiring C, Rotkis T, Cote R, Roby F, Lee W, Wilmore J (1981) Specificity of power improvements through slow and fast isokinetic training. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 51:1437–1442
Cracroft JD, Petajan JH (1977) Effect of muscle training on the pattern of firing of single motor units. Am J Phys Med 56:183–194
Francis P, Tipton C (1969) Influence of a weight training program on quadriceps reflex time. Med Sci Sports 1:91–94
HÄkkinen K, Komi PV (1983a) Electromyographic changes during strength training and detraining. Med Sci Sports Exerc 15:455–460
HÄkkinen K, Komi PV (1983b) Changes in neuromuscular performance in voluntary and reflex contraction during strength training in man. Int J Sports Med 4:282–288
HÄkkinen K, Viitasalo JT, Komi PV (1980) Die Wirkung unterschiedlich kombinierter konzentrischer und exzentrischer Muskelarbeit auf Kraft-Zeit-Merkmale der Beinstreckmuskulatur. Leistungssport 10:374–381
HÄkkinen K, Komi PV, Tesch P (1981) Effect of combined concentric and eccentric strength training and detraining on force-time, muscle fibre, and metabolic characteristics of leg extensor muscles. Scand J Sports Sci 3:50–58
HÄkkinen K, Alén M, Komi PV (1985a) Changes in isometric force- and relaxation-time, electromyographic and muscle fibre characteristics of human skeletal muscle during strength training and detraining. Acta Physiol Scand 125:573–585
HÄkkinen K, Komi PV, Alén M (1985b) Effect of explosive type strength training on isometric force- and relaxation-time, electromyographic and muscle fibre characteristics of leg extensor muscles. Acta Physiol Scand 125:587–600
HÄkkinen K, Pakarinen A, Alén M, Komi PV (1985c) Serum hormones during prolonged training of neuromuscular performance. Eur J Appl Physiol 53:287–293
Houk HC (1974) Feedback control of muscle: a synthesis of the peripheral mechanisms. In: Mountcastle WB (ed) Medical physiology (13th ed). Mosby, St. Louis Mo, pp 668–677
Ikai M (1970) Training of muscle strength and power in athletes. Presented at the FIMS Congress, Oxford
Kawakami M (1955) Training effect and electro-myogram. I spatial distribution of spike potentials. Jpn J Physiol 5:1–8
Komi PV (1986) Training of muscle strength and power: Interaction of neuromotoric, hypertrophic and mechanical factors. Int J Sport Med (in press)
Komi PV, Viitasalo J, Rauramaa R, Vihko V (1978) Effect of isometric strength training on mechanical, electrical and metabolic aspects of muscle function. Eur J Appl Physiol 40:45–55
Komi PV, Aho V-J, Tervakari M (1979) Measurement of potentiation of muscular performance after prestretching. Presented at American College of Sports Medicine Congress, Honolulu, May 24–26
Komi PV, Karlsson J, Tesch P, Suominen H, Heikkinen E (1982) Effects of heavy resistance and explosive type strength training methods on mechanical, functional and metabolic aspects of performance. In: Komi PV (ed) Exercise and sport biology. Human Kinetics Publishers, Champaign, Ill, pp90–102
MacDougall J, Elder G, Sale D, Moroz J, Sutton J (1977) Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy with respect to fibre type in humans. Can J Appl Sport Sci (Abstr) 2:229
Maynard J, Tipton C (1971) The effect of exercise training and denervation on the morphology of intrafusal muscle fibers. Int Z Angew Physiol 30:1–9
Milner-Brown H, Stein R, Lee G (1975) Synchronization of human motor units: possible roles of exercise and supraspinal reflexes. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 38:245–254
Moritani T, DeVries H (1979) Neural factors versus hypertrophy in the course of muscle strength gain. Am J Phys Med 58:115–130
Sale D, MacDougall J, Upton A, MacComas A (1979) Effect of strength training upon motoneuron excitability in man. Abstract. Med Sci Sports 11:77
Sale D, MacComas A, MacDougall J, Upton A (1982) Neuromuscular adaptation in human thenar muscles following strength training and immobilization. J Appl Physiol 53:419–424
Sukop J, Nelson R (1974) Effect of isometric training on the force-time characteristics of muscle contraction. In: Biomechanics IV. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 440–447
Viitasalo J, Saukkonen S, Komi PV (1980) Reproducibility of measurements of selected neuromuscular performance variables in man. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 20:487–501
Viitasalo JT, Aura O, HÄkkinen K, Komi PV, Nikula J (1981) Untersuchung von Trainingswirkungen auf die Krafterzeugung und Sprunghöhe. Leistungssport 11:278–281
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HÄkkinen, K., Komi, P.V. Training-induced changes in neuromuscular performance under voluntary and reflex conditions. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 55, 147–155 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00714997
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00714997